|
Cyclic Guanosine 3'-5' Monophosphate
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) is a cyclic nucleotide derived from guanosine triphosphate (GTP). cGMP acts as a second messenger much like cyclic AMP. Its most likely mechanism of action is activation of intracellular protein kinases in response to the binding of membrane-impermeable peptide hormones to the external cell surface. Synthesis Guanylate cyclase (GC) catalyzes cGMP synthesis. This enzyme converts GTP to cGMP. Peptide hormones such as the atrial natriuretic factor activate membrane-bound GC, while soluble GC (sGC) is typically activated by nitric oxide to stimulate cGMP synthesis. sGC can be inhibited by ODQ (1H-,2,4xadiazolo ,3-auinoxalin-1-one). Functions cGMP is a common regulator of ion channel conductance, glycogenolysis, and cellular apoptosis. It also relaxes smooth muscle tissues. In blood vessels, relaxation of vascular smooth muscles leads to vasodilation and increased blood flow. At presynaptic terminals in the striatum, cGMP controls the ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Nucleotide
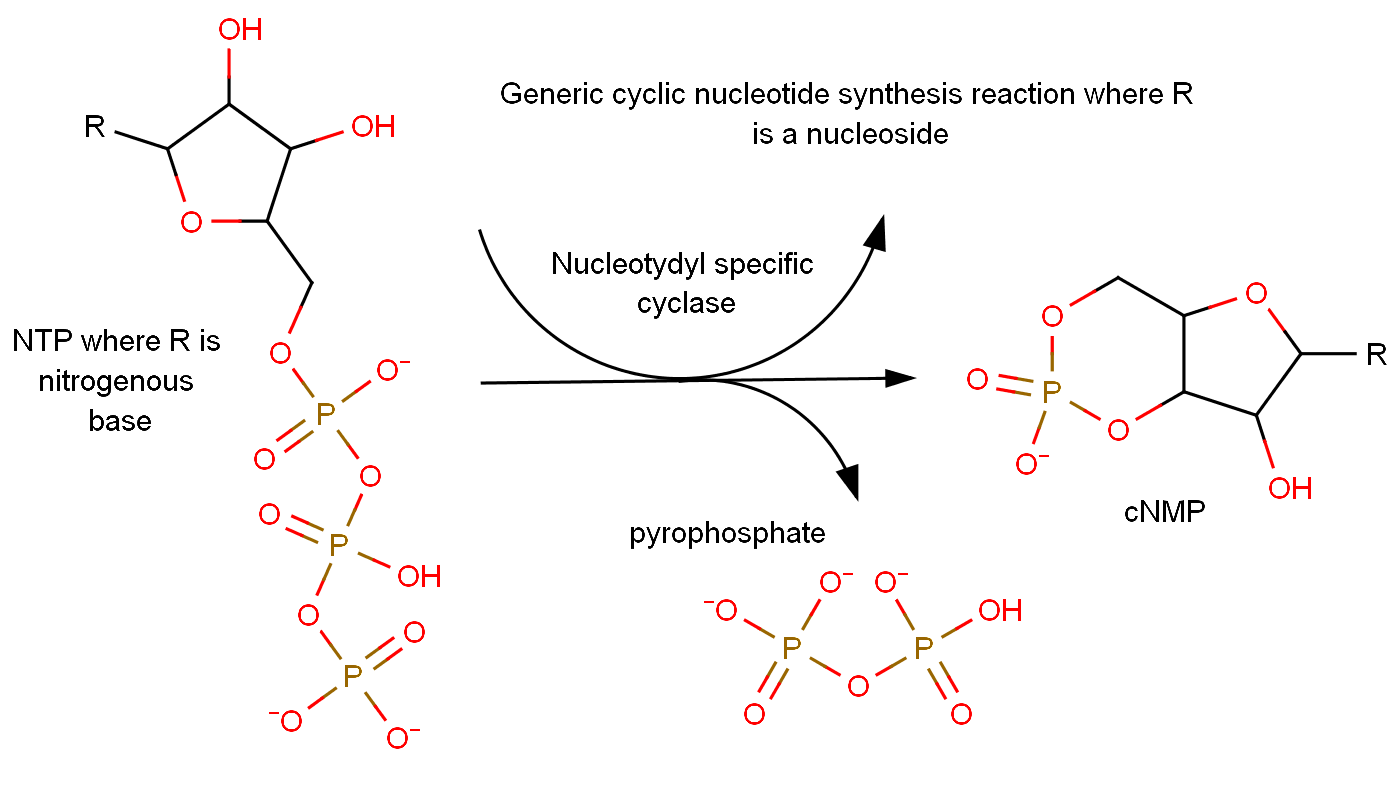
A cyclic nucleotide (cNMP) is a single-phosphate nucleotide with a cyclic bond arrangement between the sugar and phosphate groups. Like other nucleotides, cyclic nucleotides are composed of three functional groups: a sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a single phosphate group. As can be seen in the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) images, the 'cyclic' portion consists of two bonds between the phosphate group and the 3' and 5' hydroxyl groups of the sugar, very often a ribose. Their biological significance includes a broad range of protein-ligand interactions. They have been identified as secondary messengers in both hormone and ion-channel signalling in eukaryotic cells, as well as allosteric effector compounds of DNA binding proteins in prokaryotic cells. cAMP and cGMP are currently the most well documented cyclic nucleotides, however there is evidence that cCMP (cytosine) is also involved in eukaryotic cellular messaging. The ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Blood vessels are needed to sustain life, because all of the body's tissues rely on their functionality. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', meaning relating to the blood vessels, is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning vessel. Some structures – such as cartilage, the epithelium, and the lens and cornea of the eye – do not contain blood vessels and are labeled ''avascular''. Etymology * artery: late Middle English; from Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |