|
Demographic History Of Vojvodina
Vojvodina's demographic history reflects its rich history and its former location at the border of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman and Habsburg monarchy, Habsburg empires and at the confluence of various peoples, making it a hotbed of invasion, colonization, and assimilation processes. Currently there are more than 25 ethnic groups living in Vojvodina and six official languages. Demographic history The area of Vojvodina had been inhabited since the Paleolithic period. Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European peoples moved into this area during three migration waves, which are dated in 4200 BC, 3300 BC, and 2800 BC respectively. Before the Ancient Rome, Roman conquest in the 1st century BC, Indo-European peoples of Illyrians, Illyrian, Thracians, Thracian and Celts, Celtic origin inhabited the region. During the Roman administration (which extended to Syrmia and Banat), the original inhabitants were heavily Romanization (cultural), Romanized, and would later be known as Vlachs. The region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( ; sr-Cyrl, Војводина, ), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an Autonomous administrative division, autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia, located in Central Europe. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital Belgrade and the Sava and Danube Rivers. The administrative centre, Novi Sad, is the second-largest city in Serbia. The historic regions of Banat, Bačka, Syrmia and northernmost part of Mačva overlap the province. Modern Vojvodina is multi-ethnic and multi-cultural, with some 26 ethnic groups and six official languages. Fewer than two million people, nearly 27% of Serbia's population, live in the province. Name ''Vojvodina'' is also the Serbian word for voivodeship, a type of duchy overseen by a voivode. The Voivodeship of Serbia and Banat of Temeschwar, Serbian Voivodeship, a precursor to modern Vojvodina, was an Austrian province from 1849 to 1860. Its official name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, common culture and Cultural heritage, ancestry, they speak the Romanian language and live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The 2021 Romanian census found that 89.3% of Romania's citizens identified themselves as ethnic Romanians. In one interpretation of the 1989 census results in Moldova, the majority of Moldovans were counted as ethnic Romanians as well.''Ethnic Groups Worldwide: A Ready Reference Handbook By'' David Levinson (author), David Levinson, Published 1998 – Greenwood Publishing Group.At the time of the 1989 census, Moldova's total population was 4,335,400. The largest nationality in the republic, ethnic Romanians, numbered 2,795,000 persons, accounting for 64.5 percent of the population. Source U.S. Library of Congres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
History Of Hungary
Hungary in its modern (post-1946) borders roughly corresponds to the Great Hungarian Plain (the Carpathian Basin) in Central Europe. During the Iron Age, it was located at the crossroads between the cultural spheres of Scythian tribes (such as Agathyrsi, Cimmerians), the Celtic tribes (such as the Scordisci, Boii and Veneti (Gaul), Veneti), Illyrians, Dalmatian tribes (such as the Dalmatae, Histri and Liburnians, Liburni) and the Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes (such as the Lugii, Marcomanni). In 44 BC, the Sarmatians, Iazyges moved into the Great Hungarian Plain. In 8 AD, the western part of the territory (the so-called Transdanubia) of modern Hungary formed part of Pannonia, a province of the Roman Empire. Roman control collapsed with the Hunnic invasions of 370–410, the Huns created a significant empire based in present-day Hungary. In 453 they reached the height of their expansion under Attila the Hun. After the death of Attila, the empire collapsed in 455, and Pannon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jovan Radonić
Jovan Radonić (9 February 1873, Mol, Austria-Hungary — 25 November 1956, Yugoslavia) was a Serbian historian, librarian of Matica Srpska library and member of the Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts. Biography Radonić graduated from the University of Vienna, where he studied under the tutelage of Konstantin Jireček and Vatroslav Jagić, and attended seminars given by Karl Krumbacher in Munich. In 1905, he taught at the University of Belgrade. In 1948 he joined the staff of the Institute of History of the Serbian Academy of Sciences. Radonić, a Slavist and Byzantinist, devoted his research to Balkan medieval history. He translated into Serbian and expanded Jireček’s History of the Serbs (vols. 1–4, Belgrade, 1922–25; 2nd ed., Belgrade, 1952). He dedicated his first book to Ilarion Ruvarac who established critical approach of Serbian historiography. In his work ''Đurađ Kastriot Skenderbeg i Arbanija u XV veku'' he had collected major documentary and literary sour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Southeastern Europe who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of Serbia, history, and Serbian language, language. They primarily live in Serbia, Kosovo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Montenegro as well as in North Macedonia, Slovenia, Germany and Austria. They also constitute a significant diaspora with several communities across Europe, the Americas and Oceania. The Serbs share many cultural traits with the rest of the peoples of Southeast Europe. They are predominantly Eastern Orthodoxy, Eastern Orthodox Christians by religion. The Serbian language, Serbian language (a standardized version of Serbo-Croatian) is official in Serbia, co-official in Kosovo and Bosnia and Herzegovina, and is spoken by the plurality in Montenegro. Ethnology The identity of Serbs is rooted in Eastern Orthodoxy and traditions. In the 19th century, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Timočani
The Timočani (also Timochani, or Timochans; Serbian and Bulgarian: Тимочани) were a medieval South Slavic tribe that lived in the territory of present-day eastern Serbia, west of the Timok River, as well as in the regions of Banat, Syrmia and Moesia Superior. Timočani settled in the Balkans in the 6-7th century in the former Dacia Ripensis province and became later subjects of the Avar Khaganate. It is considered that with the arrival of the Bulgars in the 7th century came under Bulgarian suzerainty, but for a good period of time between the mid-8th and early 9th century local Slavs lived in anarchy until around 805 when the area was reconquered and reimposed control of the Bulgar Khanate under Khan Krum. In the beginning of the 9th century they were also attacked from the West by the Serbs. In 818 during the rule of Omurtag of Bulgaria (814-836) they, together with other border tribes of the First Bulgarian Empire, revolted because of an administrative reform of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Braničevci
The Braničevci (also Branichevci or Branichevtsi; sr-cyr, Браничевци) were a South Slavic tribe that inhabited the region of Braničevo, in what is today Serbia, during the Middle Ages. Initially subjects of the Pannonian Avars with the arrival of the Bulgars came under Bulgarian control in the late 7th century, but for a good period of time between the mid-8th and early 9th century local Slavs lived in anarchy until around 805 when the area was reconquered and reimposed control by the First Bulgarian Empire Khan Krum defeating in the process the remains of the Avar Khaganate. The annexed territories would serve as a frontier to Franks who also exerted control in Lower Pannonia. In 818 during the rule of Omurtag (814-836) Braničevci, together with other tribes of Timočani and Abodrites of the Northwestern Bulgarian frontier, revolted because of administrative reform of centralization started by Krum and continued by Omurtag that deprived them of much of their lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Abodrites
The Obotrites (, ''Abodritorum'', ''Abodritos'') or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany (see Polabian Slavs). For decades, they were allies of Charlemagne in his wars against the Germanic Saxons and the Slavic Veleti. The Obotrites under Prince Thrasco defeated the Saxons in the Battle of Bornhöved (798). The still-Pagan Saxons were dispersed by the emperor, and the part of their former land in Holstein north of Elbe was awarded to the Obotrites in 804, as a reward for their victory. This however was soon reverted through an invasion of the Danes. The Obotrite regnal style was abolished in 1167, when Pribislav was restored to power by Duke Henry the Lion, as Prince of Mecklenburg, thereby founding the Germanized House of Mecklenburg. Obotritic confederation The Bavarian Geographer, an anonymous medieval document compiled in Regensburg in 830, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Severians
The Severians, also Severyans, Siverians, or Siverianians (; ; ; ) were a tribe or tribal confederation of early East Slavs occupying areas to the east of the middle Dnieper River and southeast of the Danube River. They are mentioned by the Bavarian Geographer (9th century), Emperor Constantine VII (956–959), the Khazar ruler Joseph (c. 955), and in the Primary Chronicle (1113). Ethnonym The etymology of the name "Severian" is uncertain. The name of the Severia region originated from the Slavic tribes. One theory proposes derivation from the Slavic word for "north" (''sěver''; men of the north), but the Severians never were the northernmost tribe of Slavs. Another theory proposes an Iranic derivation, from the name of the Sarmatian ''Seuer'' tribe (''seu'' meaning "black"). Some scholars have argued that Jews called this tribe the ''Sawarta,'' based on the '' Kievan Letter'' (c. 930), written in Hebrew as ''SWRTH'' (read either as ''Sur'ata'' or ''Sever'ata''), derived from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
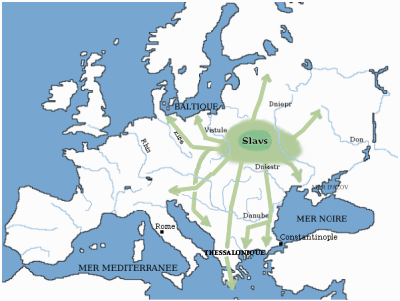
Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and Northern Asia, though there is a large Slavic minority scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, and a substantial Slavic diaspora in the Americas, Western Europe, and Northern Europe. Early Slavs lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately from the 5th to the 10th century AD), and came to control large parts of Central, Eastern, and Southeast Europe between the sixth and seventh centuries. Beginning in the 7th century, they were gradually Christianized. By the 12th century, they formed the core population of a number of medieval Christian states: East Slavs in the Kievan Rus', South Slavs in the Bulgarian Empire, the Principality of Serbia, the Duchy of Croatia and the Banate of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lombards
The Lombards () or Longobards () were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who conquered most of the Italian Peninsula between 568 and 774. The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 and 796) that the Lombards descended from a small tribe called the Winnili,: "From Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic ''wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Germanic/winnaną, winna-'', meaning "to fight, win" who dwelt in northern Germany before migrating to seek new lands. Earlier Roman-era historians wrote of the Lombards in the first century AD as being one of the Suebian peoples, also from what is now northern Germany, near the Elbe river. They migrated south, and by the end of the fifth century, the Lombards had moved into the area roughly coinciding with modern Austria and Slovakia north of the Danube. Here they subdued the Heruls and later fought frequent wars with the Gepids. The Lombard king Audoin defeated the Gepid leader Thuris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gepids
The Gepids (; ) were an East Germanic tribes, East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary, and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava, and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion and language of the Goths and Vandals. They are first mentioned by Roman sources in the third century. In the fourth century, they were among the peoples incorporated into the Huns, Hunnic Empire, within which they formed an important part. After the death of Attila, the Gepids under their leader Ardaric, led an alliance of other peoples who had been in the empire, and defeated the sons of Attila and their remaining allies at the Battle of Nedao in 454. The Gepids and their allies subsequently founded kingdoms on the Middle Danube, bordering on the Roman Empire. The Gepid Kingdom was one of the most important and long-lasting of these, centered on Sirmium, and sometimes referred to as Gepidia. It covered a large part of the Roman Dacia, former Roman province o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |