|
Duke's Disease
Dukes' disease, named after Clement Dukes (1845–1925), also known as fourth disease, Filatov-Dukes' disease (after Nil Filatov), ''Staphylococcal'' Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS), or Ritter's disease is an exanthem (rash-causing) illness primarily affecting children and historically described as a distinct bacterial infection, though its existence as a separate disease entity is now debated. It is distinguished from measles or forms of rubella, though it was considered as a form of viral rash, bacterial rash. Although Dukes identified it as a separate entity, it is thought not to be different from scarlet fever caused by exotoxin-producing ''Streptococcus pyogenes'' after Keith Powell proposed equating it with the condition currently known as staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in 1979. It was never associated with a specific pathogen, and the terminology is no longer in use. However, a mysterious rash of unknown cause in school children often gives rise to the question of wheth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nil Filatov
Nil Fyodorovich Filatov (, , or , – ) was a medical doctor who is considered the founder of Russian paediatrics. Career Having graduated from the Moscow State University, Moscow University, he practised as a country doctor in his native region. In 1872–1874, Filatov took additional training in Vienna, Berlin, Heidelberg, and Prague. In 1876, he upheld a thesis on bronchitis and pneumonia, and obtained a doctor degree.* Nil Filatov is most famous for describing infectious mononucleosis (also known as Filatov's disease) in 1887 and Dukes' disease (sometimes referred as Dukes-Filatov disease) in 1885; he was also one of the first to observe Koplik's spots (1895). In cooperation with Georgy Gabrichevsky he introduced Blood serum, serumal treatment of diphtheria in 1894. He created a number of handbooks on paediatrics, which were not only popular in Russia, but also translated into German, French, Italian, Czech and Hungarian. In 1892, Filatov established the Society of Paediatr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exanthem
An exanthem is a widespread rash eruption occurring on the outside of the body, usually presents in children, the rash is typically associated with constitutional symptoms including fever and fatigue. It is usually caused by a virus, but an exanthem can be caused by bacteria, toxins, drugs, other microorganisms, or as a result of autoimmune disease. Exanthems associated with viruses are usually not specific but some are pathognomonic for certain viruses, the rash is not caused by the virus itself but the bodies reaction to the virus. The term exanthem is from the Greek language, Greek . It can be contrasted with enanthems which occur inside the body, such as on mucous membranes. Exanthems occasionally present in association with enanthems . Infectious exanthem in 1900, the physician Clement Dukes assigned a number for the known exanthems affecting the pediatric age group which are first disease (measles), second disease (scarlet fever), third disease (rubella), and fourth disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measles
Measles (probably from Middle Dutch or Middle High German ''masel(e)'', meaning "blemish, blood blister") is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles virus. Other names include ''morbilli'', ''rubeola'', ''9-day measles, red measles'', and ''English measles''. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, Rhinitis, runny nose, and conjunctivitis, inflamed eyes. Small white spots known as Koplik's spots, Koplik spots may form inside the mouth two or three days after the start of symptoms. A red, flat rash which usually starts on the face and then spreads to the rest of the body typically begins three to five days after the start of symptoms. Common complications include diarrhea (in 8% of cases), Otitis media, middle ear infection (7%), and pneumonia (6%). These occur i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubella
Rubella, also known as German measles or three-day measles, is an infection caused by the rubella virus. This disease is often mild, with half of people not realizing that they are infected. A rash may start around two weeks after exposure and last for three days. It usually starts on the face and spreads to the rest of the body. The rash is sometimes itchy and is not as bright as that of measles. Lymphadenopathy, Swollen lymph nodes are common and may last a few weeks. A fever, sore throat, and fatigue may also occur. arthritis, Joint pain is common in adults. Complications may include bleeding problems, orchitis, testicular swelling, encephalitis, and neuritis, inflammation of nerves. Infection during early pregnancy may result in a miscarriage or a child born with congenital rubella syndrome (CRS). Symptoms of CRS manifest as problems with the eyes such as cataracts, deafness, as well as affecting the heart and brain. Problems are rare after the 20th week of pregnancy. Rubel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Rash
An exanthem is a widespread rash eruption occurring on the outside of the body, usually presents in children, the rash is typically associated with constitutional symptoms including fever and fatigue. It is usually caused by a virus, but an exanthem can be caused by bacteria, toxins, drugs, other microorganisms, or as a result of autoimmune disease. Exanthems associated with viruses are usually not specific but some are pathognomonic for certain viruses, the rash is not caused by the virus itself but the bodies reaction to the virus. The term exanthem is from the Greek . It can be contrasted with enanthems which occur inside the body, such as on mucous membranes. Exanthems occasionally present in association with enanthems . Infectious exanthem in 1900, the physician Clement Dukes assigned a number for the known exanthems affecting the pediatric age group which are first disease (measles), second disease (scarlet fever), third disease (rubella), and fourth disease (filatove-dukes) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scarlet Fever
Scarlet fever, also known as scarlatina, is an infectious disease caused by ''Streptococcus pyogenes'', a Group A streptococcus (GAS). It most commonly affects children between five and 15 years of age. The signs and symptoms include a sore throat, fever, headache, cervical lymphadenopathy, swollen lymph nodes, and a characteristic rash. The face is flushed and the Exanthem, rash is Erythema, red and Blanch (medical), blanching. It typically feels like sandpaper and the tongue may be red and bumpy. The rash occurs as a result of capillary damage by exotoxins produced by ''S.pyogenes''. On darker-pigmented skin the rash may be hard to discern. Scarlet fever develops in a small number of people who have strep throat or streptococcal skin infections. The bacteria are usually spread by people coughing or sneezing. It can also be spread when a person touches an object that has the bacteria on it and then touches their mouth or nose. The diagnosis is typically confirmed by throat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus Pyogenes
''Streptococcus pyogenes'' is a species of Gram-positive, aerotolerant bacteria in the genus '' Streptococcus''. These bacteria are extracellular, and made up of non-motile and non-sporing cocci (round cells) that tend to link in chains. They are clinically important for humans, as they are an infrequent, but usually pathogenic, part of the skin microbiota that can cause group A streptococcal infection. ''S. pyogenes'' is the predominant species harboring the Lancefield group A antigen, and is often called group A ''Streptococcus'' (GAS). However, both '' Streptococcus dysgalactiae'' and the '' Streptococcus anginosus'' group can possess group A antigen as well. Group A streptococci, when grown on blood agar, typically produce small (2–3 mm) zones of beta-hemolysis, a complete destruction of red blood cells. The name group A (beta-hemolytic) ''Streptococcus'' is thus also used. The species name is derived from Greek words meaning 'a chain' () of berries ( atiniz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS) is a dermatology, dermatological condition caused by ''Staphylococcus aureus''. Signs and symptoms The disease presents with the widespread formation of fluid-filled blisters that are thin walled and easily ruptured, and the patient can be positive for Nikolsky's sign. SSSS bears a resemblance to thermal burns or scalding, hence the condition's name. Ritter's disease of the newborn is the most severe form of SSSS, with similar signs and symptoms. SSSS often includes a widespread painful erythroderma, often involving the face, diaper, and other intertriginous areas. Extensive areas of desquamation might be present. Perioral crusting and fissuring are seen early in the course. Unlike toxic epidermal necrolysis, SSSS spares the mucous membranes. Children with SSSS may exhibit fussiness or irritability, tiredness, fever, redness of the skin, easily broken fluid-filled blisters that leave an area of moist, tender, painful skin, and large s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photo Of Childhood Rash Obtained From Measles
A photograph (also known as a photo, or more generically referred to as an ''image'' or ''picture'') is an image created by light falling on a photosensitive surface, usually photographic film or an electronic image sensor. The process and practice of creating such images is called photography. Most photographs are now created using a smartphone or camera, which uses a lens to focus the scene's visible wavelengths of light into a reproduction of what the human eye would perceive. Etymology The word ''photograph'' was coined in 1839 by Sir John Herschel and is based on the Greek φῶς (''phos''), meaning "light", and γραφή (''graphê''), meaning "drawing, writing", together meaning "drawing with light". History The first permanent photograph, a contact-exposed copy of an engraving, was made in 1822 using the bitumen-based "heliography" process developed by Nicéphore Niépce. The first photographs of a real-world scene, made using a camera obscura, followed a few years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
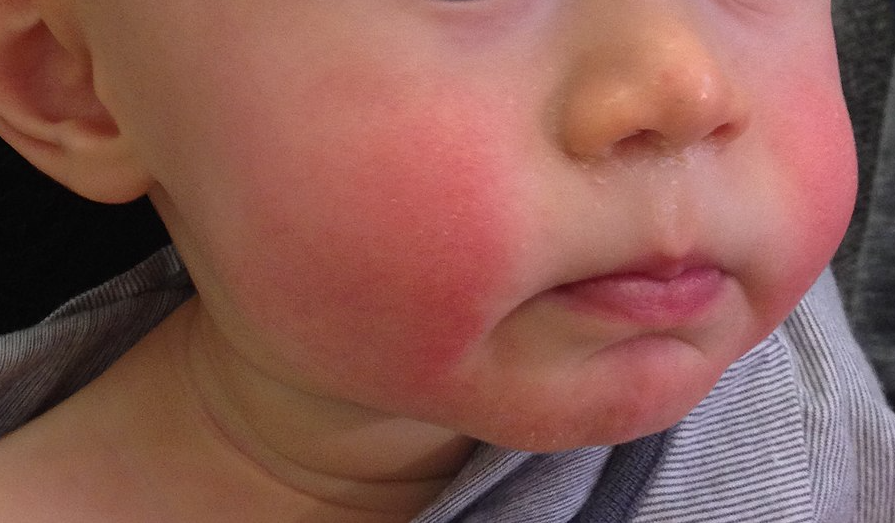
Erythema Infectiosum
Fifth disease, also known as erythema infectiosum and slapped cheek syndrome, is a common and contagious disease caused by infection with parvovirus B19. This virus was discovered in 1975 and can cause other diseases besides fifth disease. Fifth disease typically presents as a rash and is most common in children. Parvovirus B19 can affect people of all ages; about two out of ten persons infected will have no symptoms. Pathogenicity Parvovirus B19 is the only virus within the ''Parvoviridae'' family to cause disease in humans, especially in children. The most common disease derived from parvovirus B19 is fifth disease. This disease is spread in close contact through respiratory droplets, which can be from the nose, mouth, or direct contact with an infected person. Fifth disease is most commonly spread in the winter and spring seasons in children aged six to fourteen years old. Parvovirus B19 will start replicating from anywhere for four to eighteen days. Infected children will b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Aureus Under A Microscope
''Staphylococcus'', from Ancient Greek σταφυλή (''staphulḗ''), meaning "bunch of grapes", and (''kókkos''), meaning "kernel" or " Kermes", is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultative anaerobic organisms (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically). The name was coined in 1880 by Scottish surgeon and bacteriologist Alexander Ogston (1844–1929), following the pattern established five years earlier with the naming of ''Streptococcus''. It combines the prefix "staphylo-" (from ), and suffixed by the (from ). Staphylococcus was one of the leading infections in hospitals and many strains of this bacterium have become antibiotic resistant. Despite strong attempts to get rid of them, staphylococcus bacteria stay present in hospitals, where they can infect people who are most at risk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |