|
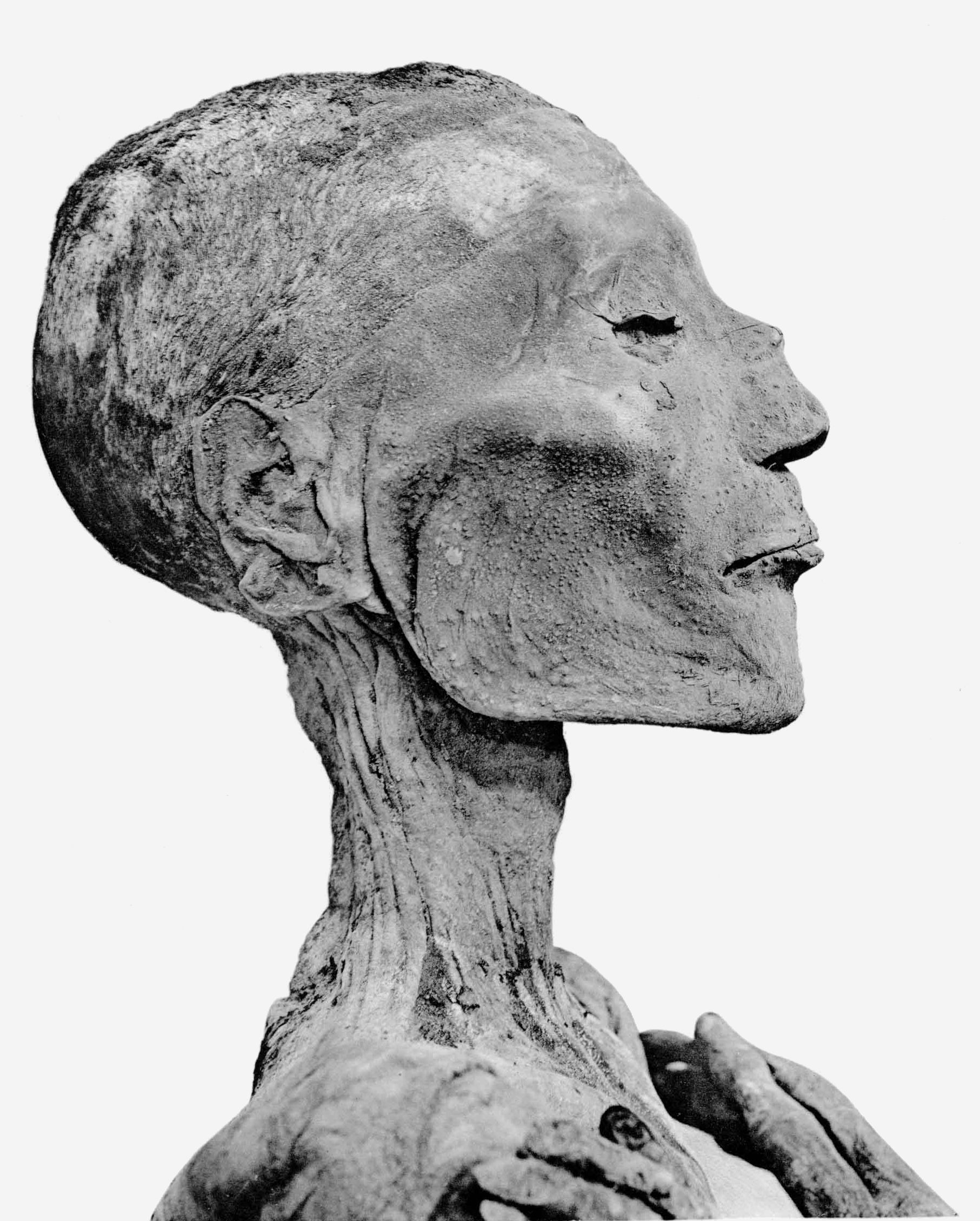
Discovery Of The Tomb Of Tutankhamun
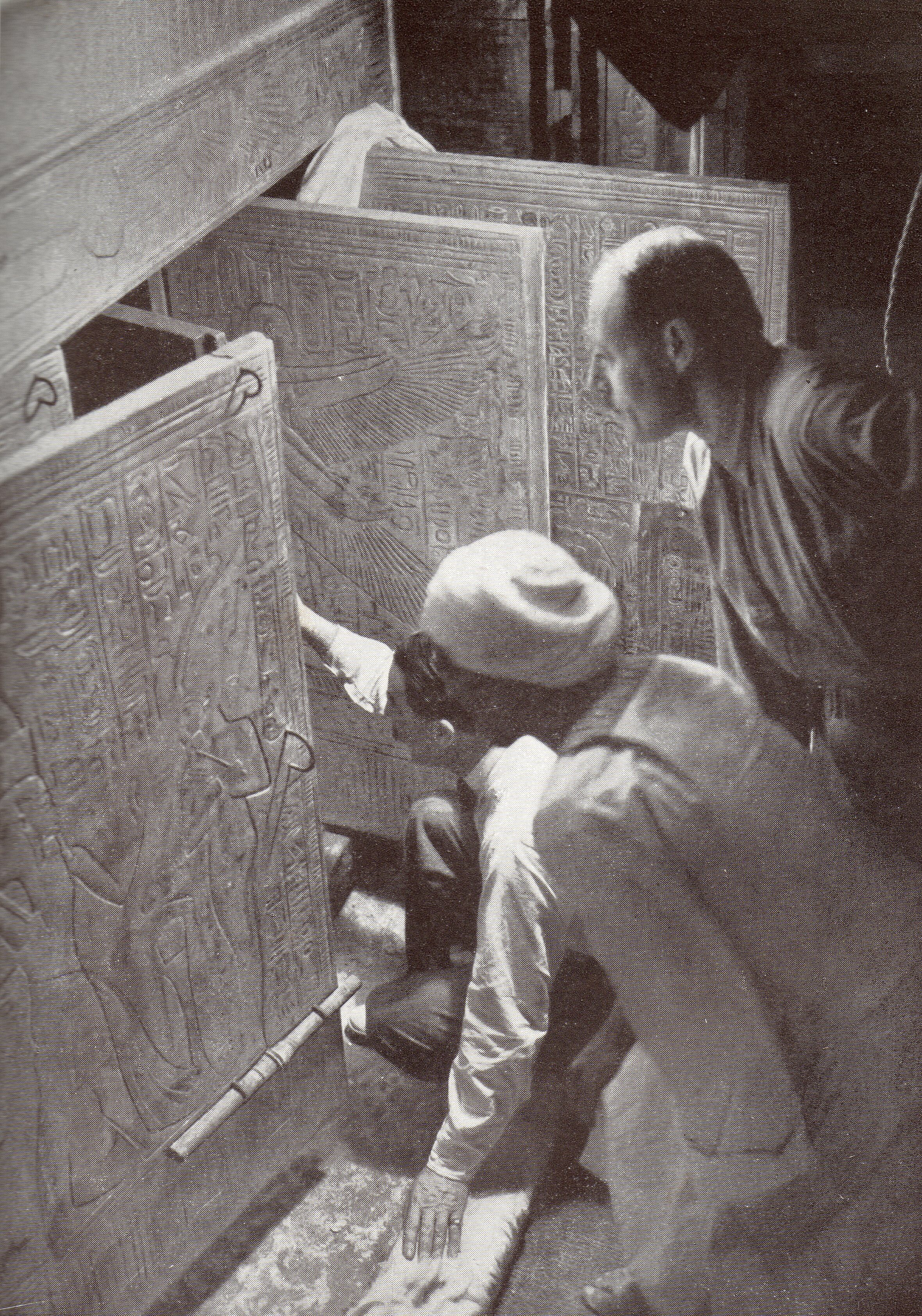
The tomb of Tutankhamun was discovered in the Valley of the Kings in 1922 by excavators led by the Egyptologist Howard Carter, more than 3,300 years after Tutankhamun's death and burial. Whereas the tombs of most pharaohs were plundered by graverobbers in ancient times, Tutankhamun's tomb was hidden by debris for most of its existence and therefore not extensively robbed. It thus became the only known near-intact royal burial from ancient Egypt. The tomb was opened beginning on 4 November 1922 during an excavation by Carter and his patron, George Herbert, 5th Earl of Carnarvon, the 5th Earl of Carnarvon. The burial consisted of more than five thousand objects, many of which were in a highly fragile state, so conserving the burial goods for removal from the tomb required an unprecedented effort. The opulence of the burial goods inspired a media frenzy and popularised ancient Egyptian-inspired designs with the Western public. To the Egyptians, who had recently become partially in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
The Moment Carter Opens The Shrine
''The'' is a grammatical Article (grammar), article in English language, English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the Most common words in English, most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Exhibitions Of Artifacts From The Tomb Of Tutankhamun
Exhibitions of artifacts from the tomb of Tutankhamun have been held at museums in several countries, notably the United Kingdom, Soviet Union, United States, Canada, Japan, and France. The Artifact (archaeology), artifacts had sparked widespread interest in ancient Egypt when they were Discovery of the tomb of Tutankhamun, discovered between 1922 and 1927, but most of them remained in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo until the 1960s, when they were first exhibited outside of Egypt. Because of these exhibitions, relics from the tomb of Tutankhamun are among the most travelled artifacts in the world. Probably the best-known tour was the ''Treasures of Tutankhamun'' from 1972 until 1981. Other exhibitions have included ''Tutankhamun Treasures'' in 1961 and 1967, ''Tutankhamen: The Golden Hereafter'' beginning in 2004, ''Tutankhamun and the Golden Age of the Pharaohs'' beginning in 2005, and ''Tutankhamun: The Golden King and the Great Pharaohs'' in 2008. Permanent exhibitions includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Egyptology
Egyptology (from ''Egypt'' and Ancient Greek, Greek , ''wiktionary:-logia, -logia''; ) is the scientific study of ancient Egypt. The topics studied include ancient Egyptian History of Egypt, history, Egyptian language, language, Ancient Egyptian literature, literature, Ancient Egyptian religion, religion, Ancient Egyptian architecture, architecture and Art of ancient Egypt, art from the 5th millennium BC until the end of its native religious practices in the 4th century AD. History First explorers The earliest explorers of ancient Egypt were the ancient Egyptians themselves. Inspired by a dream he had, Thutmose IV led an excavation of the Great Sphinx of Giza and inscribed a description of the dream on the Dream Stele. Less than two centuries later, Prince Khaemweset, fourth son of Ramesses II, would gain fame for identifying and restoring historic buildings, tombs and temples, including pyramids; and has subsequently been described as the first Egyptologist. Classical Antiqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Ambassadors Of The United Kingdom To Egypt
The ambassador of the United Kingdom to Egypt is the United Kingdom's foremost diplomatic representative in Egypt, and head of the UK's diplomatic mission in Egypt. The official title is ''His Britannic Majesty's Ambassador to the Arab Republic of Egypt''. Under the British occupation of Egypt (1882–1956), the British consul-general, high commissioner, or ambassador effectively ruled Egypt. List of heads of mission Consuls-General * 1786–1796: George Baldwin ''(post abolished in 1793 but letter did not reach Baldwin until 1796)'' * 1803–1804: Charles Lock ''(appointed but died en route to Egypt)'' * 1804–1815: Ernest Missett ''(Agent, then Consul-General)'' *1815–1827: Henry Salt *1827–1833: John Barker ''(acting until 1829)'' *1833–1839: Patrick Campbell *1839–1841: Sir George Lloyd Hodges *1841–1846: Charles John Barnett *1846–1853: Charles Murray *1853–1858: Frederick Wright-Bruce *1858–1865: Robert Gilmour Colquhoun *1865–1876: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Muhammad Ali Dynasty
The Muhammad Ali dynasty or the Alawiyya dynasty was the ruling dynasty of Egypt and Sudan from the 19th to the mid-20th century. It is named after its progenitor, the Albanians, Albanian Muhammad Ali of Egypt, Muhammad Ali, regarded as the founder of modern Egypt. Introduction Muhammad Ali was an Albanians, Albanian commander in the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Albanian army that was sent to drive Napoleon's forces out of Egypt. After Napoleon’s withdrawal, he aligned himself with Umar Makram, Omar Makram, the leader of Egyptian resistance against the French, Muhammad Ali's rise to power, rose to power with his Albanian troops, and forced the Ottoman Sultan Selim III to recognise him as Wāli (Governor) of Egypt in 1805. Demonstrating his grander ambitions, he took the far higher title of Khedive, an honorific used by the Sultan himself. His sons and successors as Egypt's ruler, Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt, Ibrahim Pasha, Abbas I of Egypt, Abbas I, and Sa'id of Egypt, Sa'id Pasha, woul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
John Gardner Wilkinson
Sir John Gardner Wilkinson (5 October 1797 – 29 October 1875) was an English traveller, writer and pioneer egyptologist of the 19th century. He is often referred to as "the Father of British egyptology". Childhood and education Wilkinson was born in Little Missenden, Buckinghamshire. His father was a Westmoreland clergyman, the Reverend John Wilkinson, an amateur enthusiast for antiquities. Wilkinson inherited a modest income from his early-deceased parents. Sent by his guardian to Harrow School in 1813, he later went up to Exeter College, Oxford in 1816.Portraits of Men of Eminence in Literature, Science, and Art, with Biographical Memoirs, Edwards, Ernest, and Lovell Reeve, 1863, Wilkinson ultimately took no degree and, suffering from ill-health, decided to travel to Italy. There in 1819 he met the antiquarian Sir William Gell and resolved to study Egyptology. First sojourn in Egypt Wilkinson first arrived in Egypt in October 1821 as a young man of 24 years, remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ramesses VI
Ramesses VI Nebmaatre-Meryamun (sometimes written Ramses or Rameses, also known under his princely name of Amenherkhepshef C) was the fifth ruler of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt. He reigned for about eight years in the mid-to-late 12th century BC and was a son of Ramesses III and queen Iset Ta-Hemdjert. As a prince, he was known as Ramesses Amunherkhepeshef and held the titles of royal scribe and cavalry general. He was succeeded by his son, Ramesses VII, Ramesses VII Itamun, whom he had fathered with queen Nubkhesbed. After the death of the ruling pharaoh, Ramesses V, who was the son of Ramesses VI's older brother, Ramesses IV, Ramesses VI ascended the throne. In the first two years after his Coronation of the pharaoh, coronation, Ramesses VI stopped frequent raids by Libyan or Egyptian marauders in Upper Egypt and buried his predecessor in what is now an unknown tomb of the Theban necropolis. Ramesses VI usurped KV9, a tomb in the Valley of the Kings planned by and for Rames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ramesses V
Usermaatre Sekheperenre Ramesses V (also written Ramses and Rameses) was the fourth pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt and was the son of Ramesses IV and Duatentopet. His mummy is now on display at the National Museum of Egyptian Civilization in Cairo. Reign Ramesses V's reign was characterized by the continued growth of the power of the priesthood of Amun, which controlled much of the temple land in the country and the state finances, at the expense of the ruling pharaohs. The Turin 1887 papyrus records a financial scandal during Ramesses' reign that involved the priests of Elephantine. Year 1 A period of domestic instability also afflicted his reign, as evidenced by the fact that, according to the Turin Papyrus Cat. 2044, the workmen of Deir el-Medina periodically stopped work on Ramesses V's KV9 tomb in this king's first regnal year, out of fear of "''the enemy''", presumably Libyan raiding parties, who had reached the town of Per-Nebyt and "''burnt its people''." Anot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Luxor
Luxor is a city in Upper Egypt. Luxor had a population of 263,109 in 2020, with an area of approximately and is the capital of the Luxor Governorate. It is among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. Luxor has frequently been characterized as the ''world's greatest open-air museum'', as the ruins of the Egyptian temple complexes at Karnak and Luxor Temple, Luxor stand within the modern city. Immediately opposite, across the River Nile, lie the monuments, temples and tombs of the West Bank Theban Necropolis, which includes the Valley of the Kings and the Valley of the Queens. Thousands of tourists from all around the world arrive annually to visit Luxor's monuments, contributing greatly to the economy of the modern city. Yusuf Abu al-Haggag is the prominent Muslim historical figure of Luxor. Etymology The name ''Luxor'' derives from the Arabic , meaning "castle" or "palace", in the plural form ''al-quṣūr'' (� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thebes, Egypt
Thebes (, , ''Thēbai''), known to the ancient Egyptians as Waset, was an ancient Egyptian city located along the Nile about south of the Mediterranean. Its ruins lie within the modern Egyptian city of Luxor. Thebes was the main city of the fourth Upper Egyptian nome (Sceptre nome) and was the capital of Egypt for long periods during the Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom eras. It was close to Nubia and the Eastern Desert, with its valuable mineral resources and trade routes. It was a religious center and the most venerated city during many periods of ancient Egyptian history. The site of Thebes includes areas on both the eastern bank of the Nile, where the temples of Karnak and Luxor stand and where the city was situated; and the western bank, where a necropolis of large private and royal cemeteries and funerary complexes can be found. In 1979, the ruins of ancient Thebes were classified by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. Toponymy The Egyptian name for Thebes was ''w� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
New Kingdom Of Egypt
The New Kingdom, also called the Egyptian Empire, refers to ancient Egypt between the 16th century BC and the 11th century BC. This period of History of ancient Egypt, ancient Egyptian history covers the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth, Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth, and Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt, Twentieth dynasties. Through radiocarbon dating, the establishment of the New Kingdom has been placed between 1570 and 1544 BC. The New Kingdom followed the Second Intermediate Period of Egypt, Second Intermediate Period and was succeeded by the Third Intermediate Period of Egypt, Third Intermediate Period. It was the most prosperous time for the Egyptians#History, Egyptian people and marked the peak of Egypt's power. In 1845, the concept of a "New Kingdom" as Periodization of ancient Egypt, one of three "golden ages" was coined by German scholar Christian Charles Josias von Bunsen; the original definition would evolve significantly throughout the 19th and 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Eighteenth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XVIII, alternatively 18th Dynasty or Dynasty 18) is classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. The Eighteenth Dynasty spanned the period from 1550/1549 to 1292 BC. This dynasty is also known as the Thutmoside Dynasty for the four pharaohs named Thutmose. Several of Egypt's most famous pharaohs were from the Eighteenth Dynasty, including Tutankhamun. Other famous pharaohs of the dynasty include Hatshepsut (c. 1479 BC–1458 BC), the longest-reigning woman pharaoh of an indigenous dynasty, and Akhenaten (c. 1353–1336 BC), the "heretic pharaoh", with his Great Royal Wife, Nefertiti. The Eighteenth Dynasty is unique among Egyptian dynasties in that it had two Queen regnant, queens regnant, women who ruled as sole pharaoh: Hatshepsut and Neferneferuaten, usually identified as Nefertiti. History Early Dynasty XVIII Dynasty XVIII was founded by Ahmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |