|
Deleted In Colorectal Cancer
Netrin receptor DCC, also known as DCC, or colorectal cancer suppressor is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''DCC'' gene. DCC has long been implicated in colorectal cancer and its previous name was ''Deleted in colorectal carcinoma''. Netrin receptor DCC is a single transmembrane receptor. Since it was first discovered in a colorectal cancer study in 1990, ''DCC'' has been the focus of a significant amount of research. ''DCC'' held a controversial place as a tumour suppressor gene for many years, and is well known as an axon guidance receptor that responds to netrin-1. More recently DCC has been characterized as a dependence receptor, and many hypotheses have been put forward that have revived interest in ''DCCs candidacy as a tumour suppressor gene, as it may be a ligand-dependent suppressor that is frequently epigenetically silenced. Background Early studies of colorectal tumours found that allelic deletions of segments of chromosome 18q occur in a very high perce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspase-3
Caspase-3 is a caspase protein that interacts with caspase-8 and caspase-9. It is encoded by the ''CASP3'' gene. ''CASP3'' orthologs have been identified in numerous mammals for which complete genome data are available. Unique orthologs are also present in birds, lizards, lissamphibians, and teleosts. The CASP3 protein is a member of the cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family. Sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes that undergo proteolytic processing at conserved aspartic residues to produce two subunits, large and small, that dimerize to form the active enzyme. This protein cleaves and activates caspases 6 and 7; and the protein itself is processed and activated by caspases 8, 9, and 10. It is the predominant caspase involved in the cleavage of amyloid-beta 4A precursor protein, which is associated with neuronal death in Alzheimer's disease. Alternative splicing of this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
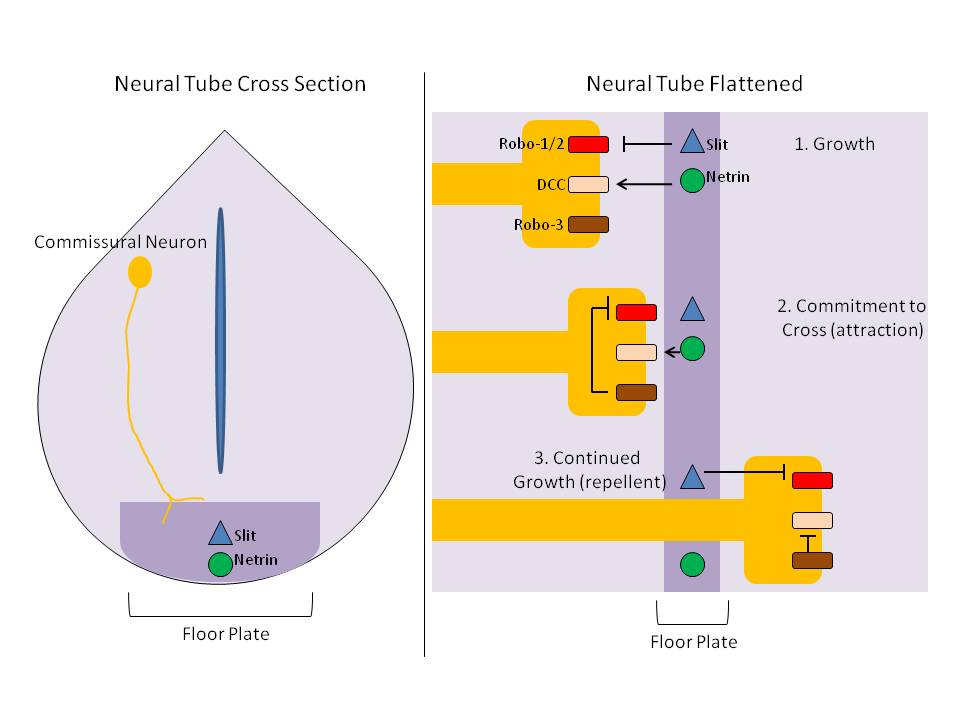
Slit (protein)
Slit is a family of secreted extracellular matrix proteins which play an important signalling role in the neural development of most bilaterians (animals with bilateral symmetry). While lower animal species, including insects and nematode worms, possess a single Slit gene, humans, mice and other vertebrates possess three Slit homologs: Slit1, Slit2 and Slit3. Human ''Slits'' have been shown to be involved in certain pathological conditions, such as cancer and inflammation. The ventral midline of the central nervous system is a key place where axons can either decide to cross and laterally project or stay on the same side of the brain. The main function of Slit proteins is to act as midline repellents, preventing the crossing of longitudinal axons through the midline of the central nervous system of most bilaterian animal species, including mice, chickens, humans, insects, nematode worms and planarians. It also prevents the recrossing of commissural axons. Its canonical recept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floor Plate
The floor plate is a structure integral to the developing nervous system of vertebrate organisms. Located on the ventral midline of the embryonic neural tube, the floor plate is a specialized glial structure that spans the anteroposterior axis from the midbrain to the tail regions. It has been shown that the floor plate is conserved among vertebrates, such as zebrafish and mice, with homologous structures in invertebrates such as the fruit fly ''Drosophila'' and the nematode ''C. elegans''. Functionally, the structure serves as an organizer to ventralize tissues in the embryo as well as to guide neuronal positioning and differentiation along the dorsoventral axis of the neural tube. Induction Induction of the floor plate during embryogenesis of vertebrate embryos has been studied extensively in chick and zebrafish and occurs as a result of a complex signaling network among tissues, the details of which have yet to be fully refined. Currently there are several competing lines o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon Guidance
Axon guidance (also called axon pathfinding) is a subfield of neural development concerning the process by which neurons send out axons to reach their correct targets. Axons often follow very precise paths in the nervous system, and how they manage to find their way so accurately is an area of ongoing research. Axon growth takes place from a region called the growth cone and reaching the axon target is accomplished with relatively few guidance molecules. Growth cone receptors respond to the guidance cues. Mechanisms Growing axons have a highly motile structure at the growing tip called the growth cone, which responds to signals in the extracellular environment that instruct the axon in which direction to grow. These signals, called guidance cues, can be fixed in place or diffusible; they can attract or repel axons. Growth cones contain receptors that recognize these guidance cues and interpret the signal into a chemotropic response. The general theoretical framework is that whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Migration
Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. Tissue formation during embryonic development, wound healing and immune responses all require the orchestrated movement of cells in particular directions to specific locations. Cells often migrate in response to specific external signals, including chemical signals and mechanical signals. Errors during this process have serious consequences, including intellectual disability, vascular disease, tumor formation and metastasis. An understanding of the mechanism by which cells migrate may lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies for controlling, for example, invasive tumour cells. Due to the highly viscous environment (low Reynolds number), cells need to continuously produce forces in order to move. Cells achieve active movement by very different mechanisms. Many less complex prokaryotic organisms (and sperm cells) use flagella or cilia to propel themselves. Eukaryot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Growth
Cell growth refers to an increase in the total mass of a cell, including both cytoplasmic, nuclear and organelle volume. Cell growth occurs when the overall rate of cellular biosynthesis (production of biomolecules or anabolism) is greater than the overall rate of cellular degradation (the destruction of biomolecules via the proteasome, lysosome or autophagy, or catabolism). Cell growth is not to be confused with cell division or the cell cycle, which are distinct processes that can occur alongside cell growth during the process of cell proliferation, where a cell, known as the mother cell, grows and divides to produce two daughter cells. Importantly, cell growth and cell division can also occur independently of one another. During early embryonic development ( cleavage of the zygote to form a morula and blastoderm), cell divisions occur repeatedly without cell growth. Conversely, some cells can grow without cell division or without any progression of the cell cycle, such as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patched
Patched (Ptc) is a conserved 12-pass transmembrane protein receptor that plays an obligate negative regulatory role in the Hedgehog signaling pathway in insects and vertebrates. Patched is an essential gene in embryogenesis for proper segmentation in the fly embryo, mutations in which may be embryonic lethal. Patched functions as the receptor for the Hedgehog protein and controls its spatial distribution, in part via endocytosis of bound Hedgehog protein, which is then targeted for lysosomal degradation. Discovery The original mutations in the ''ptc'' gene were discovered in the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'' by 1995 Nobel Laureates Eric F. Wieschaus and Christiane Nusslein-Volhard and colleagues, and the gene was independently cloned in 1989 by Joan Hooper in the laboratory of Matthew P. Scott, and by Philip Ingham and colleagues. Role in hedgehog signaling Patched is part of a negative feedback mechanism for hedgehog signaling that helps shape the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrins
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle, organization of the intracellular cytoskeleton, and movement of new receptors to the cell membrane. The presence of integrins allows rapid and flexible responses to events at the cell surface (''e.g''. signal platelets to initiate an interaction with coagulation factors). Several types of integrins exist, and one cell generally has multiple different types on its surface. Integrins are found in all animals while integrin-like receptors are found in plant cells. Integrins work alongside other proteins such as cadherins, the immunoglobulin superfamily cell adhesion molecules, selectins and syndecans, to mediate cell–cell and cell–matrix interaction. Ligands for integrins include fibronectin, vitronectin, collagen and laminin. Structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RET Proto-oncogene
The ''RET'' proto-oncogene encodes a receptor tyrosine kinase for members of the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) family of extracellular signalling molecules. ''RET'' loss of function mutations are associated with the development of Hirschsprung's disease, while gain of function mutations are associated with the development of various types of human cancer, including medullary thyroid carcinoma, multiple endocrine neoplasias type 2A and 2B, pheochromocytoma and parathyroid hyperplasia. Structure ''RET'' is an abbreviation for "rearranged during transfection", as the DNA sequence of this gene was originally found to be rearranged within a 3T3 fibroblast cell line following its transfection with DNA taken from human lymphoma cells. The human gene ''RET'' is localized to chromosome 10 (10q11.2) and contains 21 exons. The natural alternative splicing of the ''RET'' gene results in the production of 3 different isoforms of the protein RET. RET51, RET43 and RET9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Androgen Receptor
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 4), is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the nucleus. The androgen receptor is most closely related to the progesterone receptor, and progestins in higher dosages can block the androgen receptor. The main function of the androgen receptor is as a DNA-binding transcription factor that regulates gene expression; however, the androgen receptor has other functions as well. Androgen-regulated genes are critical for the development and maintenance of the male sexual phenotype. Function Effect on development In some cell types, testosterone interacts directly with androgen receptors, whereas, in others, testosterone is converted by 5-alpha-reductase to dihydrotestosterone, an even more potent agonist for androgen receptor activation. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |