|
Danish Order Of Freemasons
The Danish Order of Freemasons ( da, Den Danske Frimurerorden, abbr.: ''DDFO''), in English also known as the Grand Lodge of Denmark, is a governing body of some Masonic Lodges in Denmark. The Danish Order of Freemasons was founded on 16 November 1858. The Danish Order of Freemasons has 89 Lodges all working in accordance with the rituals of the Swedish Rite and all requiring members be baptised in the Christian faith. The Danish Order of Freemasons has approximately 7,500 members. Affiliated to the Danish Order of Freemasons are two Masonic organisations, both of which have their own Lodges and do not require members be baptised in the Christian faith: The Ancient Fraternity of Free and Accepted Masons of Denmark ( da, Det Danske Frimurerlaug af Gamle Frie & Antagne Murere) has approximately 1,300 members and 41 Lodges practising the rituals of the Emulation Rite, while the Saint John's Lodge Association ( da, Johanneslogeforbundet af Gamle, Frie og Antagne Murere) has appro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its whole consists of a shield, supporters, a crest, and a motto. A coat of arms is traditionally unique to an individual person, family, state, organization, school or corporation. The term itself of 'coat of arms' describing in modern times just the heraldic design, originates from the description of the entire medieval chainmail 'surcoat' garment used in combat or preparation for the latter. Rolls of arms are collections of many coats of arms, and since the early Modern Age centuries, they have been a source of information for public showing and tracing the membership of a noble family, and therefore its genealogy across time. History Heraldic designs came into general use among European nobility in the 12th century. System ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schröder Rite
Schröder Rite (in German: ''Schrödersche Lehrart'') is a masonic rite practiced mostly in lodges in Germany and Brazil, with fewer lodges in other countries. Developed by Friedrich Ludwig Schröder and showed to Masters in Hamburg (male), (female) en, Hamburger(s), Hamburgian(s) , timezone1 = Central (CET) , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = Central (CEST) , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal ... on July 29, 1801, it was adopted unanimously and it attracted several lodges throughout Germany and other countries, where it was practiced mainly by Freemasons of German origin and soon received the name of its founder, Schröder Rite. References Masonic rites {{Freemasonry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1858 Establishments In Denmark
Events January–March * January – **Benito Juárez (1806–1872) becomes Liberal President of Mexico. At the same time, conservatives install Félix María Zuloaga (1813–1898) as president. **William I of Prussia becomes regent for his brother, Frederick William IV, who had suffered a stroke. * January 9 ** British forces finally defeat Rajab Ali Khan of Chittagong ** Anson Jones, the last president of the Republic of Texas, commits suicide. * January 14 – Orsini affair: Felice Orsini and his accomplices fail to assassinate Napoleon III in Paris, but their bombs kill eight and wound 142 people. Because of the involvement of French émigrés living in Britain, there is a brief anti-British feeling in France, but the emperor refuses to support it. * January 25 – The ''Wedding March'' by Felix Mendelssohn becomes a popular wedding recessional, after it is played on this day at the marriage of Queen Victoria's daughter Victoria, Princess Royal, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
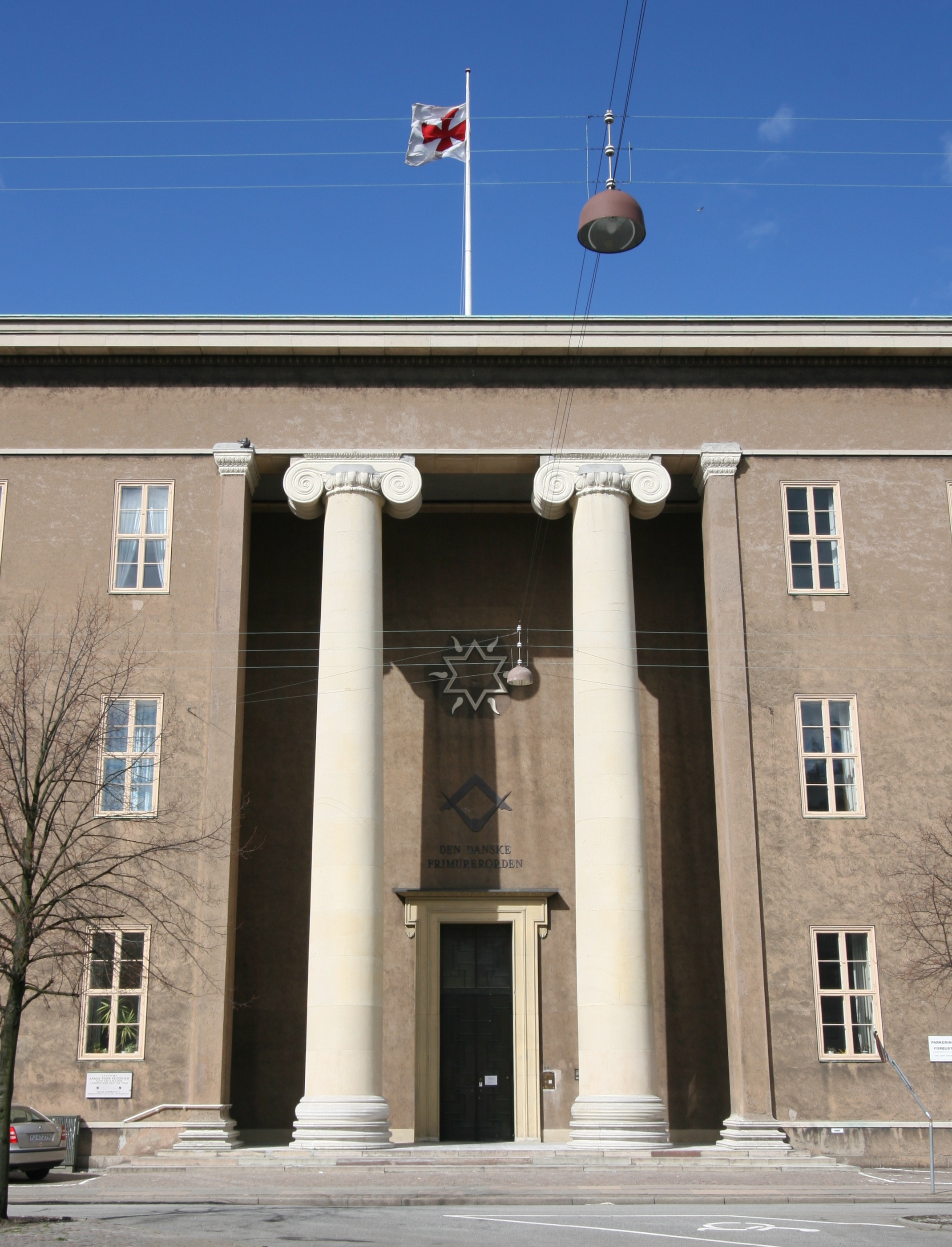
Freemasons' Hall, Copenhagen
Freemasons' Hall ( da, Ordenens Stamhus) located on Blegdamsvej in Copenhagen's Østerbro district, Denmark, is the headquarters of the Danish Order of Freemasons and a meeting place for the Masonic Lodges in the Copenhagen area. History The Danish Order of Freemasons had moved between various addresses and at the beginning of the 20th century was based in Klerkegade in Copenhagen. When the municipal authorities in Copenhagen sold off a strip of land along Blegdamsvej, previously part of the park Fælledparken, the Danish Order of Freemasons acquired a piece of land. In 1920, a competition was held among its architect members for the design of a new headquarters. Martin Nyrop, architect of Copenhagen City Hall and himself a Freemason, sat on the panel of judges. The winning entry was submitted by Holger Rasmussen, a relatively unknown Danish architect who had mainly designed modest buildings for Danish State Railways. The Freemasons' Hall was of a different stature entirely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freemasonry In Denmark
Freemasonry in Denmark was first established in 1743 and is today represented by a number of Grand Lodges. The oldest and biggest Masonic Grand Lodge in Denmark is the Danish Order of Freemasons ( da, Den Danske Frimurerorden), in English also known as the Grand Lodge of Denmark. History Freemasonry came to Denmark in 1743 with the founding of the Lodge of ''St. Martin''. Named after Martin of Tours, the Lodge was founded in Copenhagen by several Danish Masons, who were also members of Grand Lodges abroad. 1745 saw the founding of Denmark's second Lodge, ''Zorobabel'', also in Copenhagen. From Copenhagen, Freemasonry began to spread throughout the Kingdom of Denmark-Norway with the founding in 1749 of the Lodge ''St. Olai'' in Oslo as well as Lodges in Bergen and Trondheim. In 1767 ''St. Martin'' and ''Zorobabel'' merged to form ''Zorobabel til Nordstjernen''. This Lodge took over ''St. Martins role as Mother Lodge to the Freemasons' Lodges in Norway. In 1855 ''Zorobabel til No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schalburg Corps
The Germanic SS () was the collective name given to paramilitary and political organisations established in parts of German-occupied Europe between 1939 and 1945 under the auspices of the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS). The units were modeled on the '' Allgemeine SS'' in Nazi Germany and established in Belgium, Denmark, the Netherlands, and Norway whose populations were considered in Nazi ideology to be especially "racially suitable". They typically served as local security police augmenting German units of the Gestapo, ''Sicherheitsdienst'' (SD), and other departments of the German Reich Security Main Office. Establishment The Nazi idea behind co-opting additional Germanic people into the SS stems to a certain extent from the '' Völkisch'' belief that the original Aryan-Germanic homeland rested in Scandinavia and that, in a racial-ideological sense, people from there or the neighbouring northern European regions were a human reservoir of Nordic/Germanic blood. Conquest of Western Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denmark In World War II
At the outset of World War II in September 1939, Denmark declared itself neutral. For most of the war, the country was a protectorate and then an occupied territory of Germany. The decision to occupy Denmark was taken in Berlin on 17 December 1939. On 9 April 1940, Germany occupied Denmark in Operation Weserübung. The Danish government and king functioned as relatively normal in a ''de facto'' protectorate over the country until 29 August 1943, when Germany placed Denmark under direct military occupation, which lasted until the Allied victory on 5 May 1945. Contrary to the situation in other countries under German occupation, most Danish institutions continued to function relatively normally until 1945. Both the Danish government and king remained in the country in an uneasy relationship between a democratic and a totalitarian system until the Danish government stepped down in a protest against German demands to institute the death penalty for sabotage. Just over 3,000 Danes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian X Of Denmark
Christian X ( da, Christian Carl Frederik Albert Alexander Vilhelm; 26 September 1870 – 20 April 1947) was King of Denmark from 1912 to his death in 1947, and the only King of Iceland as Kristján X, in the form of a personal union rather than a real union between 1918 and 1944. He was a member of the House of Glücksburg, a branch of the House of Oldenburg, and the first monarch since King Frederick VII born into the Danish royal family; both his father and his grandfather were born as princes of a ducal family from Schleswig. Among his siblings was King Haakon VII of Norway. His son became Frederick IX of Denmark. His character has been described as authoritarian and he strongly stressed the importance of royal dignity and power. His reluctance to fully embrace democracy resulted in the Easter Crisis of 1920, in which he dismissed the democratically elected Social Liberal cabinet with which he disagreed, and installed one of his own choosing. This was in accordanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Østerbro
Østerbro () (literally, "Eastern Bridge") is one of the 10 official districts of Copenhagen, Denmark. It is located just north of the city centre, outside the old city gate Østerport which, after it was moved around 1700, used to be located close to present-day Østerport Station. From the beginning, Østerbro has been a wealthy district, and it remains one of the most affluent areas in Copenhagen. Geography Østerbro has an area of and a population of 68,769. It is bordered by Nørrebro to the west, Hellerup to the north and Øresund to the east. Landmarks * Danish Meteorological Institute * Den Frie Udstilling * Gasværket * Frihavn * Fælledparken * Garrison's Cemetery * Parken, the National Stadium * Rigshospitalet * Trianglen (“The Triangle”) * Østerport Station * Kastellet * Nordre Frihavnsgade * '' The Little Mermaid'' In popular culture *In the popular children's novel, ''Number the Stars'', Østerbrogade is a road on which the Annemarie and her friends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emulation Lodge Of Improvement
Emulation Lodge of Improvement is a Lodge of Instruction which first met on 2 October 1823, and is held under the sanction of Lodge of Unions No. 256 in the English Constitution. It restricts admission to Master Masons in good standing. The aim of the lodge is to preserve Masonic ritual as closely as is possible to that which was formally accepted by the newly formed United Grand Lodge of England in 1816 and as amended since. History After the Union of 1813 (in December of that year) that formed the United Grand Lodge of England, it was necessary that the ritual be standardised, with approval of the Grand Lodges of Ireland and Scotland. A result of this was the International Compact, which governs relations between the three Grand Lodges. Emulation Ritual The ritual to be used in United Grand Lodge of England''Emulation Ritual'' pub 1991, London. and in Lodges under that constitution were produced by the Lodge of Reconciliation, formed following the union of the Antients and M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blegdamsvej
Blegdamsvej is a street in Copenhagen, Denmark, connecting Sankt Hans Torv in Nørrebro to Trianglen in Østerbro. The busy artery Fredensgade separates the Nørrebro and Østerbro sections of the street from each other. The north side of the street is dominated by the Panum Building and Rigshospitalet, located on either side of Tagensvej. History The bleaching ponds and Blegdam Common Blegdamsvej is first mentioned in 1694 and takes its name after the 24 ponds on the west side of Sortedam and Peblinge Lake, which was used for textile bleaching. They were established in about 1772 and had numbers from south to north, beginning at present day Sankt Hans Torv. On the other side of the ponds was Blegedam Common, the oldest of Copenhagen's commons, where the bleachers left the cloth to bleach in the sun. Lined with trees on both sides, mainly Aesculus hippocastanum, horse chestnut, willow and Tilia, lime trees. Early industry From the middle of the 19th century, the narrow l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus is the Son of God, whose coming as the messiah was prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testament. Christianity began as a Second Temple Judaic sect in the 1st century Hellenistic Judaism in the Roman province of Judea. Jesus' apostles and their followers spread around the Levant, Europe, Anatolia, Mesopotamia, the South Caucasus, Ancient Carthage, Egypt, and Ethiopia, despite significant initial persecution. It soon attracted gentile God-fearers, which led to a departure from Jewish customs, and, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


