|
Dimasa People
The Dimasa people or Dimasa Kachari people are an ethnolinguistic community presently inhabiting in Assam and Nagaland states in Northeastern India. They speak Dimasa, a Tibeto-Burman language. This community is fairly homogeneous and exclusive, with members required to draw from both parents' separate clans. The Dimasa kingdom, one of many early states in Assam following the downfall of Kamarupa kingdom, was established by these people. The Dimasas are one of the oldest inhabitants of the Northeastern part of India and are one of the many Kachari tribes. Dimasa appear to be one of the earliest indigenous ethnic groups of northeastern India. They are a part of the greater Bodo-Kachari family of ethnolinguistic groups of Northeast India which includes Boro, Tripuri, Rabha, Garo, Tiwa, Koch, Moran etc. peoples of northeast India. They speak Dimasa language a Boro-Garo language of the Tibeto-Burman family. Etymology It stands for ''Di-ma-sa'' meaning ''people of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Assam
Assam (, , ) is a state in Northeast India, northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra Valley, Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . It is the second largest state in Northeast India, northeastern India by area and the largest in terms of population, with more than 31 million inhabitants. The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur to the east; Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram and Bangladesh to the south; and West Bengal to the west via the Siliguri Corridor, a strip of land that connects the state to the rest of India. Assamese language, Assamese and Bodo language, Bodo are two of the official languages for the entire state and Meitei language, Meitei (Manipuri language, Manipuri) is recognised as an additional official language in three districts of Barak Valley and Hojai district. in Hojai district and for the Barak valley region, alongside Bengali language, Bengali, which is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kamarupa Kingdom
Kamarupa (; also called Pragjyotisha or Pragjyotisha-Kamarupa), an early state during the Classical period on the Indian subcontinent, was (along with Davaka) the first historical kingdom of Assam. The Kamrupa word first appeared in the Samudragupta Allahabad Edict before that there is no mention of existence of this word. Though Kamarupa prevailed from 350 to 1140 CE, Davaka was absorbed by Kamarupa in the 5th century CE."As regards the eastern limits of the kingdom, Davaka was absorbed within Kamarupa under Kalyanavarman and the outlying regions were brought under subjugation by Mahendravarman." Ruled by three dynasties from their capitals in present-day Guwahati, North Guwahati and Tezpur, Kamarupa at its height covered the entire Brahmaputra Valley, parts of North Bengal, Bhutan and northern part of Bangladesh, and at times portions of what is now West Bengal, Bihar and Sylhet. Though the historical kingdom disappeared by the 12th century to be replaced by smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, and O. Zolina, 2021Water Cycle Changes. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1055–1210, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.010. A drought can last for days, months or years. Drought often has large impacts on the ecosystems and agriculture of affected regions, and causes harm to the local economy. Annua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lunar Months
In lunar calendars, a lunar month is the time between two successive syzygies of the same type: new moons or full moons. The precise definition varies, especially for the beginning of the month. Variations In Shona, Middle Eastern, and European traditions, the month starts when the young crescent moon first becomes visible, at evening, after conjunction with the Sun one or two days before that evening (e.g., in the Islamic calendar). In ancient Egypt, the lunar month began on the day when the waning moon could no longer be seen just before sunrise. Others run from full moon to full moon. Yet others use calculation, of varying degrees of sophistication, for example, the Hebrew calendar, the Chinese calendar, or the ecclesiastical lunar calendar. Calendars count integer days, so months may be 29 or 30 days in length, in some regular or irregular sequence. Lunar cycles are prominent, and calculated with great precision in the ancient Hindu Panchangam calendar, widely use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Brahmaputra River
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Southwestern China, Northeastern India, and Bangladesh. It is known as Brahmaputra or Luit in Assamese language, Assamese, Yarlung Tsangpo in Lhasa Tibetan, Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachal languages, Arunachali, and Jamuna River (Bangladesh), Jamuna River in Bengali language, Bengali. By itself, it is the 9th List of rivers by discharge, largest river in the world by discharge, and the 15th List of rivers by length, longest. It originates in the Manasarovar Lake region, near Mount Kailash, on the northern side of the Himalayas in Burang County of Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet where it is known as the Yarlung Tsangpo River. The Brahmaputra flows along southern Tibet to break through the Himalayas in great gorges (including the Yarlung Tsangpo Grand Canyon) and into Arunachal Pradesh. It enters India near the village of Gelling, Arunachal Pradesh, Gelling in Arunachal Pradesh and flows southwest through t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lohit River
The Lohit River, whose name came from the Assamese word ''Lohit'' meaning 'blood', also known as the Zayul Chu by the Tibetans, Tilao by the Ahoms and Tellu by the Mishmis, is a river in China and India, which joins the Brahmaputra River in the state of Assam. It is formed in the Zayul County of the Tibet Autonomous Region, through a merger of two rivers: the Kangri Karpo Chu (also called Rongto Chu and Zayul Ngu Chu), which originates in the Kangri Karpo range, and Zayul Chu (), which originates to its northeast. The two rivers merge below the town of Rima. The combined river descends through this mountainous region and surges through Arunachal Pradesh in India for before entering the plains of Assam where it is known as the Lohit River. Tempestuous and turbulent, and known as the river of blood partly attributable to the lateritic soil, it flows through the Mishmi Hills, to meet the Siang (Brahmaputra) at the head of the Brahmaputra valley. Course Thickly f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tibeto-Burman
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non- Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people speak Tibeto-Burman languages. The name derives from the most widely spoken of these languages, Burmese and the Tibetic languages, which also have extensive literary traditions, dating from the 12th and 7th centuries respectively. Most of the other languages are spoken by much smaller communities, and many of them have not been described in detail. Though the division of Sino-Tibetan into Sinitic and Tibeto-Burman branches (e.g. Benedict, Matisoff) is widely used, some historical linguists criticize this classification, as the non-Sinitic Sino-Tibetan languages lack any shared innovations in phonology or morphology to show that they comprise a clade of the phylogenetic tree. History During the 18th century, several scholars noticed parallel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Boro–Garo Languages
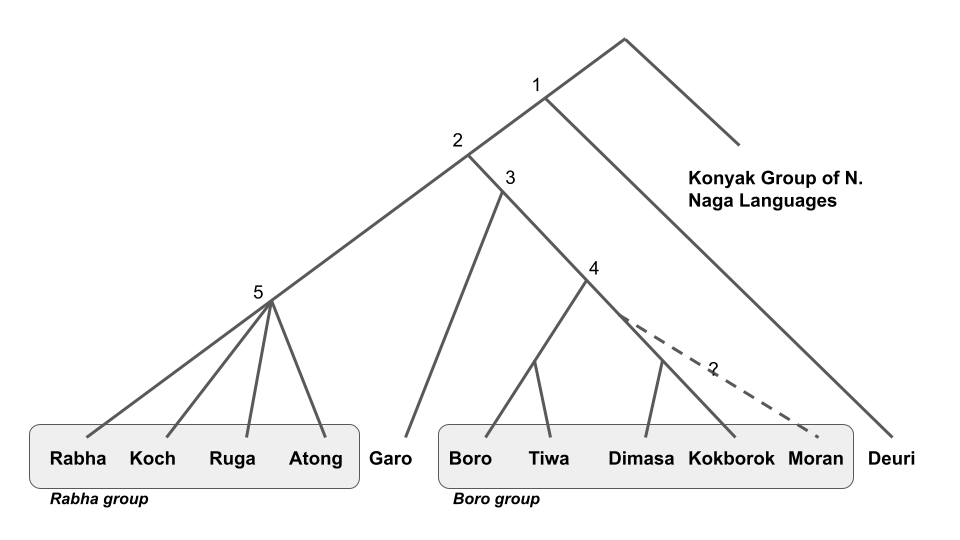
The Boro–Garo languages are a branch of Sino-Tibetan languages, spoken primarily in Northeast India and parts of Bangladesh. The Boro–Garo languages form four groups: Boro, Garo, Koch and Deori. Boro–Garo languages were historically very widespread throughout the Brahmaputra Valley and in what are now the northern parts of Bangladesh, and it is speculated that the proto-Boro-Garo language was the lingua franca of the Brahmaputra valley before it was replaced by Assamese, to which it has made major contributions. Branches The Boro-Garo languages were identified in the Grierson's Language Survey of India, and the names of the languages and their modern equivalents are given below in the table. Sub groups The Boro-Garo languages have been further divided into four subgroups by Burling. *Koch languages: Atong, Koch, Ruga, Rabha * Garo languages: Garo, Megam *Bodo languages: Bodo, Dimasa, Barman, Tiwa, Kokborok (Tripuri), Kachari, Moran * Deori language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Moran People
The Moran are an ethnic group found in the northeast Indian states of Assam and Arunachal Pradesh. They are of Tibeto-Burman origin and belong to the Kachari family. They speak Assamese language, though they used to speak Moran language which was alive until the early 20th century and was closely related to the Dimasa language."I have recently been able to demonstrate that Gurdon’s dialect is a variety of Dimasa, since it retains all the features examined here: it has the same consonant clusters and diphthongs as Dimasa." They once shared the same allied customs with other Kachari groups, but after their conversion to Vaishnavism, the customs began to diminish, but still, those customs can be seen intermixed with Vaishnavism. The Morans were initiated under the fold of Ekasarana Dharma in the tenure of Mayamara abbot Chaturbhujdeva. Distribution They are mainly concentrated in the districts of Upper Assam (Tinsukia, Dibrugarh, Jorhat Jorhat ( /) is a major city in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Koch People
The Koch are a small trans-border ethnic group of Assam and Meghalaya in India and northern Bangladesh. The group consists of nine matrilineal and strictly exogamous clans, with some of them preserving a hitherto sparsely documented Boro-Garo language called Koch, whereas others have switched to local varieties of Indo-Aryan languages. It is a Scheduled Tribe in Meghalaya, India. Koches want to preserve language and culture and heritage. The Koch people in this group are those who have preserved their languages, their animistic religions and follow non-Hindu customs and traditions. They are related but distinguished from the empire building Koch (the Rajbongshi people) and the Hindu caste called Koch in Upper Assam which receives converts from different tribes. Etymology of ''Koch'' According to Tabaqat-i-Nasiri, western Kamrud (Kamrup) was inhabited by the ''Koch'', '' Mech'' & '' Tharu''. In Yogini Tantra, Koches were called as Kuvachas. According to the Fatiyah-i-I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tiwa Puebloans
The Tiwa, less commonly Tigua, are a group of related Tanoan Pueblo peoples in New Mexico that traditionally speak a Tiwa language (although some speakers have switched to Spanish and/or English), and are divided into the two Northern Tiwa groups, in Taos and Picuris, and the Southern Tiwa in Isleta and Sandia, around what is now Albuquerque, and in Ysleta del Sur near El Paso, Texas. Name ''Tiwa'' is the English name for these peoples, which is derived from the Spanish term ''Tigua'' and put into use by Frederick Webb Hodge. The Spanish term has also been used in English writings although the term ''Tiwa'' now is dominant. In Spanish ''Tigua'' only was applied to the Southern Tiwa groups (in Tiguex territory). Spanish variants of ''Tigua'' include ''Cheguas'', ''Chiguas'', ''Téoas'', ''Tiguas'', ''Tigües'', ''Tiguesh'', ''Tigüex'', ''Tiguex'', ''Tigüez'', ''Tihuex'', ''Tioas'', ''Tziquis''. The names ''Atzigues'', ''Atziqui'', ''Tihues'', and ''Tziquis'' were origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Garo People
The Garo people are a Tibeto-Burman ethnic group who live mostly in the Northeast Indian state of Meghalaya, with a smaller number in neighbouring Bangladesh. They are the second-largest indigenous people in Meghalaya after the Khasi and comprise about a third of the local population. They are also found in the Mymensingh Division including Jamalpur, Sherpur, and Mymensingh districts of Bangladesh. Ethnonyms Historically, the name Garo was used for a large number of different peoples living on the southern bank of Brahmaputra River, but now refers primarily to those who call themselves A∙chik Mande (literally " hill people," from ''A∙chik'' "bite soil" and ''mande'' "people") or simply A∙chik or Mande, with the name "Garo" is now being used by outsiders as an exonym.Official Homepage of Meghalaya State of Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |