|
Duchy Of Poland (c. 960–1025)
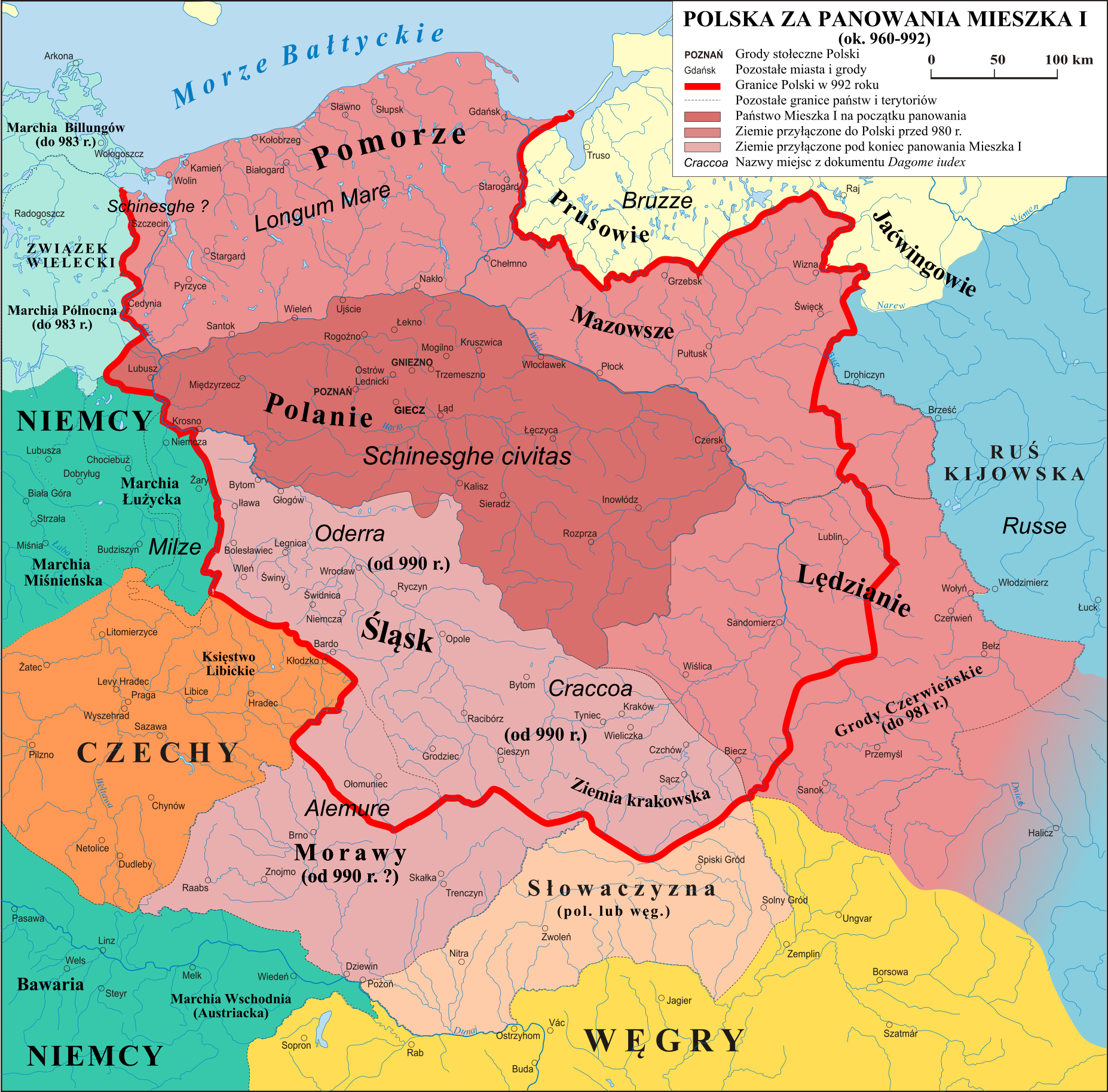
Civitas Schinesghe (; ), also known as the Duchy of Poland or the Principality of Poland, is the historiographical name given to a polity in Central Europe, which existed during the medieval period and was the predecessor state of the Kingdom of Poland. States and territories disestablished in the 1020s Etymology Civitas Schinesghe, meaning "Gniezno State", is the first recorded name related to Poland as a political entity, dating to the year 991 and attested to in a later papal regesta called '' Dagome iudex'' from 1080. The document states that the Piast duke Mieszko I and his wife, Oda von Haldensleben, had given the guidance of ''unam civitatem in integro, que vocatur Schinesghe'' ("a whole state, which is called Schinesghe") over to the Holy See. Though the proper Latin name for Poland, ''Polonia'', which came into use some time later, is not explicitly used in the document, the name ''Schinesghe'' presumably refers to Gniezno, which was one of the main gord stronghol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
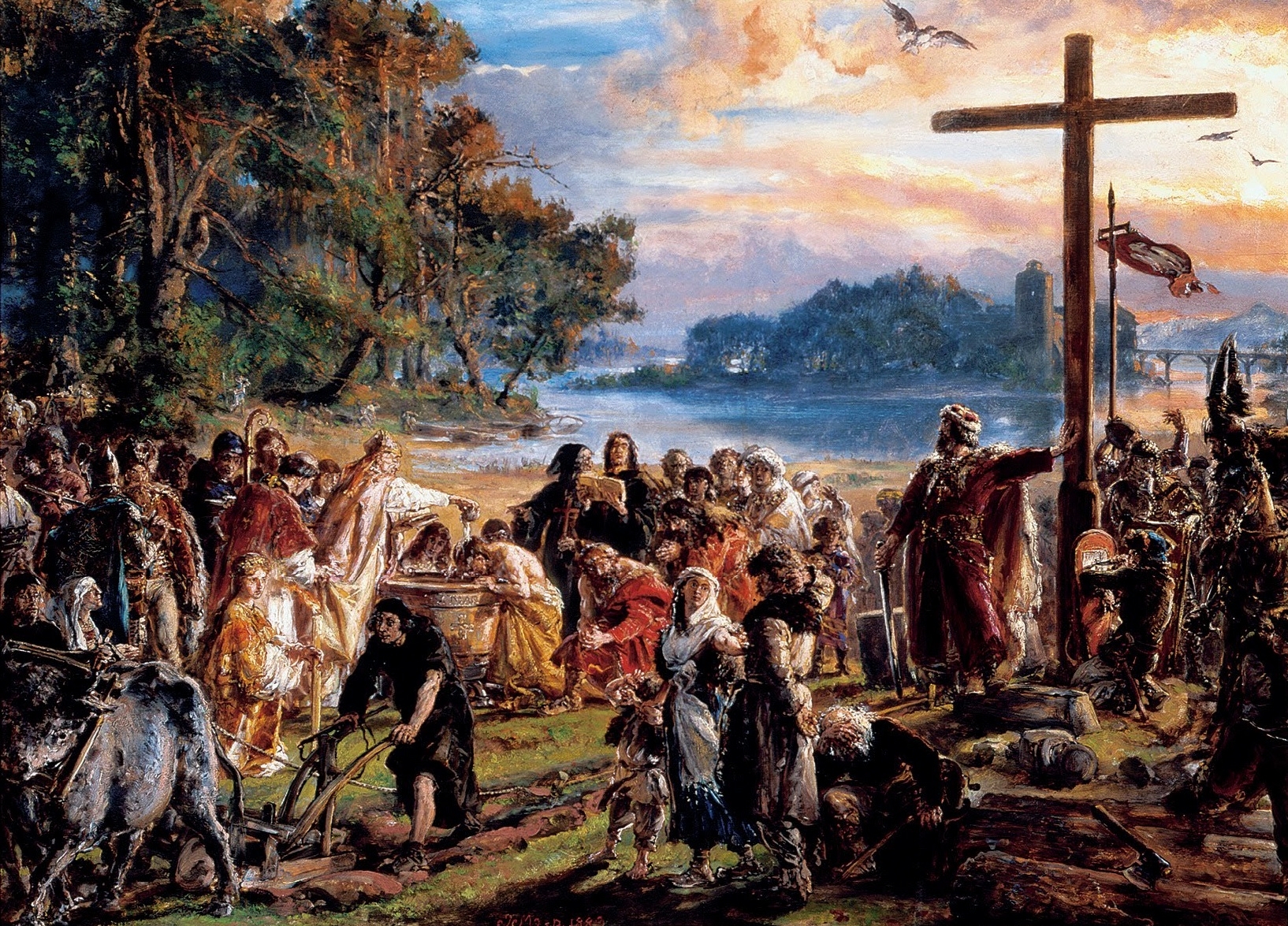
Baptism Of Poland
The Christianization of Poland ( ) refers to the introduction and subsequent spread of Christianity in Poland. The impetus to the process was the Baptism of Poland ( ), the personal baptism of Mieszko I, the first ruler of the future Polish state, and much of his court. The ceremony took place on Holy Saturday, 14 April 966 (under the Julian pre-Gregorian calendar, equivalent to 19 April 966 Gregorian), although the exact location is disputed by historians, with the cities of Poznań and Gniezno being the most likely sites. Mieszko's wife, Dobrawa of Bohemia, is often seen as a major influence on Mieszko's decision to accept Christianity. While the spread of Christianity in Poland took centuries to finish, the process was ultimately successful, as within several decades Poland joined the rank of established European states recognised by the papacy and the Holy Roman Empire. According to historians, the baptism of Poland marks the beginning of Polish statehood. Nevertheless, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regesta
Papal regesta are the copies, generally entered in special registry volumes, of the papal letters and official documents that are kept in the papal archives. The name is also used to indicate subsequent publications containing such documents, in chronological order, with summaries of their essential contents, for which the science of diplomatics – when written in English – usually uses the term "calendar". Early history The growth of the correspondence of the Holy See is evident even by the end of the 2nd century. Probably from a very early date a copy was made of papal documents before their dispatch, and that the collection of these documents was preserved at the seat of the central administration of the Roman Church. At that time high officials of the Roman State administration, the imperial chancery, the Senate, the consuls, the provincial governments, had all official documents entered in such volumes and preserved in the archives. The books in which these documents were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world, each overseen by one or more Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose coming as the Messiah#Christianity, messiah (Christ (title), Christ) was Old Testament messianic prophecies quoted in the New Testament, prophesied in the Old Testament and chronicled in the New Testament. It is the Major religious groups, world's largest and most widespread religion with over 2.3 billion followers, comprising around 28.8% of the world population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in Christianity by country, 157 countries and territories. Christianity remains Christian culture, culturally diverse in its Western Christianity, Western and Eastern Christianity, Eastern branches, and doctrinally diverse concerning Justification (theology), justification and the natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
01000 Bolizavs - Gnezdvn Civitas (-1000)
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latinisation Of Names
Latinisation (or Latinization) of names, also known as onomastic Latinisation (or onomastic Latinization), is the practice of rendering a ''non''-Latin name in a Neo-Latin, modern Latin style. It is commonly found with historical proper names, including personal names and toponyms, and in the standard binomial nomenclature of the life sciences. It goes further than romanisation, which is the transliteration of a word to the Latin alphabet from another script (e.g. Cyrillic). For authors writing in Latin, this change allows the name to function grammatically in a sentence through declension. In a scientific context, the main purpose of Latinisation may be to produce a name which is internationally consistent. Latinisation may be carried out by: * transforming the name into Latin sounds (e.g. for ), or * adding Latinate suffixes to the end of a name (e.g. for ''Heinrich Meibom (doctor), Meibom),'' or * translating a name with a specific meaning into Latin (e.g. for Italian ; b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philology
Philology () is the study of language in Oral tradition, oral and writing, written historical sources. It is the intersection of textual criticism, literary criticism, history, and linguistics with strong ties to etymology. Philology is also defined as the study of literary texts and oral and written records, the establishment of their authentication, authenticity and their original form, and the determination of their meaning. A person who pursues this kind of study is known as a philologist. In older usage, especially British, philology is more general, covering comparative linguistics, comparative and historical linguistics. Classical philology studies classical languages. Classical philology principally originated from the Library of Pergamum and the Library of Alexandria around the fourth century BC, continued by Greeks and Romans throughout the Roman Empire, Roman and Byzantine Empire. It was eventually resumed by European scholars of the Renaissance humanism, Renaissance, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polans (western)
The Polans ( Polish: ''Polanie''; Latin: ''Polani'', ''Polanos''), also known as Polanians or Western Polans ( Polish: ''Polanie Zachodni''; Latin: ''Polani Occidentis''), were a West Slavic and Lechitic tribe who inhabited the Warta River basin of the contemporary Greater Poland region starting in the 6th century. They were one of Central Europe's main tribes and closely related to the Vistulans, Masovians, Czechs and Slovaks. According to Zygmunt Gloger, their name was derived from the word "pole", meaning "field", thus denoting them as "men of the fields". History In the 9th century, the Polans united several West Slavic (Lechitic) groups to the north of Great Moravia. The union led by the Piast dynasty developed into the Duchy of Poland, whose name derives from that of the Polans. The earliest Polan rulers mentioned by name are the legendary figures of Piast the Wheelwright and Popiel (8th–9th centuries). The first historical ruler was Mieszko I (960–992), wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Slavs
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic languages diversified into their historically attested forms over the 10th to 14th centuries. Today, groups which speak West Slavic languages include the Poles, Czechs, Slovaks, Silesians, Kashubians, and Sorbs. From the ninth century onwards, most West Slavs converted to Roman Catholicism, thus coming under the cultural influence of the Latin Church, adopting the Latin alphabet, and tending to be more closely integrated into cultural and intellectual developments in western Europe than the East Slavs, who converted to Eastern Orthodox Christianity and adopted the Cyrillic alphabet. Linguistically, the West Slavic group can be divided into three subgroups: Lechitic, including Polish, Silesian, Kashubian, and the extinct Polabian and Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gord (archaeology)
A gord is a medieval Slavonic fortified settlement, usually built on strategic sites such as hilltops, riverbanks, lake islets or peninsulas between the 6th and 12th centuries in Central and Eastern Europe. A typical gord consisted of a group of wooden houses surrounded by a wall made of earth and wood, and a palisade running along the top of the bulwark. Etymology The term ultimately descends from the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European root '' ǵʰortós'' 'enclosure'. The Proto-Slavic word ''*gordъ'' later differentiated into grad (Cyrillic: град), gorod (Cyrillic: город), gród in Polish, gard in Kashubian, etc. It is the root of various words in modern Slavic languages pertaining to fences and fenced-in areas (Belarusian гарадзіць, Ukrainian городити, Slovak ohradiť, Czech ohradit, Russian оградить, Serbo-Croatian ograditi, and Polish ogradzać, grodzić, to fence off). It also has evolved into words for a garden in certain l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy See
The Holy See (, ; ), also called the See of Rome, the Petrine See or the Apostolic See, is the central governing body of the Catholic Church and Vatican City. It encompasses the office of the pope as the Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishop of the apostolic see, apostolic episcopal see of Diocese of Rome, Rome, and serves as the spiritual and administrative authority of the worldwide Catholic Church and Vatican City. Under international law, the Legal status of the Holy See, Holy See holds the status of a sovereign juridical entity. According to Sacred tradition, Catholic tradition and historical records, the Holy See was founded in the first century by Saint Peter and Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul. By virtue of the doctrines of Primacy of Peter, Petrine and papal primacy, papal primacy, it is the focal point of full communion for Catholics around the world. The Holy See is headquartered in, operates from, and exercises "exclusive dominion" over Vatican City, an independent c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oda Von Haldensleben
Oda of Haldensleben ( 955/60 – 1023) was Duchess of the Polans by marriage to Mieszko I of Poland. Life Oda was the eldest child of Dietrich of Haldensleben, Margrave of the North March. She grew up in the monastery of Kalbe, near to Milde river in the north of Magdeburg. Eventually she became a nun there, and later was married to Duke Mieszko I of Poland. They had: #Mieszko (born 979 – died after 992/95). # Świętopełk (born 980 – died before 991?). # Lambert (born 981 – died after 992/95). Some 80 years later a reference in an obscure church book mentions "Ote and Dago(me)". There is no actual document and the church book mentioning from c. 1080 is known as ''Dagome iudex'' and thus assumed to be one of the earliest Polish legal documents. It's a principal source for this portion of the history of Poland under the Piast dynasty. The undated mentioning from 1080 states that "Dago(me)" (assumed to be Mieszko I) gifted his territory to Pope John XV and received his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |