|
Dot And Cross Diagram
Lewis structuresalso called Lewis dot formulas, Lewis dot structures, electron dot structures, or Lewis electron dot structures (LEDs)are diagrams that show the bonding between atoms of a molecule, as well as the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule. Introduced by Gilbert N. Lewis in his 1916 article ''The Atom and the Molecule'', a Lewis structure can be drawn for any covalently bonded molecule, as well as coordination compounds. Lewis structures extend the concept of the electron dot diagram by adding lines between atoms to represent shared pairs in a chemical bond. Lewis structures show each atom and its position in the structure of the molecule using its chemical symbol. Lines are drawn between atoms that are bonded to one another (pairs of dots can be used instead of lines). Excess electrons that form lone pairs are represented as pairs of dots, and are placed next to the atoms. Although main group elements of the second period and beyond usually react b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formal Charge
In chemistry, a formal charge (F.C. or ), in the covalent view of chemical bonding, is the hypothetical charge assigned to an atom in a molecule, assuming that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, regardless of relative electronegativity. In simple terms, formal charge is the difference between the number of valence electrons of an atom in a neutral free state and the number assigned to that atom in a Lewis structure. When determining the best Lewis structure (or predominant resonance structure) for a molecule, the structure is chosen such that the formal charge on each of the atoms is as close to zero as possible. The formal charge of any atom in a molecule can be calculated by the following equation: q^ = V - L - \frac where is the number of valence electrons of the neutral atom in isolation (in its ground state); is the number of non-bonding valence electrons assigned to this atom in the Lewis structure of the molecule; and is the total num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Formula
The skeletal formula, line-angle formula, bond-line formula or shorthand formula of an organic compound is a type of minimalist structural formula representing a molecule's Atom, atoms, structural isomer, bonds and some details of its molecular geometry, geometry. The lines in a skeletal formula represent bonds between carbon atoms, unless labelled with another element. Labels are optional for carbon atoms, and the hydrogen atoms attached to them. An early form of this representation was first developed by organic chemist August Kekulé, while the modern form is closely related to and influenced by the Lewis structure of molecules and their valence electrons. Hence they are sometimes termed Kekulé structures or Lewis–Kekulé structures. Skeletal formulas have become ubiquitous in organic chemistry, partly because they are relatively quick and simple to draw, and also because the Arrow pushing, curved arrow notation used for discussions of reaction mechanisms and Resonance ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butane
Butane () is an alkane with the formula C4H10. Butane exists as two isomers, ''n''-butane with connectivity and iso-butane with the formula . Both isomers are highly flammable, colorless, easily liquefied gases that quickly vaporize at room temperature and pressure. Butanes are a trace components of natural gases (NG gases). The other hydrocarbons in NG include propane, ethane, and especially methane, which are more abundant. Liquefied petroleum gas is a mixture of propane and some butanes. The name butane comes from the root but- (from butyric acid, named after the Greek word for butter) and the suffix -ane (for organic compounds). History The first synthesis of butane was accidentally achieved by British chemist Edward Frankland in 1849 from ethyl iodide and zinc, but he had not realized that the ethyl radical dimerized and misidentified the substance. It was discovered in crude petroleum in 1864 by Edmund Ronalds, who was the first to describe its proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
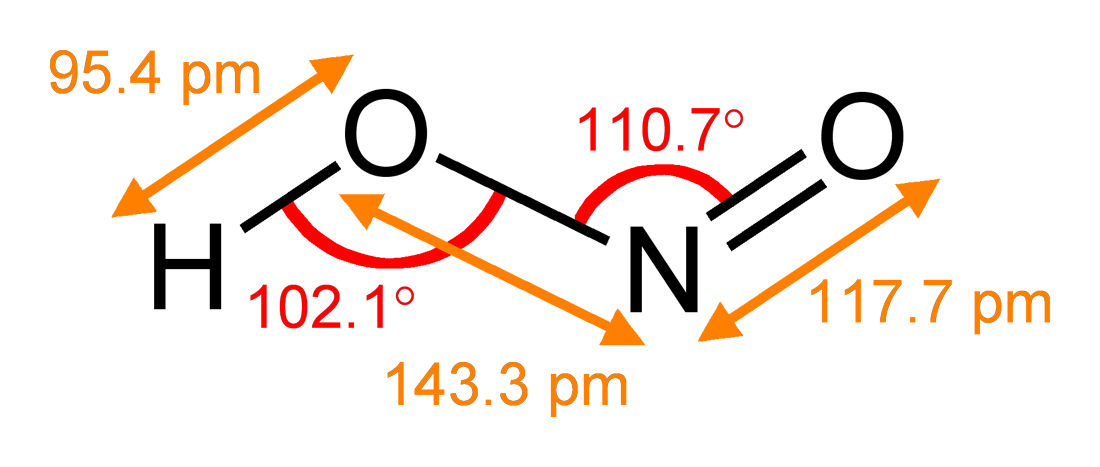
Nitrite
The nitrite polyatomic ion, ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid. Production Sodium nitrite is made industrially by passing a mixture of nitrogen oxides into aqueous sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate solution: : : The product is purified by recrystallization. Alkali metal nitrites are thermally stable up to and beyond their melting point (441 °C for KNO2). Ammonium nitrite can be made from dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3, which is formally the anhydride of nitrous acid: :2 NH3 + H2O + N2O3 → 2 NH4NO2 Structure The nitrite ion has a symmetrical structure (C2v molecular point group, symmetry), with both N–O bonds having equal length and a bond angle of about 115°. In valence bond theory, it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Hexafluoride
Sulfur hexafluoride or sulphur hexafluoride ( British spelling) is an inorganic compound with the formula SF6. It is a colorless, odorless, non-flammable, and non-toxic gas. has an octahedral geometry, consisting of six fluorine atoms attached to a central sulfur atom. It is a hypervalent molecule. Typical for a nonpolar gas, is poorly soluble in water but quite soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. It has a density of 6.12 g/L at sea level conditions, considerably higher than the density of air (1.225 g/L). It is generally stored and transported as a liquefied compressed gas. has 23,500 times greater global warming potential (GWP) than as a greenhouse gas (over a 100-year time-frame) but exists in relatively minor concentrations in the atmosphere. Its concentration in Earth's troposphere reached 12.06 parts per trillion (ppt) in February 2025, rising at 0.4 ppt/year. The increase since 1980 is driven in large part by the expanding electric power sector, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypervalent Molecules
In chemistry, a hypervalent molecule (the phenomenon is sometimes colloquially known as expanded octet) is a molecule that contains one or more main group elements apparently bearing more than eight electrons in their valence shells. Phosphorus pentachloride (), sulfur hexafluoride (), chlorine trifluoride (), the chlorite () ion in chlorous acid and the triiodide () ion are examples of hypervalent molecules. Definitions and nomenclature Hypervalent molecules were first formally defined by Jeremy I. Musher in 1969 as molecules having central atoms of group 15–18 in any valence other than the lowest (i.e. 3, 2, 1, 0 for Groups 15, 16, 17, 18 respectively, based on the octet rule). Several specific classes of hypervalent molecules exist: * Hypervalent iodine compounds are useful reagents in organic chemistry (e.g. Dess–Martin periodinane) * Tetra-, penta- and hexavalent phosphorus, silicon, and sulfur compounds (e.g. PCl5, PF5, SF6, sulfuranes and persulfuranes) * Noble gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Charge
In atomic physics, a partial charge (or net atomic charge) is a non-integer charge value when measured in elementary charge units. It is represented by the Greek lowercase delta (𝛿), namely 𝛿− or 𝛿+. Partial charges are created due to the asymmetric distribution of electrons in chemical bonds. For example, in a polar covalent bond like HCl, the shared electron oscillates between the bonded atoms. The resulting partial charges are a property only of zones within the distribution, and not the assemblage as a whole. For example, chemists often choose to look at a small space surrounding the nucleus of an atom: When an electrically neutral atom bonds chemically to another neutral atom that is more electronegative, its electrons are partially drawn away. This leaves the region about that atom's nucleus with a partial positive charge, and it creates a partial negative charge on the atom to which it is bonded. In such a situation, the distributed charges taken as a group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical reaction occurs. A chemical mechanism is a theoretical conjecture that tries to describe in detail what takes place at each stage of an overall chemical reaction. The detailed steps of a reaction are not observable in most cases. The conjectured mechanism is chosen because it is thermodynamically feasible and has experimental support in isolated intermediates (see next section) or other quantitative and qualitative characteristics of the reaction. It also describes each reactive intermediate, activated complex, and transition state, which bonds are broken (and in what order), and which bonds are formed (and in what order). A complete mechanism must also explain the reason for the reactants and catalyst used, the stereochemistry observed in reactants and products, all products formed and the amount of each. The electron or arrow pushing method is often used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |