|
Delphi Method
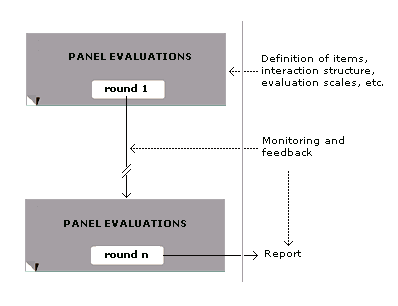
The Delphi method or Delphi technique ( ; also known as Estimate-Talk-Estimate or ETE) is a structured communication technique or method, originally developed as a systematic, interactive forecasting method that relies on a panel of experts. Delphi has been widely used for business forecasting and has certain advantages over another structured forecasting approach, prediction markets. Delphi can also be used to help reach expert consensus and develop professional guidelines. It is used for such purposes in many health-related fields, including clinical medicine, public health, and research. Delphi is based on the principle that forecasts (or decisions) from a structured group of individuals are more accurate than those from unstructured groups. The experts answer questionnaires in two or more rounds. After each round, a facilitator or change agent provides an anonymised summary of the experts' forecasts from the previous round as well as the reasons they provided for their judgment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forecasting
Forecasting is the process of making predictions based on past and present data. Later these can be compared with what actually happens. For example, a company might Estimation, estimate their revenue in the next year, then compare it against the actual results creating a variance actual analysis. Prediction is a similar but more general term. Forecasting might refer to specific formal statistical methods employing time series, cross-sectional data, cross-sectional or longitudinal study, longitudinal data, or alternatively to less formal judgmental methods or the process of prediction and assessment of its accuracy. Usage can vary between areas of application: for example, in hydrology the terms "forecast" and "forecasting" are sometimes reserved for estimates of values at certain specific future times, while the term "prediction" is used for more general estimates, such as the number of times floods will occur over a long period. Risk and uncertainty are central to forecasting an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandwagon Effect
The bandwagon effect is a psychological phenomenon where people adopt certain behaviors, styles, or attitudes simply because others are doing so. More specifically, it is a cognitive bias by which public opinion or behaviours can alter due to particular actions and beliefs rallying amongst the public. It is a psychological phenomenon whereby the rate of uptake of beliefs, ideas, fads and trends increases with respect to the proportion of others who have already done so. As more people come to believe in something, others also "hop on the bandwagon" regardless of the underlying evidence. Following others' actions or beliefs can occur because of conformism or deriving information from others. Much of the influence of the bandwagon effect comes from the desire to 'fit in' with peers; by making similar selections as other people, this is seen as a way to gain access to a particular social group. An example of this is fashion trends wherein the increasing popularity of a certain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Dysfunction–associated Steatotic Liver Disease
Metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), previously known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is a type of chronic liver disease. This condition is diagnosed when there is excessive fat build-up in the liver (hepatic steatosis), and at least one metabolic risk factor. When there is also increased alcohol (drug), alcohol intake, the term MetALD, or metabolic dysfunction and alcohol associated/related liver disease is used, and differentiated from Alcoholic liver disease, alcohol-related liver disease (ALD) where alcohol is the predominant cause of the steatotic liver disease. The terms non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH, now MASH) have been used to describe different severities, the latter indicating the presence of further hepatitis, liver inflammation. NAFL is less dangerous than NASH and usually does not progress to it, but this progression may eventually lead to complications, such as cirrhosis, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the determinants of health of a population and the threats it faces is the basis for public health. The ''public'' can be as small as a handful of people or as large as a village or an entire city; in the case of a pandemic it may encompass several continents. The concept of ''health'' takes into account physical, psychological, and Well-being, social well-being, among other factors.What is the WHO definition of health? from the Preamble to the Constitution of WHO as adopted by the Internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocol (science)
In natural and social science research, a protocol is most commonly a predefined procedural method in the design and implementation of an experiment. Protocols are written whenever it is desirable to standardize a laboratory method to ensure successful replication of results by others in the same laboratory or by other laboratories. Additionally, and by extension, protocols have the advantage of facilitating the assessment of experimental results through peer review. In addition to detailed procedures, equipment, and instruments, protocols will also contain study objectives, reasoning for experimental design, reasoning for chosen sample sizes, safety precautions, and how results were calculated and reported, including statistical analysis and any rules for predefining and documenting excluded data to avoid bias. Similarly, a protocol may refer to the procedural methods of health organizations, commercial laboratories, manufacturing plants, etc. to ensure their activities (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Guideline
A medical guideline (also called a clinical guideline, standard treatment guideline, or clinical practice guideline) is a document with the aim of guiding decisions and criteria regarding diagnosis, management, and treatment in specific areas of healthcare. Such documents have been in use for thousands of years during the entire history of medicine. However, in contrast to previous approaches, which were often based on tradition or authority, modern medical guidelines are based on an examination of current evidence within the paradigm of evidence-based medicine. They usually include summarized consensus statements on best practice in healthcare. A healthcare provider is obliged to know the medical guidelines of their profession, and has to decide whether to follow the recommendations of a guideline for an individual treatment. Background Modern clinical guidelines identify, summarize and evaluate the highest quality evidence and most current data about prevention, diagnosis, pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-democracy
E-democracy (a blend of the terms Electronic publishing, electronic and democracy), also known as digital democracy or Internet democracy, uses information and communication technology (ICT) in politics, political and governance processes. The term is credited to digital activist Steven Clift. By using 21st-century ICT, e-democracy seeks to enhance democracy, including aspects like civic technology and E-government. Proponents argue that by promoting transparency in decision-making processes, e-democracy can empower all citizens to observe and understand the proceedings. Also, if they possess overlooked data, perspectives, or opinions, they can contribute meaningfully. This contribution extends beyond mere informal disconnected debate; it facilitates citizen engagement in the Direct democracy, proposal, development, and actual creation of a country's laws. In this way, e-democracy has the potential to incorporate crowdsourced analysis more directly into the policy-making process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technological Forecasting And Social Change
''Technological Forecasting and Social Change'' (formerly ''Technological Forecasting'') is a peer-reviewed academic journal published by Elsevier covering futures studies, technology assessment, and technology forecasting. Articles focus on methodology and actual practice, and have been published since 1969. The editors-in-chief are Scott Cunningham ( University of Strathclyde) and Mei-Chih Hu ( National Tsing Hua University). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2022 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 12.0. References External links * Futurology journals Elsevier academic journals English-language journals Academic journals established in 1969 Science and technology studies journals {{Social-science-journ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELAC Action Plans
''' in international relations, is an intergovernmental strategy that conceives of information and communications technologies (ICTs) as instruments for economic development and social inclusion in Latin America and the Caribbean. It is based on a public-private sector partnership"Foresight tools for participative policy-making in inter-governmental processes in developing countries: Lessons learned from the eLAC Policy Priorities Delphi" Martin Hilbert, Ian Miles and Julia Othmer (2009), |
Economic Indicator
An economic indicator is a statistic about an Economics, economic activity. Economic indicators allow analysis of economic performance and predictions of future performance. One application of economic indicators is the study of business cycles. Economic indicators include various indices, earnings reports, and economic summaries: for example, the unemployment rate, quits rate (quit rate in American English), housing starts, consumer price index (a measure for inflation (economics), inflation), inverted yield curve, consumer leverage ratio, industrial production, bankruptcies, gross domestic product, broadband internet access, broadband internet penetration, retail sales, price index, and changes in credit conditions. The leading business cycle dating committee in the United States, United States of America is the private National Bureau of Economic Research. The Bureau of Labor Statistics is the principal fact-finding agency for the U.S. government in the field of labor economics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines. Automation has been achieved by various means including Mechanical system, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical, electronic devices, and computers, usually in combination. Complicated systems, such as modern Factory, factories, airplanes, and ships typically use combinations of all of these techniques. The benefit of automation includes labor savings, reducing waste, savings in electricity costs, savings in material costs, and improvements to quality, accuracy, and precision. Automation includes the use of various equipment and control systems such as machinery, processes in factories, boilers, and heat-treating ovens, switching on telephone networks, steering, Stabilizer (ship), stabilization of ships, aircraft and other applic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |