|
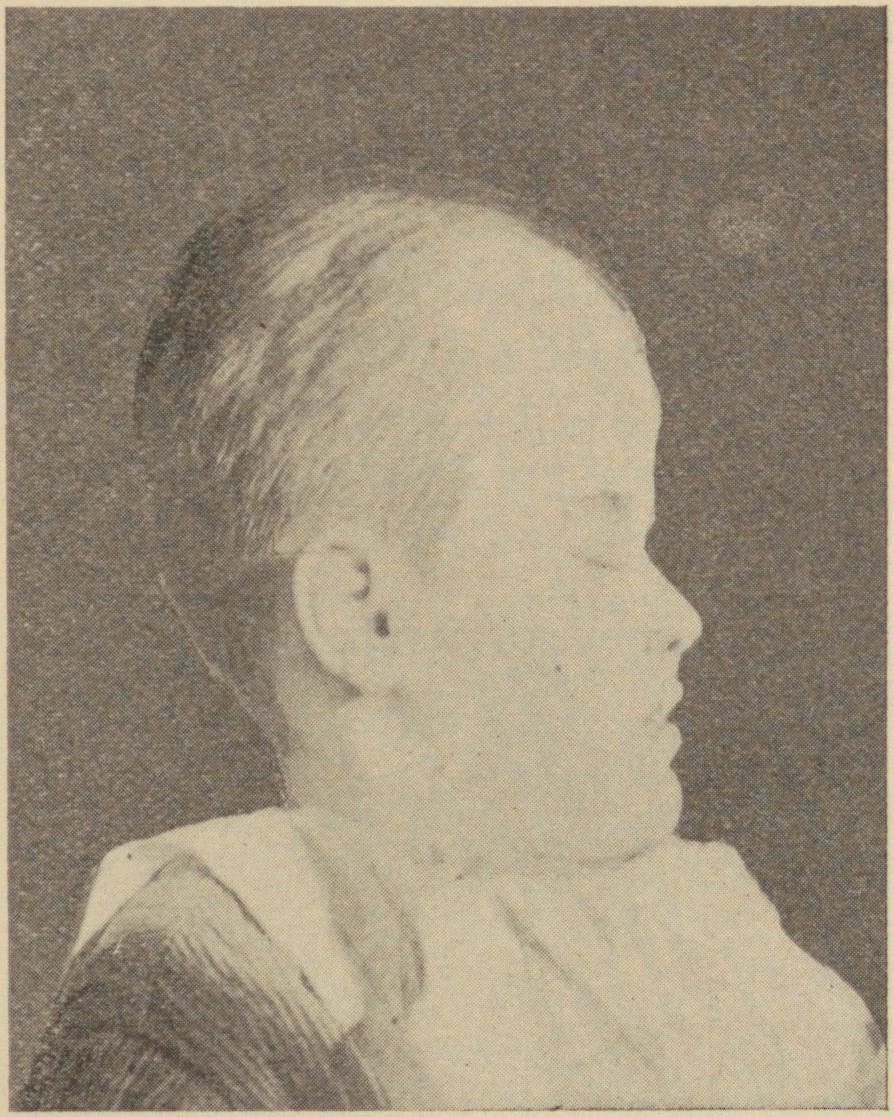
Crouzon Syndrome
Crouzon syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder known as a branchial arch syndrome. Specifically, this syndrome affects the first branchial (or pharyngeal) arch, which is the precursor of the maxilla and mandible. Since the branchial arches are important developmental features in a growing embryo, disturbances in their development create lasting and widespread effects. This syndrome is named after Octave Crouzon, a French physician who first described this disorder. First called "craniofacial dysostosis" ("craniofacial" refers to the skull and face, and " dysostosis" refers to malformation of bone), the disorder was characterized by a number of clinical features which can be described by the rudimentary meanings of its former name. This syndrome is caused by a mutation in the fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (''FGFR2''), located on chromosome 10. The developing fetus's skull and facial bones fuse early or are unable to expand. Thus, normal bone growth cannot occur. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Genetics
Medical genetics is the branch tics in that human genetics is a field of scientific research that may or may not apply to medicine, while medical genetics refers to the application of genetics to medical care. For example, research on the causes and inheritance of genetic disorders would be considered within both human genetics and medical genetics, while the diagnosis, management, and counselling people with genetic disorders would be considered part of medical genetics. In contrast, the study of typically non-medical phenotypes such as the genetics of eye color would be considered part of human genetics, but not necessarily relevant to medical genetics (except in situations such as albinism). ''Genetic medicine'' is a newer term for medical genetics and incorporates areas such as gene therapy, personalized medicine, and the rapidly emerging new medical specialty, predictive medicine. Scope Medical genetics encompasses many different areas, including clinical practice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sutures From Top
Suture, literally meaning "seam", may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Suture'' (album), a 2000 album by American Industrial rock band Chemlab * ''Suture'' (film), a 1993 film directed by Scott McGehee and David Siegel * Suture (band), an early 1990s band with Kathleen Hanna, Sharon Cheslow, and Doug Birdzell Healthcare * Suture (anatomy), a rigid joint between hard parts of animals ** Suture (joint), concerning the major joints in the bones of the cranium ** Ammonitic suture, the intersection of the septum with the outer shell in Ammonites ** Facial suture (trilobite), divisions in the cephalon (head) of most trilobites, along which the exoskeleton splits during molting * Surgical suture, a stitch used by doctors and surgeons to hold tissue together Science * Suture (geology), a major fault through an orogen An orogenic belt, or orogen, is a zone of Earth's crust affected by orogeny. An orogenic belt develops when a continental plate crumples and is uplifted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exophthalmos
Exophthalmos (also called exophthalmus, exophthalmia, proptosis, or exorbitism) is a bulging of the eye anteriorly out of the orbit. Exophthalmos can be either bilateral (as is often seen in Graves' disease) or unilateral (as is often seen in an orbital tumor). Complete or partial dislocation from the orbit is also possible from trauma or swelling of surrounding tissue resulting from trauma. In the case of Graves' disease, the displacement of the eye results from abnormal connective tissue deposition in the orbit and extraocular muscles, which can be visualized by CT or MRI. If left untreated, exophthalmos can cause the eyelids to fail to close during sleep, leading to corneal dryness and damage. Another possible complication is a form of redness or irritation called superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis, in which the area above the cornea becomes inflamed as a result of increased friction when blinking. The process that is causing the displacement of the eye may also compre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambdoidal Suture
The lambdoid suture (or lambdoidal suture) is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint on the posterior aspect of the skull that connects the parietal bones with the occipital bone. It is continuous with the occipitomastoid suture. Structure The lambdoid suture is between the paired parietal bones and the occipital bone of the skull. It runs from the asterion on each side. Nerve supply The lambdoid suture may be supplied by a branch of the supraorbital nerve, a branch of the frontal branch of the trigeminal nerve. Clinical significance At birth, the bones of the skull do not meet. If certain bones of the skull grow too fast, then craniosynostosis (premature closure of the sutures) may occur. This can result in skull deformities. If the lambdoid suture closes too soon on one side, the skull will appear twisted and asymmetrical, a condition called " plagiocephaly". Plagiocephaly refers to the shape and not the condition. The condition is craniosynostosis. The lambdoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxycephaly
Turricephaly is a type of cephalic disorder where the head appears tall with a small length and width. It is due to premature closure of the coronal suture plus any other suture, like the lambdoid, or it may be used to describe the premature fusion of all sutures. It should be differentiated from Crouzon syndrome. Oxycephaly (or acrocephaly) is a form of turricephaly where the head is cone-shaped, and is the most severe of the craniosynostoses. Presentation Common associations It may be associated with: * 8th cranial nerve lesion * Optic nerve compression * Intellectual disability * Syndactyly Diagnosis Treatment See also * Acrocephalosyndactylia Acrocephalosyndactyly is a group of autosomal dominant congenital disorders characterized by craniofacial (craniosynostosis) and hand and foot (syndactyly) abnormalities. When polydactyly is present, the classification is acrocephalopolysyndactyl ... References Further reading NINDS Overview* External links Congenita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronal Suture
The coronal suture is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint that separates the two parietal bones from the frontal bone of the skull. Structure The coronal suture lies between the paired parietal bones and the frontal bone of the skull. It runs from the pterion on each side. Nerve supply The coronal suture is likely supplied by a branch of the trigeminal nerve. Development The coronal suture is derived from the paraxial mesoderm. Clinical significance If certain bones of the skull grow too fast then premature fusion of the sutures may occur. This can result in skull deformities. There are two possible deformities that can be caused by the premature closure of the coronal suture: * a high, tower-like skull called "oxycephaly" or "turret skull". * a twisted and asymmetrical skull called "plagiocephaly". References * "Sagittal suture." ''Stedman's Medical Dictionary, 27th ed.'' (2000). * Moore, Keith L., and T.V.N. Persaud. ''The Developing Human: Clinically Orie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambdoid
The lambdoid suture (or lambdoidal suture) is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint on the posterior aspect of the skull that connects the parietal bones with the occipital bone. It is continuous with the occipitomastoid suture. Structure The lambdoid suture is between the paired parietal bones and the occipital bone of the skull. It runs from the asterion on each side. Nerve supply The lambdoid suture may be supplied by a branch of the supraorbital nerve, a branch of the frontal branch of the trigeminal nerve. Clinical significance At birth, the bones of the skull do not meet. If certain bones of the skull grow too fast, then craniosynostosis (premature closure of the sutures) may occur. This can result in skull deformities. If the lambdoid suture closes too soon on one side, the skull will appear twisted and asymmetrical, a condition called "plagiocephaly". Plagiocephaly refers to the shape and not the condition. The condition is craniosynostosis. The lambdoid sut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plagiocephaly
Plagiocephaly, also known as flat head syndrome, is a condition characterized by an asymmetrical distortion (flattening of one side) of the skull. A mild and widespread form is characterized by a flat spot on the back or one side of the head caused by remaining in a supine position for prolonged periods. Plagiocephaly is a diagonal asymmetry across the head shape. Often it is a flattening which is to one side at the back of the head and there is often some facial asymmetry. Depending on whether synostosis is involved, plagiocephaly divides into two groups: synostotic, with one or more fused cranial sutures, and non-synostotic (deformational). Surgical treatment of these groups includes the deference method; however, the treatment of deformational plagiocephaly is controversial. Brachycephaly describes a very wide head shape with a flattening across the whole back of the head. Causes Slight plagiocephaly is routinely diagnosed at birth and may be the result of a restrictive int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagittal Suture
The sagittal suture, also known as the interparietal suture and the ''sutura interparietalis'', is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint between the two parietal bones of the skull. The term is derived from the Latin word ''sagitta'', meaning arrow. Structure The sagittal suture is formed from the fibrous connective tissue joint between the two parietal bones of the skull. It has a varied and irregular shape which arises during development. The pattern is different between the inside and the outside. Two anatomical landmarks are found on the sagittal suture: the bregma, and the vertex of the skull. The bregma is formed by the intersection of the sagittal and coronal sutures. The vertex is the highest point on the skull and is often near the midpoint of the sagittal suture. Development At birth, the bones of the skull do not meet. The gap that remains, which is approximately 5 mm wide, allows for the brain to continue to grow normally after birth. The inner parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolichocephaly
Dolichocephaly (derived from the Ancient Greek δολιχός 'long' and κεφαλή 'head') is a condition where the head is longer than would be expected, relative to its width. In humans, scaphocephaly is a form of dolichocephaly. Dolichocephalic dogs (such as German Shepherds) have elongated noses. This makes them vulnerable to fungal diseases of the nose such as aspergillosis. In humans the anterior–posterior diameter (length) of dolichocephaly head is more than the transverse diameter (width). It can be present in cases of Sensenbrenner syndrome, Crouzon syndrome, Sotos syndrome, CMFTD as well as Marfan syndrome Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with long arms, legs, fingers, and toes. They also typically have exceptionally flexible joints a .... See also * Brachycephaly * Cephalic index * Plagiocephaly References External links Congenit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachycephaly
Brachycephaly (derived from the Ancient Greek '' βραχύς'', 'short' and '' κεφαλή'', 'head') is the shape of a skull shorter than typical for its species. It is perceived as a desirable trait in some domesticated dog and cat breeds, notably the pug and Persian, and can be normal or abnormal in other animal species. In humans, the cephalic disorder is known as flat head syndrome, and results from premature fusion of the coronal sutures, or from external deformation. The coronal suture is the fibrous joint that unites the frontal bone with the two parietal bones of the skull. The parietal bones form the top and sides of the skull. This feature can be seen in Down syndrome. In anthropology, human populations have been characterized as either dolichocephalic (long-headed), mesaticephalic (moderate-headed), or brachycephalic (short-headed). The usefulness of the cephalic index was questioned by Giuseppe Sergi, who argued that cranial morphology provided a better ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metopic Suture
The frontal suture is a fibrous connective tissue, fibrous suture (joint), joint that divides the two halves of the frontal bone of the human skull, skull in infants and children. Typically, it completely fuses between three and nine months of age, with the two halves of the frontal bone being fused together. It is also called the metopic suture, although this term may also refer specifically to a ''persistent frontal suture''. If the suture is not present at birth because both frontal bones have fused (craniosynostosis), it will cause a keel-shaped deformity of the skull called trigonocephaly. Its presence in a fetal skull, along with other cranial suture (joint), sutures and fontanelles, provides a malleability to the skull that can facilitate movement of the head through the cervical canal and vagina during delivery. The dense connective tissue found between the frontal bones is replaced with bone tissue as the child grows older. Persistent frontal suture In some individuals, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)