|
Daemonelix (fossil Beaver Burrow) (Harrison Formation, Middle Miocene; Sioux County, Nebraska, USA)
''Palaeocastor'' ('ancient beaver') is an extinct genus of beavers that lived in the North American Badlands during the late Oligocene period to early Miocene, 29.5~18.5 million years ago. ''Palaeocastor'' was much smaller than modern beavers. There are several species including ''Palaeocastor fossor, Palaeocastor magnus,'' ''Palaeocastor wahlerti'', and ''Palaeocastor peninsulatus.'' The animals first became known on grounds of their fossilized burrows, the "Devil's corkscrews." Biology Some members of this genus made corkscrew-shaped burrows and tunnels. Like many early castorids, ''Palaeocastor'' was predominantly a burrowing animal instead of an aquatic animal. Fossil evidence suggests they may have lived in family groups like modern beavers and employed a K reproductive strategy instead of the normal r-strategy of most rodents. Based on size and habitat, ''Palaeocastor fossor'' has been compared to a black-tailed prairie dog ('' Cynomys ludovicianus''). "Devil's corksc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
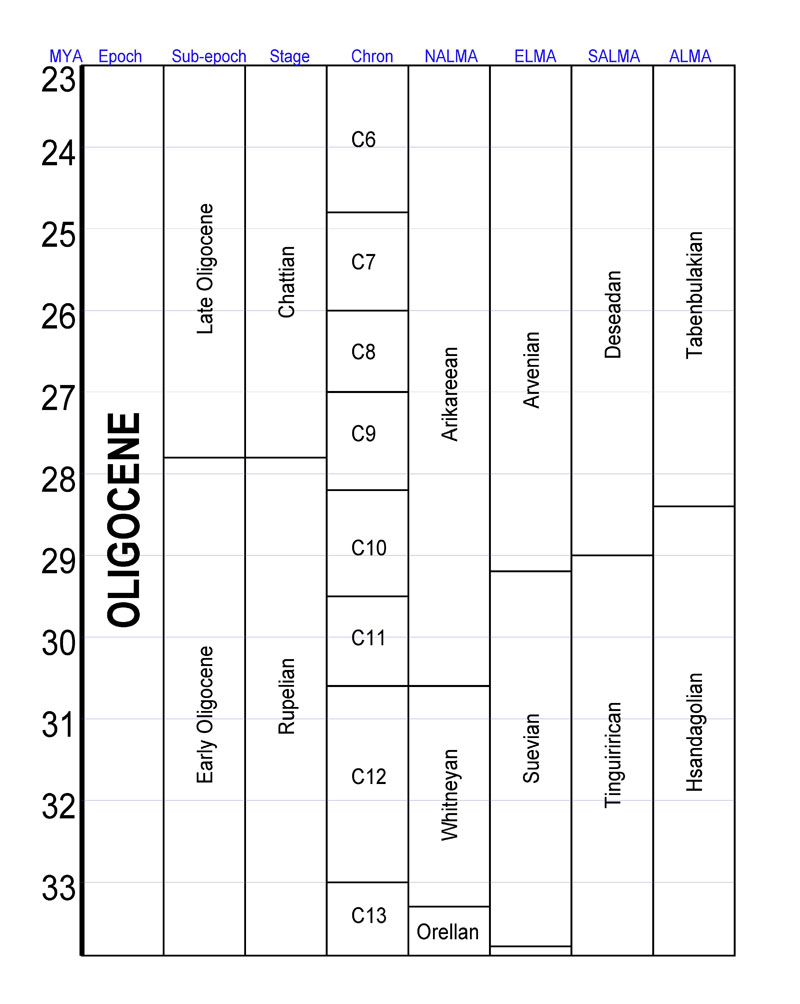
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of Neontology, extant forms of Mollusca, molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harrison, Nebraska
Harrison is a village in Sioux County, Nebraska, Sioux County, Nebraska, United States. The population was 239 at the United States Census, 2020, 2020 census. It is the county seat of Sioux County. History Harrison was originally called Bowen, and under that name was platted in 1886, when the Fremont, Elkhorn, & Missouri Valley Railroad was extended to that point. It was renamed Harrison in 1887, in honor of Benjamin Harrison. Harrison was incorporated in 1889. Geography Harrison is located on the American Great Plains. According to the United States Census Bureau, the village has a total area of , all land. At , Harrison has the highest elevation of any town in Nebraska, prompting it to bill itself as "Nebraska's Top Town". The area around Harrison largely consists of grass-covered plains. Grasses and other flora present include little bluestem, prairie sandreed, blue grama, and needle and thread grass. Wildflowers in the area include lupin, spiderwort, wallflower, western w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligocene Rodents
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of extant forms of molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major changes during the Oligocene included a global expansion of gras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene Rodents
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the connections between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Beavers
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing having spread to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. It is based on an old conception of history that without written records there could be no history. The most common conception today is that history is based on evidence, however the concept of prehistory hasn't been completely discarded. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, whereas armadillos, anteaters and other animals in the order Edentata have none. Structure Adult humans normally have eight incisors, two of each type. The types of incisors are: * maxillary central incisor (upper jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * maxillary lateral incisor (upper jaw, beside the maxillary central incisor) * mandibular central incisor (lower jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * mandibular lateral incisor (lower jaw, beside the mandibular central incisor) Children with a full set of deciduous teeth (primary teeth) also have eight incisors, named the same way as in permanent teeth. Young children may have from zero to eight incisors depending on the stage of their tooth eruption and tooth development. Typic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zodiolestes
''Zodiolestes'' is a genus of mustelids, now extinct, which existed during the Miocene period. The genus was first described in 1942, by E. S. Riggs, who identified the sister genus '' Promartes'' at the same time, and assigned to the family Procyonidae. In 1998 it was assigned to the subfamily Oligobuninae of the family Mustelidae The Mustelidae (; from Latin , weasel) are a diverse family of carnivora, carnivoran mammals, including weasels, badgers, otters, polecats, martens, grisons, and wolverines. Otherwise known as mustelids (), they form the largest family in the s .... Two species have been identified in the genus: ''Z. daimonelixensis'' and ''Z. freundi''. ''Z. daimonelixensis'' showed digging adaptations, and one fossil was found curled up in the "corkscrew" burrow of the Miocene beaver, '' Palaeocastor''. ''Zodiolestes'' was most likely a predator of these fossorial beavers. This situation was analogous to the modern day prairie dog (genus '' Cynomys'') and its p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Andrea Cook
Sir Theodore Andrea Cook (28 March 1867 – 16 September 1928) was a British art critic and writer. Sporting activities Theodore Cook spent his early years in Wantage after his father, Henry Cook, became the headmaster of King Alfred's School in 1868, a year after his eldest son was born. He subsequently studied at Radley College, where he also pursued sporting activities becoming captain of the football and boating teams. He continued his studies in Classics, at Wadham College, Oxford where he was a member of the boat club, and participated for Oxford in the 1889 Boat Race. He stayed in Oxford after graduation and in 1891 founded the "University Fencing Club". He continued being interested in fencing and was captain of the English Fencing Team in the 1903 championships in Paris and the 1906 championships in Athens. He was involved in the arrangements for the Olympic Games of 1908 in London, being one of the three British representatives on the International Olympic Commit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gopher
Pocket gophers, commonly referred to simply as gophers, are burrowing rodents of the family Geomyidae. The roughly 41 speciesSearch results for "Geomyidae" on thASM Mammal Diversity Database are all endemic to North and Central America. They are commonly known for their extensive tunneling activities and their ability to destroy farms and gardens. The name "pocket gopher" on its own may refer to any of a number of genera within the family Geomyidae. These are the "true" gophers, but several ground squirrels in the distantly related family Sciuridae are often called "gophers", as well. The origin of the word "gopher" is uncertain; the French , meaning waffle, has been suggested, on account of the gopher tunnels resembling the honeycomb-like pattern of holes in a waffle; another suggestion is that the word is of Muskogean origin. Description Pocket gophers weigh around , and are about in body length, with a tail long. A few species reach weights approaching . Within any p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Fuchs
Theodor Fuchs (15 September 1842 in Eperies – 5 October 1925 in Steinach am Brenner) was an Austrian geologist and paleontologist. He studied geology and paleontology at the University of Vienna as a pupil of Eduard Suess (doctorate 1863). Following graduation, he worked as an assistant at the '' Hofmineralienkabinett'' in Vienna, being named its curator in 1880. From 1889 to 1904 he was director of the geologic-paleontological department at the Natural History Museum in Vienna. In 1897 he became an associate professor of paleontology at the university.Fuchs Theodor In: Österreichisches Biographisches Lexikon 1815–1950 (ÖBL). Band 1, Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The American Naturalist
''The American Naturalist'' is the monthly Peer review, peer-reviewed scientific journal of the American Society of Naturalists, whose purpose is "to advance and to diffuse knowledge of organic evolution and other broad biological principles so as to enhance the conceptual unification of the biological sciences." It was established in 1867 and is published by the University of Chicago Press. The journal covers research in ecology, evolutionary biology and Ethology, behavior. As of 2023, the editor-in-chief is Volker H. W. Rudolf. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal had a 2023 impact factor of 2.4. History The journal was founded by Alpheus Hyatt, Edward Sylvester Morse, Edward S. Morse, Alpheus Spring Packard Jr., Alpheus S. Packard Jr., and Frederick Ward Putnam, Frederick W. Putnam at the Essex Institute in Salem, Massachusetts. The first issue appeared in print dated March 1867."American Naturalist," in International Magazine Co., ''Periodicals,'' vol. 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |