|
Działdowo Railway Station
Działdowo (; , ) is a town in northern Poland with 20,935 inhabitants as of December 2021, the capital of Działdowo County. As part of Masuria, it is situated in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship (since 1999), Działdowo belonged previously to Ciechanów Voivodeship (1975–1998). The town is a major railroad junction connecting the capital city of Warsaw with Gdańsk and Olsztyn to the north. History The first settlement in the vicinity, known as ''Sasinowie'' in Polish and ''Sassen'' in German, was established by the Old Prussians, an indigenous Baltic tribe. The Teutonic Knights conquered the region and built a castle, a wing of which still remains. The new settlement near the castle founded by Mikołaj z Karbowa and named Soldov was granted town privileges on 14 August 1344 by the Grand Master Ludolf König. The name Dzialdoff was first written on a 1409 map during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. In 1444, the town joined the anti-Teutonic Prussian Confederation, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at 1.86 million residents within a Warsaw metropolitan area, greater metropolitan area of 3.27 million residents, which makes Warsaw the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 6th most-populous city in the European Union. The city area measures and comprises List of districts and neighbourhoods of Warsaw, 18 districts, while the metropolitan area covers . Warsaw is classified as an Globalization and World Cities Research Network#Alpha 2, alpha global city, a major political, economic and cultural hub, and the country's seat of government. It is also the capital of the Masovian Voivodeship. Warsaw traces its origins to a small fishing town in Masovia. The city rose to prominence in the late 16th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
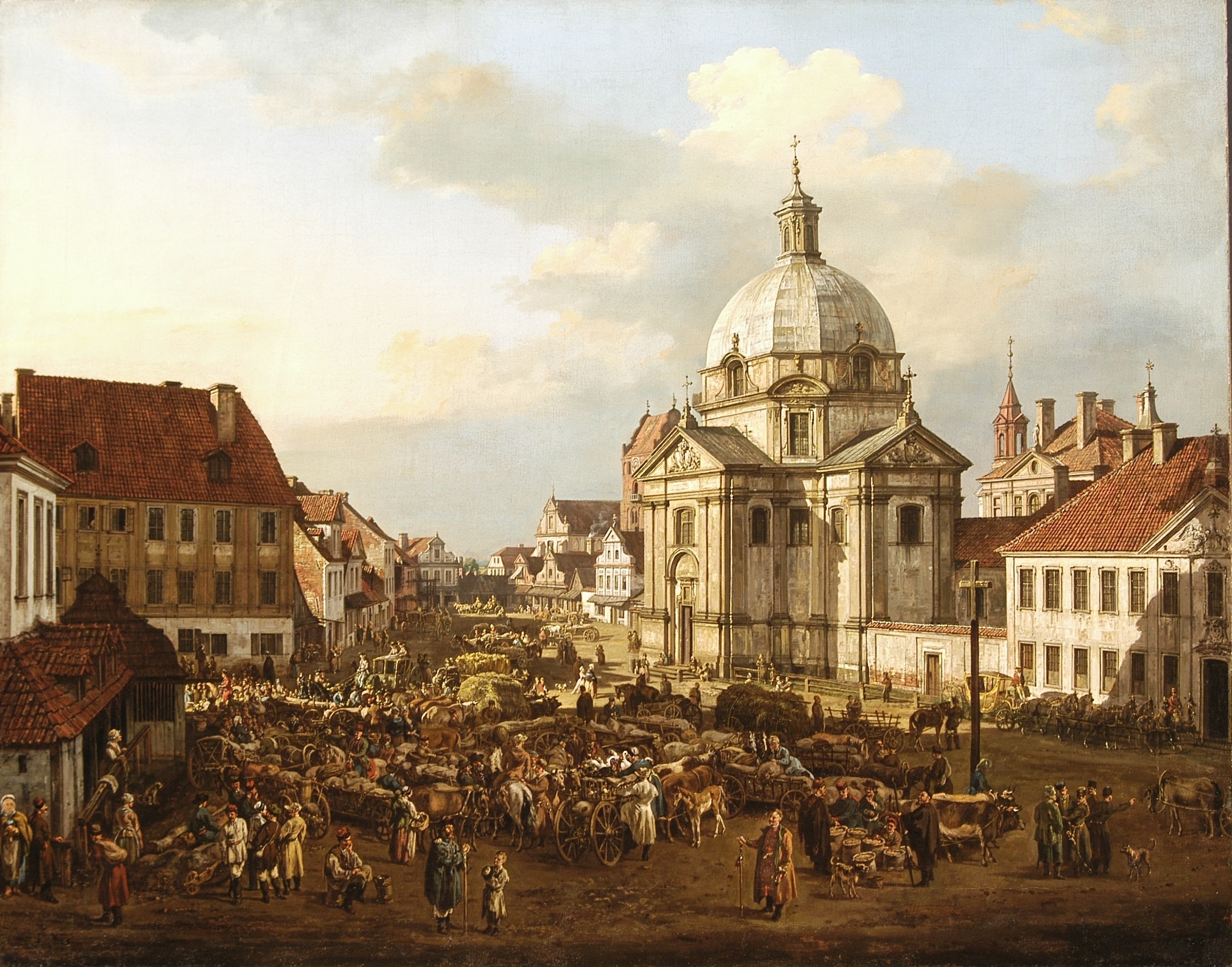
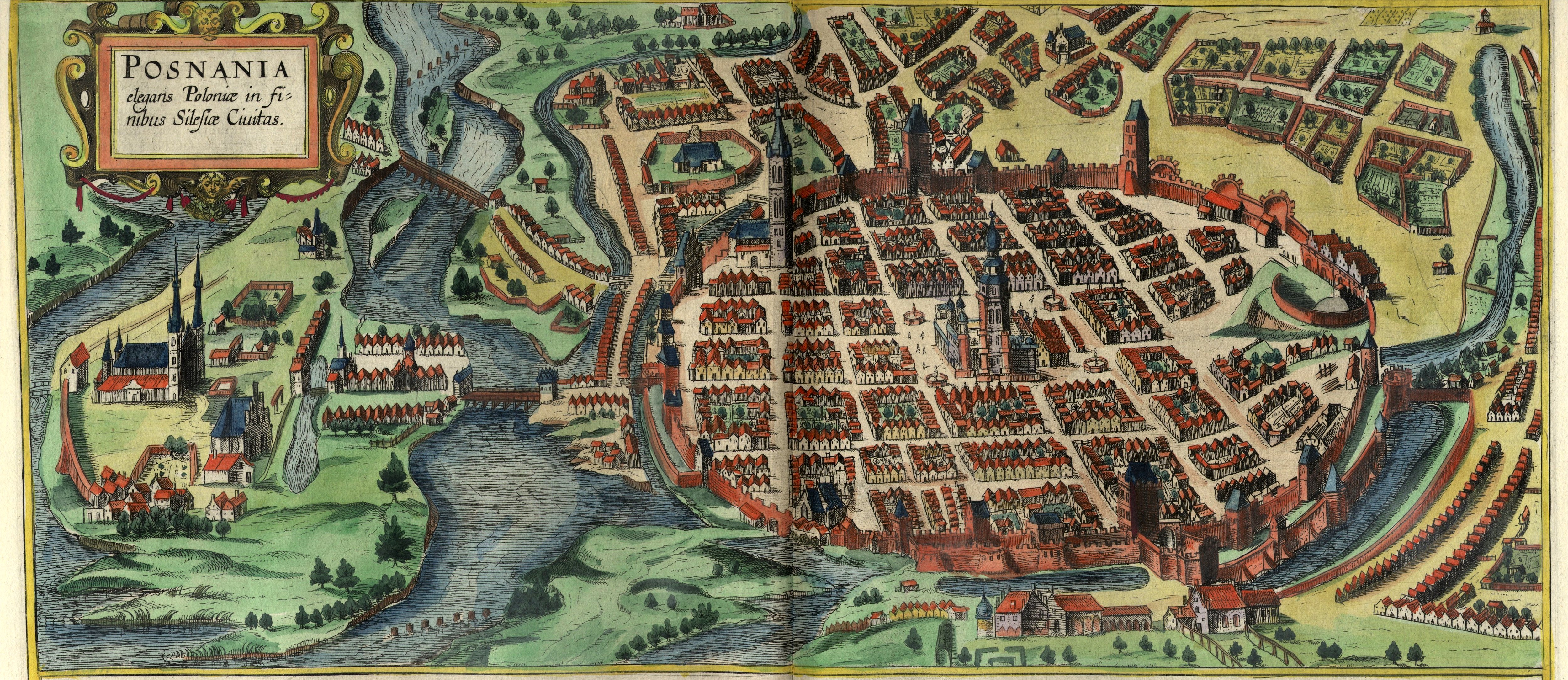
Poznań
Poznań ( ) is a city on the Warta, River Warta in west Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business center and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's Fair, Poznań, Saint John's Fair (''Jarmark Świętojański''), traditional St. Martin's croissant, Saint Martin's croissants and a local dialect. Among its most important heritage sites are the Renaissance in Poland, Renaissance Old Town, Poznań Town Hall, Town Hall and Poznań Cathedral. Poznań is the fifth-largest List of cities and towns in Poland#Cities, city in Poland. As of 2023, the city's population is 540,146, while the Poznań metropolitan area (''Metropolia Poznań'') comprising Poznań County and several other communities is inhabited by over 1.029 million people. It is one of four historical capitals of medieval Poland and the ancient capital of the Greater Poland region, currently the administrative capital of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Of The Kingdom Of Poland
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland (; ) was a political and legal concept formed in the 14th century in the Kingdom of Poland, assuming unity, indivisibility and continuity of the state. Under this idea, the state was no longer seen as the Patrimonialism, patrimonial property of the monarch or dynasty, but became a common good of the political community of the kingdom. This notion allowed the state to maintain stability even during periods of interregnum and paved the way for a unique political system in Poland, characterized by a noble-based parliament and the Free election (Poland), free election of the monarch. Additionally, the concept of the Crown extended beyond existing borders, asserting that previously lost territories still rightfully belonged to it. The term ''Crown of the Kingdom of Poland'' also referred to all the lands under the rule of the Polish king. This meaning became especially significant after the Union of Lublin, union with the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
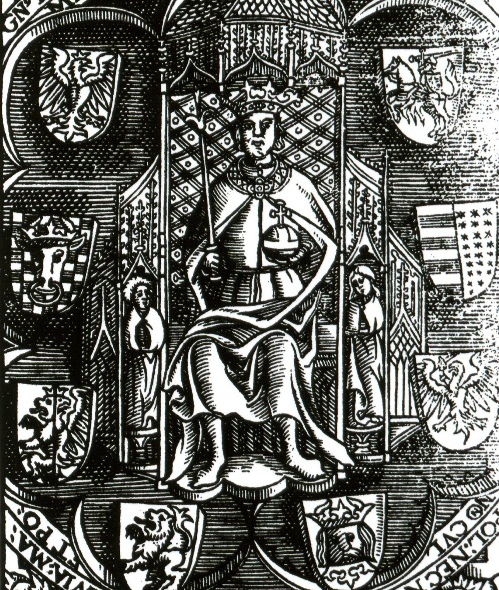
Casimir IV Jagiellon
Casimir IV (Casimir Andrew Jagiellon; ; Lithuanian: ; 30 November 1427 – 7 June 1492) was Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1440 and King of Poland from 1447 until his death in 1492. He was one of the most active Polish-Lithuanian rulers; under him, Poland defeated the Teutonic Knights in the Thirteen Years' War and recovered Pomerania. The Jagiellonian dynasty became one of the leading royal houses in Europe. The great triumph of his reign was bringing Prussia under Polish rule. The rule of Casimir corresponded to the age of "new monarchies" in western Europe. By the 15th century, Poland had narrowed the distance separating it from Western Europe and became a significant power in international relations. The demand for raw materials and semi-finished goods stimulated trade, producing a positive balance, and contributed to the growth of crafts and mining in the entire country. He was a recipient of the English Order of the Garter (KG), the highest order of chivalry and the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian Confederation
The Prussian Confederation (, ) was an organization formed on 21 February 1440 at Marienwerder (present-day Kwidzyn) by a group of 53 nobles and clergy and 19 cities in Prussia, to oppose the arbitrariness of the Teutonic Knights. It was based on an earlier similar organization, the Lizard Union established in 1397 by the nobles of Chełmno Land. In 1454, the leader of the Confederation, Johannes von Baysen (Jan Bażyński), formally asked King Casimir IV Jagiellon, to incorporate Prussia into the Kingdom of Poland. This marked the beginning of the Thirteen Years' War between the Order's State and Poland, with the cities co-financing the military costs of the latter. Background According to the 1411 First Peace of Thorn which followed the Teutonic Knights' defeat in the Battle of Grunwald, the Teutonic Order had to pay high reparations to the Kingdom of Poland. The monastic state imposed high taxes on the cities to raise the funds as well as to re-arm for another war again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War
The Polish–Lithuanian — Teutonic War, also known as the Great Teutonic War, occurred between 1409 and 1411 between the Teutonic Knights and the allied History of Poland (1385–1569), Kingdom of Poland and Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Inspired by the local Samogitian uprising, the war began with a Teutonic invasion of Poland in August 1409. As neither side was ready for a full-scale war, Wenceslaus IV of Bohemia brokered a nine-month truce. After the truce expired in June 1410, the military-religious monks were decisively defeated in the Battle of Grunwald, one of the largest battles in medieval Europe. Most of the Teutonic leadership was killed or taken prisoner. Although they were defeated, the Teutonic Knights Siege of Marienburg (1410), withstood the siege on their capital in Marienburg (Malbork) and suffered only minimal territorial losses in the Peace of Thorn (1411). Territorial disputes lasted until the Peace of Melno of 1422. However, the Knights never recovered their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludolf König
Ludolf is a Germanic surname or given name. It is derived from two stems: Hlud meaning "fame" and olf meaning "wolf". An alternate spelling of the name is Ludolph. People with the name include: * George Philipp Ludolf von Beckedorff (1778-1858), prominent Prussian Roman Catholic convert and parliamentarian Surname * Hiob Ludolf (1624–1704), German orientalist * Heinrich Wilhelm Ludolf (1655–1712), German diplomat and linguist * Jaan Ludolf (born 1940), Estonian chess master * Julius Ludolf (1893–1947), SS officer and concentration camp commandant executed for war crimes Given name * Ludolf von Alvensleben (Major General) (1844–1912), Prussian major general * Ludolf von Alvensleben (1901-1970), Nazi official convicted ''in absentia'' for war crimes, son of the above * Ludolf Jakob von Alvensleben (1899-1953), Nazi official * Ludolf Bakhuizen (1630–1708), Dutch painter * Ludolf Nielsen (1876-1939), Danish composer, violinist, conductor, and pianist * Ludolf von Krehl (1861- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Masters Of The Teutonic Knights
The grand master of the Teutonic Order (; ) is the supreme head of the Teutonic Order. It is equivalent to the grand master of other military orders and the superior general in non-military Roman Catholic religious orders. ''Hochmeister'', literally "high master", is only used in reference to the Teutonic Order, as ''Großmeister'' ("grand master") is used in German to refer to the leaders of other orders of knighthood. An early version of the full title in Latin was ''Magister Hospitalis Sanctae Mariae Alemannorum Hierosolymitani''. Since 1216, the full title ''Magister Hospitalis Domus Sanctae Mariae Teutonicorum Hierosolymitani'' ("Master of the Hospital House of the Blessed Virgin Mary of the Germans of Jerusalem") was used. The offices of ''Hochmeister'' and ''Deutschmeister'' (''Magister Germaniae'') were united in 1525. The title of ''Magister Germaniae'' had been introduced in 1219 as the head of the bailiwicks in the Holy Roman Empire, from 1381 also those in Ita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kulm Law
Kulm law, Culm law or Chełmno Law (; ; ) was a legal constitution for a municipal form of government used in several Central European cities in the Middle Ages and early modern period. It was initiated on 28 December 1233 in the Monastic State of the Teutonic Knights by Grand Master of the Teutonic Order, Grand Master Hermann von Salza and Hermann Balk when the towns of Toruń (''Thorn'') and Chełmno (''Kulm'') received German town law, in particular as a modification of Magdeburg rights. Named after the town it was signed in, the original document (''Kulmer Handfeste'') was lost in 1244 when the town hall burned due to an attack by Świętopełk II, Duke of Pomerania. The renewed charter of 1 October 1251 was based on a copy in Toruń, but the rights were reduced. The town hall in Chełmno was the seat of the higher court of Chełmno law until 1458. This type of law was mostly granted by the Teutonic Order to cities within their monastic state, and by the neighboring Duchy of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to the Holy Land and to establish hospitals. Its members have commonly been known as the Teutonic Knights, having historically served as a crusading military order for supporting Catholic rule in the Holy Land and the Northern Crusades during the Middle Ages, as well as supplying military protection for Catholics in Eastern Europe. Purely religious since 1810, the Teutonic Order still confers limited honorary knighthoods. The Bailiwick of Utrecht of the Teutonic Order, a Protestant chivalric order, is descended from the same medieval military order and also continues to award knighthoods and perform charitable work. Name The name of the Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem is in and in Latin . Thus the term "T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |