|
Dacia
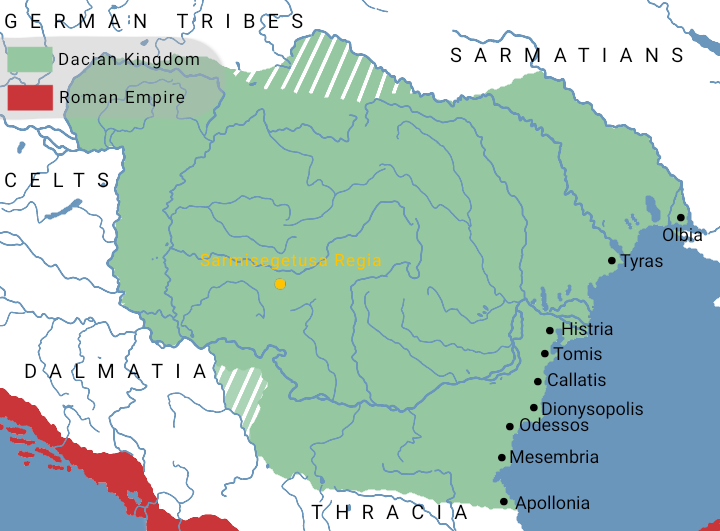
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus roughly corresponds to present-day Romania, as well as parts of Moldova, Bulgaria, Serbia, Hungary, Slovakia, Czech Republic, Poland and Ukraine. A Dacian kingdom that united the Dacians and the Getae was formed under the rule of Burebista in 82 BC and lasted until the Roman conquest in AD 106. As a result of the Trajan's Dacian Wars, wars with the Roman Empire, after the conquest of Dacia, the population was dispersed, and the capital city, Sarmizegetusa Regia, was destroyed by the Romans. However, the Romans built a settlement bearing the same name, Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa, Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetuza, 40 km away, to serve as the capital of the newly established Roman Dacia, Roman province of Dacia. A group of "Free Dacians" may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacians
The Dacians (; ; ) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often considered a subgroup of the Thracians. This area includes mainly the present-day countries of Romania and Moldova, as well as parts of Ukraine, Moravian Banovina, Eastern Serbia, Northern Bulgaria, Slovakia, Hungary and Southern Poland. The Dacians and the related Getae spoke the Dacian language, which has a debated relationship with the neighbouring Thracian language and may be a subgroup of it. Dacians were somewhat culturally influenced by the neighbouring Scythians and by the Celtic invasion of the Balkans, Celtic invaders of the 4th century BC. Name and etymology Name The Dacians were known as ''Geta'' (plural ''Getae'') in Ancient Greek writings, and as ''Dacus'' (plural ''Daci'') or ''Getae'' in Roman Empire, Roman documents, but also as ''Dagae'' and ''Gaete'' as depicted on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacian Language
Dacian () is an extinct language generally believed to be a member of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family that was spoken in the ancient region of Dacia. The Dacian language is poorly documented. Unlike Phrygian language, Phrygian, which is documented by c. 200 inscriptions, only one Dacian inscription is believed to have survived. The List of Dacian plant names, Dacian names for a number of medicinal plants and herbs may survive in ancient literary texts, including about 60 plant-names in Dioscorides. About 1,150 personal names and 900 toponyms may also be of Dacian origin. A few hundred words in modern Romanian language, Romanian and Albanian language, Albanian may have originated in ancient Balkan languages such as Dacian (see List of Romanian words of possible Dacian origin). Linguists have reconstructed about 100 List of reconstructed Dacian words, Dacian words from placenames using established techniques of comparative linguistics, although only 20� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burebista
Burebista () was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area located between the Danube, Tisza, and Dniester rivers, and modern day Romania and Moldova. In the 7th and 6thcenturies BC it became home to the Thracian peoples, including the Getae and the Dacians. From the 4thcentury to the middle of the 2ndcentury BC the Dacian peoples were influenced by La Tène Celts who brought new technologies with them into Dacia. Sometime in the 2ndcentury BC, the Dacians expelled the Celts from their lands. Dacians often warred with neighbouring tribes, but the relative isolation of the Dacian peoples in the Carpathian Mountains allowed them to survive and even to thrive. By the 1stcentury BC the Dacians had become the dominant power. From 61 BC onwards Burebista pursued a series of conquests that expanded the Dacian kingdom. The tribes of the Boii and Taurisci we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decebalus
Decebalus (; ), sometimes referred to as Diurpaneus, was the last Dacians, Dacian king. He is famous for fighting three wars, with varying success, against the Roman Empire under two emperors. After raiding south across the Danube, he defeated a Roman invasion in the reign of Domitian, securing a period of independence during which Decebalus consolidated his rule. When Trajan came to power, his armies invaded Dacia to weaken its threat to the Roman border territories of Moesia. Decebalus was defeated in 102 AD, and his own sister was abducted within this timeframe and forcibly wed into Roman nobility, causing some historians to infer that she was the ancestress of the usurper, Regalianus, who claimed to be a kinsman of Decebalus. He remained in power as a client king, but continued to assert his independence, leading to a final and overwhelming Roman invasion north of the Danube in 105 AD. Trajan reduced the Dacian capital Sarmizegetusa Regia, Sarmizegetusa to ruins in 106 AD, abso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarmizegetusa Regia
Sarmizegetusa Regia (also known as ''Sarmisegetusa'', ''Sarmisegethusa'', ''Sarmisegethuza''; ) was the capital and the most important military, religious and political centre of the Dacians before the wars with the Roman Empire. Built on top of a 1200 m high mountain, the fortress, consisting of six citadels, was the core of a strategic and defensive system in the Orăștie Mountains (in present-day Romania). Sarmizegetusa Regia should not be confused with Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa, the Roman capital of Dacia built by Roman Emperor Trajan some 40 km away, which was not the Dacian capital. Sarmizegetusa Ulpia was discovered earlier, was known already in the early 1900s, and was initially mistaken for the Dacian capital, a confusion which led to incorrect conclusions being made regarding the military history and organization of the Dacians. Etymology Several hypotheses have been advanced to explain the origin of the name ''Sarmizegetusa''. The most important of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trajan's Dacian Wars
Trajan's Dacian Wars (101–102, 105–106) were two military campaigns fought between the Roman Empire and Dacia during Roman Emperor, Emperor Trajan's rule. The conflicts were triggered by the constant Dacian threat on the Danube, Danubian Roman Province, province of Moesia and also by the increasing need for resources of the economy of the Empire. Background Throughout the 1st century, Roman policy dictated that threats from neighbouring nations and provinces were to be contained promptly. Dacia had been on the Roman agenda since before the days of Caesar when the Dacians defeated a Roman army at the Battle of Histria. Domitian's Dacian War had re-established peace with Dacia in 89 AD. However, the Dacian king Decebalus used the Roman annual subsidy of 8 million sestercesJones (1992), p150. and craftsmen in trades devoted to both peace and war, and war machines intended to defend the empire's borders to fortify his own defences instead. Despite some co-operation on the dip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domitian's Dacian War
Domitian's Dacian War was a conflict between the Roman Empire and the Dacian Kingdom, which had invaded the province of Moesia. The war occurred during the reign of the Roman emperor Domitian, in the years 86–88 AD. Background Since the reign of Burebista, widely considered the greatest Dacian king (r. 82-44 BC), the Dacians had represented a threat to the Roman Empire. Caesar himself had drawn up a plan to launch a campaign against Dacia. The threat was reduced when dynastic struggles in Dacia led to a division into four (or five, depending on the source) separately governed tribal states after Burebista died in 44 BC. Augustus later came into conflict with Dacia after it sent envoys offering its support against Mark Antony in exchange for "requests". Augustus rejected the offer and Dacia supported Antony. In 29 BC, Augustus sent several punitive expeditions into Dacia led by Marcus Licinius Crassus Dives, the consul of the prior year, that inflicted heavy casualties a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorilo
Scorilo (died maybe 70) was a Dacian king who may have been the father of Decebalus. Evidence for his life and reign is fragmentary. Sources A Dacian king (''dux Dacorum'') called Scorylo is also mentioned by Frontinus, who says he was in power during a period of turmoil in Rome.Bǎrbulescu, Mihai, et al, ''The History of Transylvania: (Until 1541)'', Romanian Cultural Institute, 2005, pp.87-9. The Roman historian Jordanes lists a series of Dacian-Getic kings before Decebalus, placing a ruler called "Coryllus" between Comosicus and Dorpaneus. Coryllus is supposed to have presided over a long peaceful 40-year rule. Modern scholars sometimes equate this otherwise unknown successor Dorpaneus with the king Duras attested in other sources. The name Coryllus is not mentioned by any other historian as well, and it has been argued that it "is a misspelling of Scorilo, a relatively common Dacian name". On this basis, the Coryllus mentioned by Jordanes has been equated with the Scory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to the east, and the Black Sea to the southeast. It has a mainly continental climate, and an area of with a population of 19 million people. Romania is the List of European countries by area, twelfth-largest country in Europe and the List of European Union member states by population, sixth-most populous member state of the European Union. Europe's second-longest river, the Danube, empties into the Danube Delta in the southeast of the country. The Carpathian Mountains cross Romania from the north to the southwest and include Moldoveanu Peak, at an altitude of . Bucharest is the country's Bucharest metropolitan area, largest urban area and Economy of Romania, financial centre. Other major urban centers, urban areas include Cluj-Napoca, Timiș ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duras (Dacian King)
Duras (ruled c.69–87), also known as Duras-Diurpaneus, was king of the Dacians between maybe AD 69 and 87, during the time that Domitian ruled the Roman Empire. Duras' immediate successor was Decebalus. Duras and Diurpaneus Duras is mentioned in the Constantinian Excerpts, a Byzantine text collection that quotes the Roman historian Cassius Dio in the relevant passages. Duras may be identical to the "Diurpaneus" (or "Dorpaneus") identified in Roman sources as the Dacian leader who, in the winter of 85, ravaged the southern banks of the Danube, which the Romans defended for many years. Many authors refer to him as "Duras-Diurpaneus". Other scholars argue that Duras and Diurpaneus are different individuals, or that Diurpaneus is identical to Decebalus. In Jordanes' king-list Dorpaneus succeeds "Coryllus". This name is sometimes hypothesized to be a corruption of Scorilo, another Dacian leader mentioned in Roman sources. War with Rome Dacian power was expanding in the decennia i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comosicus
Comosicus was a Dacian king and high priest who lived in the 1st century BC. The only reference to Comosicus is a passage in the writings of the Roman historian Jordanes. Sources Jordanes refers to Burebista as king of Dacia, but then goes on to discuss a high priest called Dicineus who taught the Dacians astronomy and whose wisdom was revered. He then says that "after the death of Dicienus, they held Comosicus in almost equal honour, because he was not inferior in knowledge. By reason of his wisdom he was accounted their priest and king, and he judged the people with the greatest uprightness. When he too had departed Coryllus ascended the throne as king of the Goths etaeand for forty years ruled his people in Dacia." Interpretations "Coryllus" is widely believed to be identical to Scorilo Scorilo (died maybe 70) was a Dacian king who may have been the father of Decebalus. Evidence for his life and reign is fragmentary. Sources A Dacian king (''dux Dacorum'') called Scory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |