|
Daylighting
Daylighting is the practice of placing windows, skylights, other openings, and reflective surfaces so that sunlight (direct or indirect) can provide effective internal lighting. Particular attention is given to daylighting while designing a building when the aim is to maximize visual comfort or to reduce energy use. Energy savings can be achieved from the reduced use of artificial (electric) lighting or from passive solar heating. Artificial lighting energy use can be reduced by simply installing fewer electric lights where daylight is present or by automatically dimming/switching off electric lights in response to the presence of daylight – a process known as daylight harvesting. The amount of daylight received in an internal space can be analyzed by measuring illuminance on a grid or undertaking a daylight factor calculation. Computer programs such as Radiance allow an architect or engineer to quickly calculate benefits of a particular design. The human eye's response ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
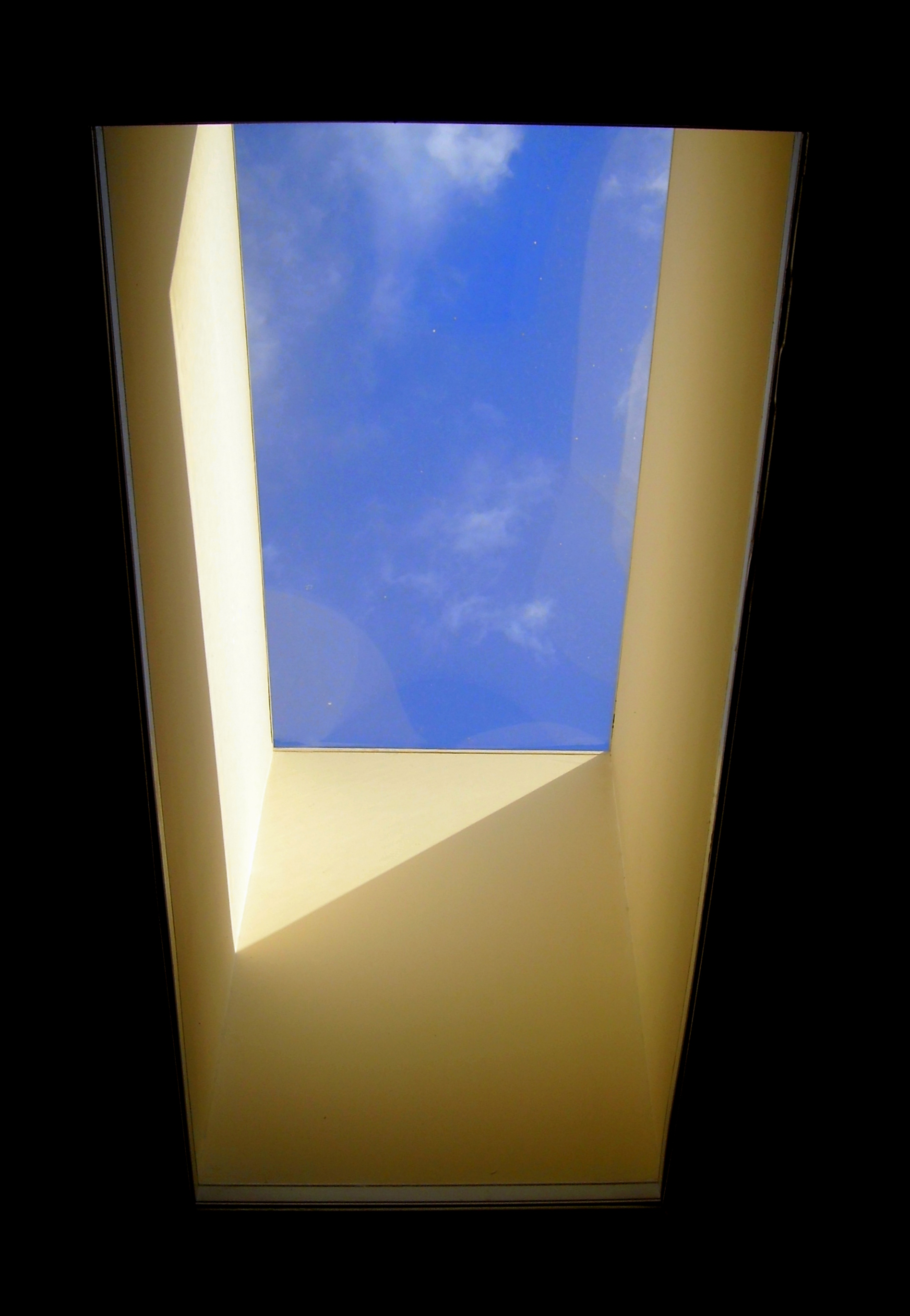
Daylighting - Skylight
Daylighting is the practice of placing windows, skylights, other openings, and reflective surfaces so that sunlight (direct or indirect) can provide effective internal lighting. Particular attention is given to daylighting while designing a building when the aim is to maximize visual comfort or to reduce energy use. Energy savings can be achieved from the reduced use of artificial (electric) lighting or from passive solar heating. Artificial lighting energy use can be reduced by simply installing fewer electric lights where daylight is present or by automatically dimming/switching off electric lights in response to the presence of daylight – a process known as daylight harvesting. The amount of daylight received in an internal space can be analyzed by measuring illuminance on a grid or undertaking a daylight factor calculation. Computer programs such as Radiance allow an architect or engineer to quickly calculate benefits of a particular design. The human eye's response to li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
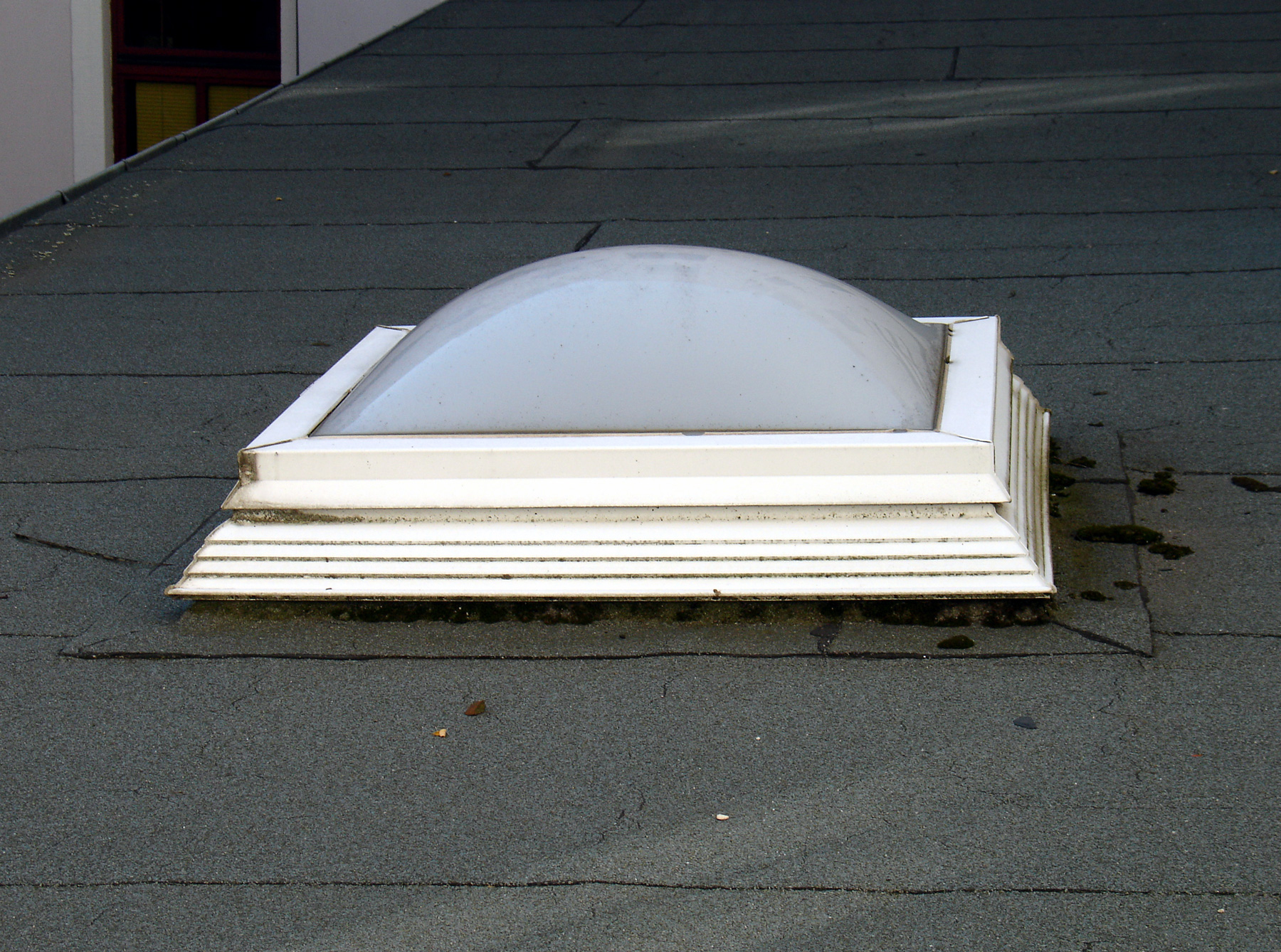
Skylight
A skylight (sometimes called a rooflight) is a light-permitting structure or window, usually made of transparent or translucent glass, that forms all or part of the roof space of a building for daylighting and ventilation purposes. History Open skylights were used in Ancient Roman architecture, such as the oculus of the Pantheon. Glazed 'closed' skylights have been in use since the Industrial Revolution made advances in glass production manufacturing. Mass production units since the mid-20th century have brought skylights to many uses and contexts. Energy conservation has brought new motivation, design innovation, transmission options, and efficiency rating systems for skylights. Prior to the Industrial Revolution, it was Spain and France that probably had the leading technology in architectural glass. One of the earliest forms of glass skylight can be seen at the Burgos Cathedral in the Chapel of the Constable. Other early form of glass skylight can be seen at the Pal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daylight Harvesting
Daylight harvesting systems use daylight to offset the amount of electric lighting needed to properly light a space, in order to reduce energy consumption. This is accomplished using lighting control systems that are able to dim or switch electric lighting in response to changing daylight availability. The term Daylight Harvesting has become the standard in the fields of lighting, sustainable architecture, and active daylighting industries. System design and components Daylight harvesting systems are typically designed to maintain a minimum recommended light level. This light level will vary according to the needs and use of the space; for example, the commonly recommended light level for offices is 500 Lux (or around 50 foot-candles) on the desktop. Photosensors All daylight harvesting systems use a light level sensor, a photosensor, to detect the prevailing light level, luminance or brightness, in open-loop or closed-loop systems. Photosensors are used to adjust electric ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Solar
In passive solar building design, windows, walls, and floors are made to collect, store, reflect, and distribute solar energy, in the form of heat in the winter and reject solar heat in the summer. This is called passive solar design because, unlike active solar heating systems, it does not involve the use of mechanical and electrical devices. The key to designing a passive solar building is to best take advantage of the local climate performing an accurate site analysis. Elements to be considered include window placement and size, and glazing type, thermal insulation, thermal mass, and shading. Passive solar design techniques can be applied most easily to new buildings, but existing buildings can be adapted or "retrofitted". Passive energy gain ''Passive solar'' technologies use sunlight without active mechanical systems (as contrasted to ''active solar'', which uses thermal collectors). Such technologies convert sunlight into usable heat (in water, air, and thermal mass), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clerestory
In architecture, a clerestory ( ; , also clearstory, clearstorey, or overstorey) is a high section of wall that contains windows above eye level. Its purpose is to admit light, fresh air, or both. Historically, ''clerestory'' denoted an upper level of a Roman basilica or of the nave of a Romanesque or Gothic church, the walls of which rise above the rooflines of the lower aisles and are pierced with windows. Similar structures have been used in transportation vehicles to provide additional lighting, ventilation, or headroom. History Ancient world The technology of the clerestory appears to originate in the temples of ancient Egypt. The term "clerestory" is applicable to Egyptian temples, where the lighting of the hall of columns was obtained over the stone roofs of the adjoining aisles, through gaps left in the vertical slabs of stone. Clerestory appeared in Egypt at least as early as the Amarna period. In the Minoan palaces of Crete such as Knossos, by contrast, lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Window
A window is an opening in a wall, door, roof, or vehicle that allows the exchange of light and may also allow the passage of sound and sometimes air. Modern windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translucent material, a sash set in a frame in the opening; the sash and frame are also referred to as a window. Many glazed windows may be opened, to allow ventilation, or closed, to exclude inclement weather. Windows may have a latch or similar mechanism to lock the window shut or to hold it open by various amounts. In addition to this, many modern day windows may have a window screen or mesh, often made of aluminum or fibreglass, to keep bugs out when the window is opened. Types include the eyebrow window, fixed windows, hexagonal windows, single-hung, and double-hung sash windows, horizontal sliding sash windows, casement windows, awning windows, hopper windows, tilt, and slide windows (often door-sized), tilt and turn windows, transom windo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Shelves
A light shelf is a horizontal surface that reflects daylight deep into a building. Light shelves are placed above eye-level and have high-reflectance upper surfaces, which reflect daylight onto the ceiling and deeper into the space. Light shelves are typically used in high-rise and low-rise office buildings, as well as institutional buildings. This design is generally used on the equator-facing side of the building, which is where maximum sunlight is found, and as a result is most effective. Not only do light shelves allow light to penetrate through the building, they are also designed to shade near the windows, due to the overhang of the shelf, and help reduce window glare. Exterior shelves are generally more effective shading devices than interior shelves. A combination of exterior and interior shelves will work best in providing an even illumination gradient. Benefits Architectural light shelves have been proven to reduce the need for artificial lighting in buildings. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sliding Glass Door
A sliding glass door, patio door, or doorwall A sliding glass door, patio door, or doorwall is a type of predominantly glass sliding door, in architecture and construction, that is situated in an external wall to provide egress from a room and access to a backyard or patio, providing "a pleasant view" and, when not fully covered, passive daylighting. Like a window, when open it also provides fresh air and copious natural light. It is considered a single unit consisting of two or more panel sections, some or all being mobile to slide open. Another design, a wall-sized glass pocket door has one or more panels movable and sliding into wall pockets, completely disappearing for a 'wide open' indoor-outdoor room experience. The sliding glass door was introduced as a significant element of pre-war International style architecture in Europe and North America. Their predecessor is the sliding Shōji and Fusuma panel door in traditional Japanese architecture. The post-war building ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimmer
A dimmer is a device connected to a light fixture and used to lower the brightness of the light. By changing the voltage waveform applied to the lamp, it is possible to lower the intensity of the light output. Although variable-voltage devices are used for various purposes, the term ''dimmer'' is generally reserved for those intended to control light output from resistive incandescent, halogen, and (more recently) compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) and light-emitting diodes (LEDs). More specialized equipment is needed to dim fluorescent, mercury-vapor, solid-state, and other arc lighting. Dimmers range in size from small units the size of domestic light switches to high-power units used in large theatrical or architectural lighting installations. Small domestic dimmers are generally directly controlled, although remote control systems (such as X10) are available. Modern professional dimmers are generally controlled by a digital control system like DMX or DALI. In newer syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropic Of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer, which is also referred to as the Northern Tropic, is the most northerly circle of latitude on Earth at which the Sun can be directly overhead. This occurs on the June solstice, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun to its maximum extent. It also reaches 90 degrees below the horizon at solar midnight on the December Solstice. Using a continuously updated formula, the circle is currently north of the Equator. Its Southern Hemisphere counterpart, marking the most southerly position at which the Sun can be directly overhead, is the Tropic of Capricorn. These tropics are two of the five major circles of latitude that mark maps of Earth, the others being the Arctic and Antarctic circles and the Equator. The positions of these two circles of latitude (relative to the Equator) are dictated by the tilt of Earth's axis of rotation relative to the plane of its orbit, and since the tilt changes, the location of these two circles also changes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daylight
Daylight is the combination of all direct and indirect sunlight during the daytime. This includes direct sunlight, diffuse sky radiation, and (often) both of these reflected by Earth and terrestrial objects, like landforms and buildings. Sunlight scattered or reflected by astronomical objects is generally not considered daylight. Therefore, daylight excludes moonlight, despite it being reflected indirect sunlight. Definition Daylight is present at a particular location, to some degree, whenever the Sun is above the local horizon. (This is true for slightly more than 50% of the Earth at any given time. For an explanation of why it is not exactly half, see here). However, the outdoor illuminance can vary from 120,000 lux for direct sunlight at noon, which may cause eye pain, to less than 5 lux for thick storm clouds with the Sun at the horizon (even <1 lux for the most extreme case), which may make shadows from distant [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Tube
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 terahertz, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). In physics, the term "light" may refer more broadly to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. The primary properties of light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum and polarization. Its speed in a vacuum, 299 792 458 metres a second (m/s), is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Like all types of electromagnetic radiation, visible light propagates by massless elementary particles called photons that represents the quanta of electromagnetic field, and can be analyzed as both waves and particl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpg)