|
Day Of Reconciliation
The Day of Reconciliation is a public holiday in South Africa held annually on 16 December. The holiday came into effect in 1995 after the end of apartheid, with the intention of fostering reconciliation and national unity for the country. Recognising the need for racial harmony, the government chose the date for its significance to both Afrikaner and indigenous South African cultures. The celebration of the Day of Reconciliation can take the form of remembering past history, recognising veteran's contributions, marching, and other festivities. The origins of the celebration for Afrikaners goes back to the Day of the Vow, which commemorates the Voortrekker victory over the Zulus at the Battle of Blood River on 16 December 1838. For black and indigenous South Africans, the date marks both peaceful protests against racial injustice and the founding of the Umkhonto we Sizwe paramilitary wing of the African National Congress (ANC) on 16 December 1961. Nelson Mandela and the Sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of South Africa
The national flag of South Africa was designed in March 1994 and adopted on 27 April 1994, during South Africa's South African general election, 1994, 1994 general election, to replace the Flag of South Africa (1928–1994), previous flag used from 1928–1994. The flag has horizontal bands of red (on the top) and blue (on the bottom), of equal width, separated by a central green band which splits into a horizontal "Y" shape, the arms of which end at the corners of the hoist side (and follow the flag's diagonals). The "Y" embraces a black isosceles triangle from which the arms are separated by narrow yellow or gold fimbriation, bands; the red and blue bands are separated from the green band and its arms by narrow white stripes. The stripes at the fly end are in the 5:1:3:1:5 ratio. Three of the flag's colours were taken from the flag of the South African Republic, itself derived from the flag of the Netherlands, as well as the Union Jack, while the remaining three colours were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parade
A parade is a procession of people, usually organized along a street, often in costume, and often accompanied by marching bands, floats, or sometimes large balloons. Parades are held for a wide range of reasons, but are usually some variety of celebration. The term "parade" may also be used for multiple different subjects; for example, in the Canadian Armed Forces, "parade" is used both to describe the procession and in other informal connotations. Protest demonstrations can also take the form of a parade, but such cases are usually referred to as a march instead. History The first parades date back to , only being used for religious or military purposes. The Babylonians celebrated Akitu by parading their deities and performing rituals. To celebrate the federal government's victory in the American Civil War, 145,000 Union soldiers marched in a two-day Grand Review of the Armies in Washington, D.C. They passed before the President, the Cabinet, and senior officers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
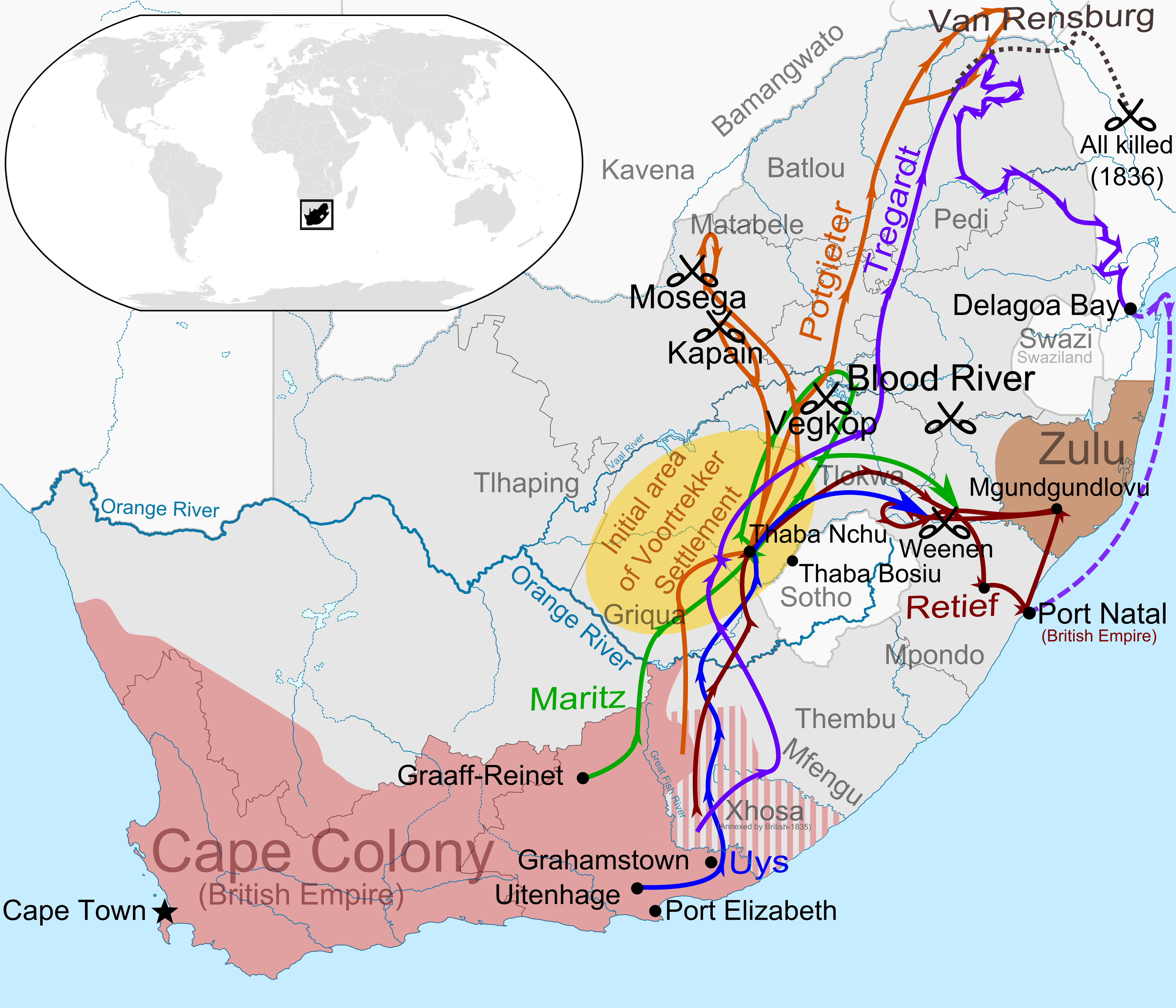
Voortrekker
The Great Trek (, ) was a northward migration of Dutch-speaking settlers who travelled by wagon trains from the Cape Colony into the interior of modern South Africa from 1836 onwards, seeking to live beyond the Cape's British colonial administration. The Great Trek resulted from the culmination of tensions between rural descendants of the Cape's original European settlers, known collectively as Boers, and the British. It was also reflective of an increasingly common trend among individual Boer communities to pursue an isolationist and semi-nomadic lifestyle away from the developing administrative complexities in Cape Town. Boers who took part in the Great Trek identified themselves as ''voortrekkers'', meaning "pioneers" or "pathfinders" in Dutch and Afrikaans. The Great Trek led directly to the founding of several autonomous Boer republics, namely the South African Republic (also known simply as the Transvaal), the Orange Free State and the Natalia Republic. It also led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of South Africa
The Constitution of South Africa is the supreme law of the Republic of South Africa. It provides the legal foundation for the existence of the republic, it sets out the human rights and duties of its citizens, and defines the structure of the Government. The current constitution, the country's fifth, was drawn up by the Parliament elected in 1994 general election. It was promulgated by President Nelson Mandela on 18 December 1996 and came into effect on 4 February 1997, replacing the Interim Constitution of 1993. The first constitution was enacted by the South Africa Act 1909, the longest-lasting to date. Since 1961, the constitutions have promulgated a republican form of government. Since 1997, the Constitution has been amended by eighteen amendments. The Constitution is formally entitled the "Constitution of the Republic of South Africa, 1996." It was previously also numbered as if it were an Act of ParliamentAct No. 108 of 1996but, since the passage of the Citation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlotte Maxeke
Charlotte Makgomo (née Mannya) Maxeke (7 April 1871 – 16 October 1939) was a South African religious leader, social and political activist. By graduating with a B.Sc. from Wilberforce University, Ohio, in 1903, she became the first black woman in South Africa to graduate with a university degree as well as the first African woman to graduate from an American university. Early life Charlotte Makgomo Mannya was born in Ga-Ramokgopa, Limpopo, South Africa, on 7 April 1871 and grew up in Fort Beaufort, Eastern Cape. She was the daughter of John Kgope Mannya, the son of headman Modidima Mannya of the Batlokwa people, under Chief Mamafa Ramokgopa and Anna Manci, a Xhosa woman from Fort Beaufort. Mannya's father was a roads foreman and Presbyterian lay preacher, and her mother was a teacher. Mannya's grandfather served as a key adviser to the King of the Basothos. Soon after her birth, Mannya's family moved to Fort Beaufort, where her father had gained employment at a road con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Language
An indigenous language, or autochthonous language, is a language that is native to a region and spoken by its indigenous peoples. Indigenous languages are not necessarily national languages but they can be; for example, Aymara is both an indigenous language and an official language of Bolivia. Also, national languages are not necessarily indigenous to the country. Many indigenous peoples worldwide have stopped the generational passage of their ancestral languages and have instead adopted the majority language as part of their acculturation into their host culture. Furthermore, many indigenous languages have been subject to linguicide (language killing). Recognizing their vulnerability, the United Nations proclaimed 2019 the International Year of Indigenous Languages "to draw attention to the critical loss of indigenous languages and the urgent need to preserve, revitalize and promote indigenous languages." Language loss Indigenous languages are disappearing for various ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albertina Sisulu
Albertina Sisulu Order for Meritorious Service, OMSG ( Nontsikelelo Thethiwe; 21 October 1918 – 2 June 2011) was a South African anti-apartheid activist. A member of the African National Congress (ANC), she was the founding co-president of the United Democratic Front (South Africa), United Democratic Front. In South Africa, where she was affectionately known as Ma Sisulu, she is often called a Mother of the Nation, mother of the nation. Born in rural Transkei District, Transkei, Sisulu moved to Johannesburg in 1940 and was a nurse by profession. She entered politics through her marriage to Walter Sisulu and became increasingly engaged in activism after his imprisonment in the Rivonia Trial. In the 1980s she emerged as a community leader in her hometown of Soweto, assuming a prominent role in the establishment of the UDF and the revival of the Federation of South African Women. Between 1964 and 1989, she was subject to a near-continuous string of Banning order, banning orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivonia Trial
The Rivonia Trial was a trial that took place in apartheid-era South Africa between 9 October 1963 and 12 June 1964, after a group of anti-apartheid activists were arrested on Liliesleaf Farm in Rivonia. The farm had been the secret location for meetings of uMkhonto we Sizwe (MK), the newly-formed armed wing of the African National Congress. The trial took place in Pretoria at the Palace of Justice and the Old Synagogue. Men who were convicted and sentenced to prison for their activities included Nelson Mandela, Walter Sisulu, Govan Mbeki, Ahmed Kathrada, Denis Goldberg, Raymond Mhlaba, Elias Motsoaledi, Andrew Mlangeni.Church Square, the Old Synagogue and the Old Governmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headstone
A gravestone or tombstone is a marker, usually stone, that is placed over a grave. A marker set at the head of the grave may be called a headstone. An especially old or elaborate stone slab may be called a funeral stele, stela, or slab. The use of such markers is traditional for Chinese, Jewish, Christian, and Islamic burials, as well as other traditions. In East Asia, the tomb's spirit tablet is the focus for ancestral veneration and may be removable for greater protection between rituals. Ancient grave markers typically incorporated funerary art, especially details in stone relief. With greater literacy, more markers began to include inscriptions of the deceased's name, date of birth, and date of death, often along with a personal message or prayer. The presence of a frame for photographs of the deceased is also increasingly common. Use The stele (plural: stelae), as it is called in an archaeological context, is one of the oldest forms of funerary art. Originally, a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maki Skosana
Maki Skosana ( – July 20, 1985) was a black South African woman who was burned to death and the footage broadcast live on South Africa's state-run television. She was killed by a mob of anti-apartheid activists who suspected her of being an informant. Her death by "necklacing" elicited outrage beyond the nation. The Truth and Reconciliation Commission has identified Skosana as the first known victim of necklacing, although it is more likely that she was not the first such death, only the first filmed. Death Maki Skosana, 24, was an unmarried factory worker and single mother to a five-year-old son. On July 20, 1985, the 24-year-old Skosana was the first of a series of victims in South Africa to be filmed being killed by necklacing. Necklacing was a brutal practice that occurred in townships. Skosana's death occurred in the township of Duduza, west of Nigel on the East Rand, Gauteng. Suspected of being a police informer, Skosana was killed for her presumed involvement in the dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necklacing
Necklacing is a method of extrajudicial summary execution and torture carried out by forcing a rubber tire drenched with gasoline around a victim's chest and arms, and setting it on fire. The term "necklace" originated in the 1980s in black townships of apartheid South Africa where suspected apartheid collaborators were publicly executed in this fashion. South Africa Necklacing was used by the black community to punish its members who were perceived as collaborators with the apartheid Apartheid ( , especially South African English: , ; , ) was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. It was characterised by an ... government. Necklacing was primarily used on black police informants; the practice was often carried out in the name of the struggle, although the executive body of the African National Congress (ANC), the most broadly supported South African oppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freedom Park (South Africa)
Freedom Park is a park situated on Salvokop in Pretoria. It includes a memorial with a list of the names of those killed in the South African Wars (1879–1915), South African Wars, World War I, World War II as well as during the South Africa under apartheid, apartheid era. Construction Construction of the park occurred in various phases and was dealt with by Stefanutti Stocks, WBHO, Trencon, Concor and others. The Project was overseen in totality by Mongane Wally Serote. Name Inclusion In March 2009, twenty-four deceased liberation struggle heroes were proposed for inclusion to the memorial. Some of the national leaders chosen include Steve Biko, Oliver Tambo, Helen Joseph, Albert Lutuli, and Bram Fischer. International and continental leaders were also among those considered for their contribution to the liberation of South Africa or the repressed in general. The continental leaders included Mozambican President Samora Machel and Amílcar Cabral. Amongst the international l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |