|
Constant Conjunction
In philosophy, constant conjunction is a relationship between two events, where one event is invariably followed by the other: if the occurrence of A is always followed by B, A and B are said to be ''constantly conjoined''. A critical philosophical question concerns the relationship between constant conjunction and causation, which has implications in the philosophy of science. Overview The philosopher David Hume used the phrase frequently in his discussion of the limits of empiricism to explain our ideas of causation and inference. In '' An Enquiry concerning Human Understanding'' and '' A Treatise of Human Nature,'' Hume proposed that the origin of our knowledge of necessary connections arises out of observation of the ''constant conjunction'' of certain impressions across many instances, so that causation is merely constant conjunction—after observing the constant conjunction between two events A and B for a duration of time, we become convinced that A causes B. However, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some sources claim the term was coined by Pythagoras ( BCE), although this theory is disputed by some. Philosophical methods include questioning, critical discussion, rational argument, and systematic presentation. in . Historically, ''philosophy'' encompassed all bodies of knowledge and a practitioner was known as a ''philosopher''."The English word "philosophy" is first attested to , meaning "knowledge, body of knowledge." "natural philosophy," which began as a discipline in ancient India and Ancient Greece, encompasses astronomy, medicine, and physics. For example, Newton's 1687 ''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'' later became classified as a book of physics. In the 19th century, the growth of modern research universiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald O
Donald is a masculine given name derived from the Gaelic name ''Dòmhnall''.. This comes from the Proto-Celtic *''Dumno-ualos'' ("world-ruler" or "world-wielder"). The final -''d'' in ''Donald'' is partly derived from a misinterpretation of the Gaelic pronunciation by English speakers, and partly associated with the spelling of similar-sounding Germanic names, such as '' Ronald''. A short form of ''Donald'' is ''Don''. Pet forms of ''Donald'' include ''Donnie'' and ''Donny''. The feminine given name ''Donella'' is derived from ''Donald''. ''Donald'' has cognates in other Celtic languages: Modern Irish ''Dónal'' (anglicised as ''Donal'' and ''Donall'');. Scottish Gaelic ''Dòmhnall'', ''Domhnull'' and ''Dòmhnull''; Welsh '' Dyfnwal'' and Cumbric ''Dumnagual''. Although the feminine given name ''Donna'' is sometimes used as a feminine form of ''Donald'', the names are not etymologically related. Variations Kings and noblemen Domnall or Domhnall is the name of many an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford Encyclopedia Of Philosophy
The ''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' (''SEP'') combines an online encyclopedia of philosophy with peer-reviewed publication of original papers in philosophy, freely accessible to Internet users. It is maintained by Stanford University. Each entry is written and maintained by an expert in the field, including professors from many academic institutions worldwide. Authors contributing to the encyclopedia give Stanford University the permission to publish the articles, but retain the copyright to those articles. Approach and history As of August 5th, 2022, the ''SEP'' has 1,774 published entries. Apart from its online status, the encyclopedia uses the traditional academic approach of most encyclopedias and academic journals to achieve quality by means of specialist authors selected by an editor or an editorial committee that is competent (although not necessarily considered specialists) in the field covered by the encyclopedia and peer review. The encyclopedia was created in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Encyclopedia Of Philosophy
The ''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' (''IEP'') is a scholarly online encyclopedia, dealing with philosophy, philosophical topics, and philosophers. The IEP combines open access publication with peer reviewed publication of original papers. Contribution is generally by invitation, and contributors are recognized and leading international specialists within their field. History The ''IEP'' was founded by philosopher James Fieser in 1995, operating through a non-profit organization with the aim of providing accessible and scholarly information on philosophy.Kooy, B. 2015. 'Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy', in ''Reference Review,'' Vol.29, No.4, p.12; see also The current general editors are philosophers James Fieser and Bradley Dowden, with the staff also including numerous area editors as well as volunteers. The entire website was redesigned in the summer of 2009, moving from static HTML pages to the open-source publishing platform ''WordPress''. Organization The i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
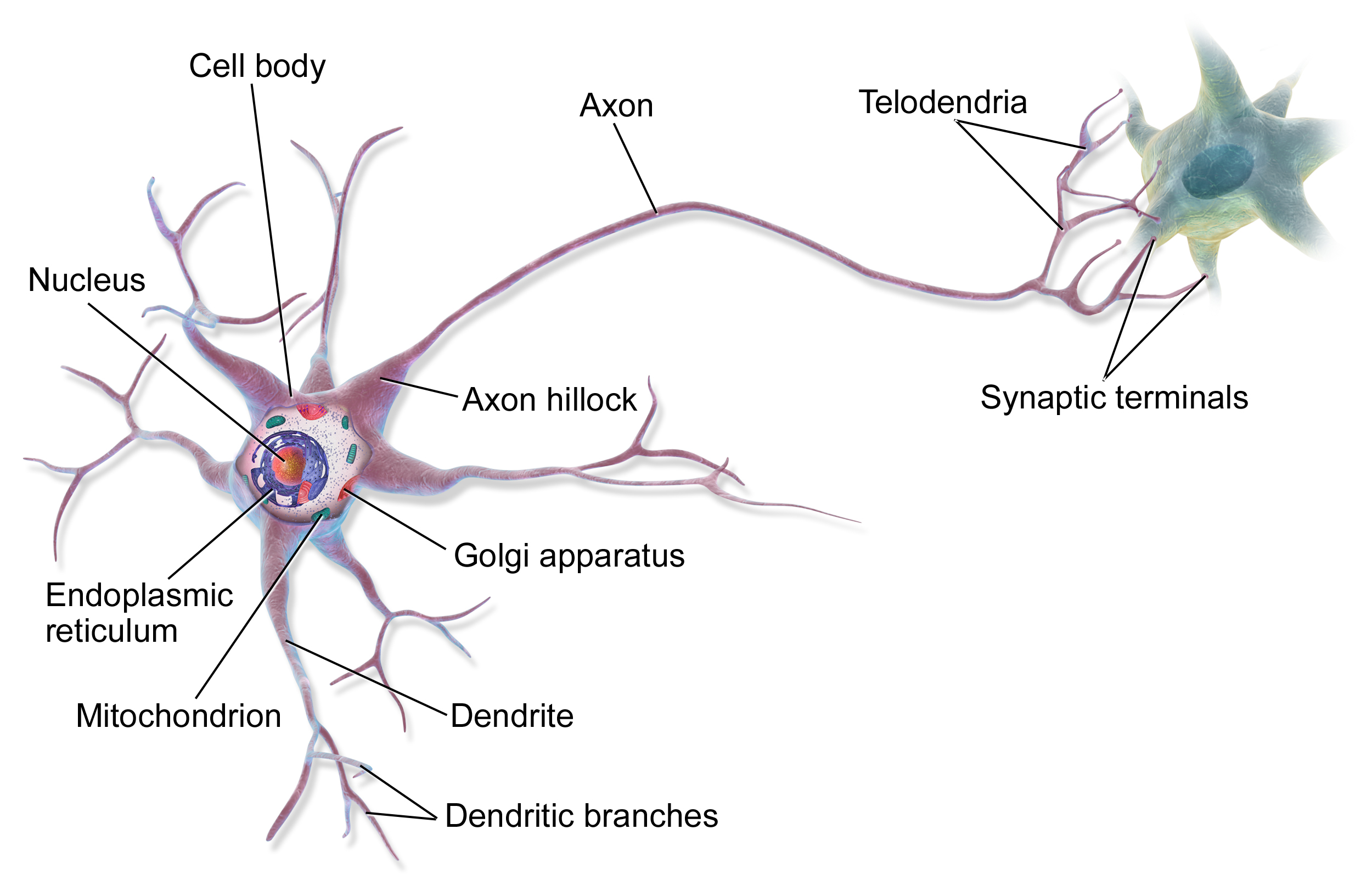
Neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions and disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, developmental biology, cytology, psychology, physics, computer science, chemistry, medicine, statistics, and Mathematical Modeling, mathematical modeling to understand the fundamental and emergent properties of neurons, glia and neural circuits. The understanding of the biological basis of learning, memory, behavior, perception, and consciousness has been described by Eric Kandel as the "epic challenge" of the Biology, biological sciences. The scope of neuroscience has broadened over time to include different approaches used to study the nervous system at different scales. The techniques used by neuroscientists have expanded enormously, from molecular biology, molecular and cell biology, cellular studies of individual neurons to neuroimaging, imaging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Assemblies
Hebbian theory is a neuroscientific theory claiming that an increase in synaptic efficacy arises from a presynaptic cell's repeated and persistent stimulation of a postsynaptic cell. It is an attempt to explain synaptic plasticity, the adaptation of brain neurons during the learning process. It was introduced by Donald Hebb in his 1949 book ''The Organization of Behavior.'' The theory is also called Hebb's rule, Hebb's postulate, and cell assembly theory. Hebb states it as follows: Let us assume that the persistence or repetition of a reverberatory activity (or "trace") tends to induce lasting cellular changes that add to its stability. ... When an axon of cell ''A'' is near enough to excite a cell ''B'' and repeatedly or persistently takes part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells such that ''A''’s efficiency, as one of the cells firing ''B'', is increased. The theory is often summarized as "Cells that fire together wire togeth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conditioned Stimulus
Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a behavioral procedure in which a biologically potent stimulus (e.g. food) is paired with a previously neutral stimulus (e.g. a triangle). It also refers to the learning process that results from this pairing, through which the neutral stimulus comes to elicit a response (e.g. salivation) that is usually similar to the one elicited by the potent stimulus. Classical conditioning is distinct from operant conditioning (also called instrumental conditioning), through which the strength of a voluntary behavior is modified by reinforcement or punishment. However, classical conditioning can affect operant conditioning in various ways; notably, classically conditioned stimuli may serve to reinforce operant responses. Classical conditioning was first studied in detail by Ivan Pavlov, who conducted experiments with dogs and published his findings in 1897. During the Russian physiologist's study of digestion, Pav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unconditioned Stimulus
Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a behavioral procedure in which a biologically potent stimulus (e.g. food) is paired with a previously neutral stimulus (e.g. a triangle). It also refers to the learning process that results from this pairing, through which the neutral stimulus comes to elicit a response (e.g. salivation) that is usually similar to the one elicited by the potent stimulus. Classical conditioning is distinct from operant conditioning (also called instrumental conditioning), through which the strength of a voluntary behavior is modified by reinforcement or punishment. However, classical conditioning can affect operant conditioning in various ways; notably, classically conditioned stimuli may serve to reinforce operant responses. Classical conditioning was first studied in detail by Ivan Pavlov, who conducted experiments with dogs and published his findings in 1897. During the Russian physiologist's study of digestion, Pav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STDP
Spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) is a biological process that adjusts the strength of connections between neurons in the brain. The process adjusts the connection strengths based on the relative timing of a particular neuron's output and input action potentials (or spikes). The STDP process partially explains the activity-dependent development of nervous systems, especially with regard to long-term potentiation and long-term depression. Process Under the STDP process, if an input spike to a neuron tends, on average, to occur immediately ''before'' that neuron's output spike, then that particular input is made somewhat stronger. If an input spike tends, on average, to occur immediately ''after'' an output spike, then that particular input is made somewhat weaker hence: "spike-timing-dependent plasticity". Thus, inputs that might be the cause of the post-synaptic neuron's excitation are made even more likely to contribute in the future, whereas inputs that are not the cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Neural Network
A neural circuit is a population of neurons interconnected by synapses to carry out a specific function when activated. Neural circuits interconnect to one another to form large scale brain networks. Biological neural networks have inspired the design of artificial neural networks, but artificial neural networks are usually not strict copies of their biological counterparts. Early study Early treatments of neural networks can be found in Herbert Spencer's ''Principles of Psychology'', 3rd edition (1872), Theodor Meynert's ''Psychiatry'' (1884), William James' ''Principles of Psychology'' (1890), and Sigmund Freud's Project for a Scientific Psychology (composed 1895). The first rule of neuronal learning was described by Hebb in 1949, in the Hebbian theory. Thus, Hebbian pairing of pre-synaptic and post-synaptic activity can substantially alter the dynamic characteristics of the synaptic connection and therefore either facilitate or inhibit signal transmission. In 1959, the neur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Pavlov
Ivan Petrovich Pavlov ( rus, Ива́н Петро́вич Па́влов, , p=ɪˈvan pʲɪˈtrovʲɪtɕ ˈpavləf, a=Ru-Ivan_Petrovich_Pavlov.ogg; 27 February 1936), was a Russian and Soviet experimental neurologist, psychologist and physiologist known for his discovery of classical conditioning through his experiments with dogs. Education and early life Ivan Petrovich Pavlov, the first of eleven children, was born in Ryazan, Russian Empire. His father, Peter Dmitrievich Pavlov (1823–1899), was a village Russian orthodox priest. His mother, Varvara Ivanovna Uspenskaya (1826–1890), was a devoted homemaker. As a child, Pavlov willingly participated in house duties such as doing the dishes and taking care of his siblings. He loved to garden, ride his bicycle, row, swim, and play gorodki; he devoted his summer vacations to these activities. Although able to read by the age of seven, Pavlov was seriously injured when he fell from a high wall onto a stone pavement. As a resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causality
Causality (also referred to as causation, or cause and effect) is influence by which one event, process, state, or object (''a'' ''cause'') contributes to the production of another event, process, state, or object (an ''effect'') where the cause is partly responsible for the effect, and the effect is partly dependent on the cause. In general, a process has many causes, which are also said to be ''causal factors'' for it, and all lie in its past. An effect can in turn be a cause of, or causal factor for, many other effects, which all lie in its future. Some writers have held that causality is metaphysically prior to notions of time and space. Causality is an abstraction that indicates how the world progresses. As such a basic concept, it is more apt as an explanation of other concepts of progression than as something to be explained by others more basic. The concept is like those of agency and efficacy. For this reason, a leap of intuition may be needed to grasp it. Accordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |