|
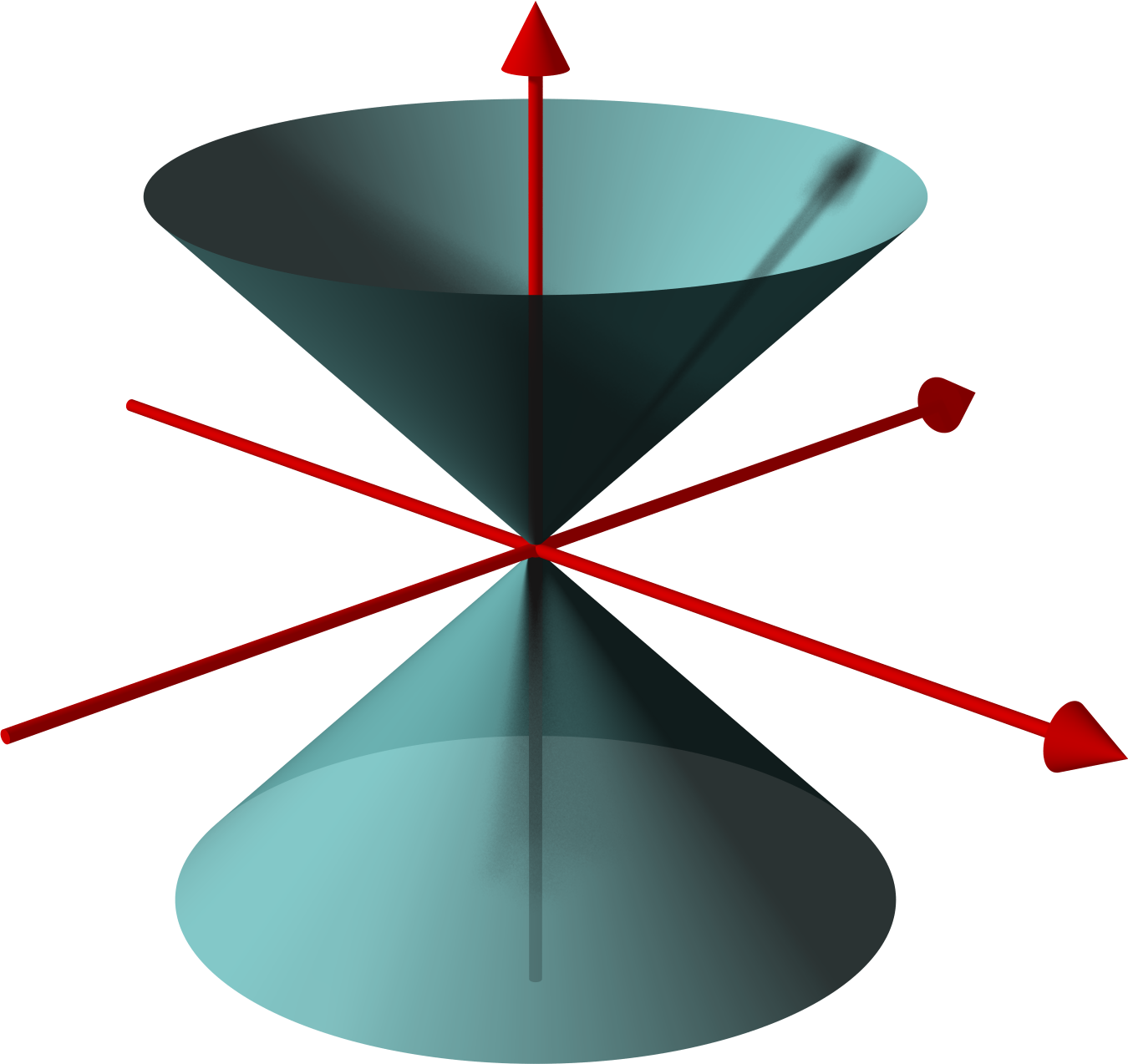
Cone Beam Reconstruction
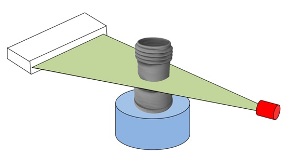
In microtomography X-ray scanners, cone beam reconstruction is one of two common scanning methods, the other being Fan beam reconstruction. Cone beam reconstruction uses a 2-dimensional approach for obtaining projection data. Instead of utilizing a single row of detectors, as fan beam methods do, a cone beam systems uses a standard charge-coupled device camera, focused on a scintillator material. The scintillator converts X-ray radiation to visible light, which is picked up by the camera and recorded. The method has enjoyed widespread implementation in microtomography, and is also used in several larger-scale systems. An X-ray source is positioned across from the detector, with the object being scanned in between. (This is essentially the same setup used for an ordinary X-ray fluoroscope). Projections from different angles are obtained in one of two ways. In one method, the object being scanned is rotated. This has the advantage of simplicity in implementation; a rotating st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtomography
X-ray microtomography, like tomography and X-ray computed tomography, uses X-rays to create cross-sections of a physical object that can be used to recreate a virtual model (3D model) without destroying the original object. The prefix ''micro-'' (symbol: µ) is used to indicate that the pixel sizes of the cross-sections are in the micrometre range. These pixel sizes have also resulted in the terms high-resolution X-ray tomography, micro–computed tomography (micro-CT or µCT), and similar terms. Sometimes the terms high-resolution CT (HRCT) and micro-CT are differentiated, but in other cases the term high-resolution micro-CT is used. Virtually all tomography today is computed tomography. Micro-CT has applications both in medical imaging and in industrial computed tomography. In general, there are two types of scanner setups. In one setup, the X-ray source and detector are typically stationary during the scan while the sample/animal rotates. The second setup, much more like a cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fan Beam Reconstruction
Fan commonly refers to: * Fan (machine), a machine for producing airflow, often used for cooling ** Hand fan, an implement held and waved by hand to move air for cooling * Fan (person), short for fanatic; an enthusiast or supporter, especially with regard to entertainment Fan, FAN or fans may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Music * Fan (song), "Fan" (song), by Pascal Michel Obispo * Fans (album), ''Fans'' (album), a 1984 album by Malcolm McLaren * Fans (song), "Fans" (song), a 2007 album track on ''Because of the Times'' by the Kings of Leon Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * Fan (film), ''Fan'' (film), a 2016 Indian Hindi film * Fan, a character in the video game ''Yie Ar Kung-Fu'' Biology * Free amino nitrogen, in brewing and winemaking, amino acids available for yeast metabolism * Sea fan, a marine animal of the cnidarian phylum Computing and mathematics * Fan (geometry), the set of all planes through a given line * Fan (order), a class of preo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cone Beam Image Cam 320x240
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequently, though not necessarily, circular) to a point called the apex or vertex. A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines connecting a common point, the apex, to all of the points on a base that is in a plane that does not contain the apex. Depending on the author, the base may be restricted to be a circle, any one-dimensional quadratic form in the plane, any closed one-dimensional figure, or any of the above plus all the enclosed points. If the enclosed points are included in the base, the cone is a solid object; otherwise it is a two-dimensional object in three-dimensional space. In the case of a solid object, the boundary formed by these lines or partial lines is called the ''lateral surface''; if the lateral surface is unbounded, it is a conical surface. In the case of line segments, the cone does not extend beyond the base, while in the case of half-lines, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-coupled Device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging. In a CCD image sensor, pixels are represented by p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitors. These MOS capacitors, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photons into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges. Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required. In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and professional digital cameras, act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scintillator
A scintillator is a material that exhibits scintillation, the property of luminescence, when excited by ionizing radiation. Luminescent materials, when struck by an incoming particle, absorb its energy and scintillate (i.e. re-emit the absorbed energy in the form of light). Sometimes, the excited state is metastable, so the relaxation back down from the excited state to lower states is delayed (necessitating anywhere from a few nanoseconds to hours depending on the material). The process then corresponds to one of two phenomena: delayed fluorescence or phosphorescence. The correspondence depends on the type of transition and hence the wavelength of the emitted optical photon. Principle of operation A scintillation detector or scintillation counter is obtained when a scintillator is coupled to an electronic light sensor such as a photomultiplier tube (PMT), photodiode, or silicon photomultiplier. PMTs absorb the light emitted by the scintillator and re-emit it in the form of ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoroscope
Fluoroscopy () is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a physician to see the internal structure and function of a patient, so that the pumping action of the heart or the motion of swallowing, for example, can be watched. This is useful for both diagnosis and therapy and occurs in general radiology, interventional radiology, and image-guided surgery. In its simplest form, a fluoroscope consists of an X-ray source and a fluorescent screen, between which a patient is placed. However, since the 1950s most fluoroscopes have included X-ray image intensifiers and cameras as well, to improve the image's visibility and make it available on a remote display screen. For many decades, fluoroscopy tended to produce live pictures that were not recorded, but since the 1960s, as technology improved, recording and playback became the norm. Fluoroscopy is simil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPECT
Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT, or less commonly, SPET) is a nuclear medicine tomographic imaging technique using gamma rays. It is very similar to conventional nuclear medicine planar imaging using a gamma camera (that is, scintigraphy), but is able to provide true 3D information. This information is typically presented as cross-sectional slices through the patient, but can be freely reformatted or manipulated as required. The technique needs delivery of a gamma-emitting radioisotope (a radionuclide) into the patient, normally through injection into the bloodstream. On occasion, the radioisotope is a simple soluble dissolved ion, such as an isotope of gallium(III). Most of the time, though, a marker radioisotope is attached to a specific ligand to create a radioligand, whose properties bind it to certain types of tissues. This marriage allows the combination of ligand and radiopharmaceutical to be carried and bound to a place of interest in the body, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cone Beam Image Closeup 45 320x240
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequently, though not necessarily, circular) to a point called the apex or vertex. A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines connecting a common point, the apex, to all of the points on a base that is in a plane that does not contain the apex. Depending on the author, the base may be restricted to be a circle, any one-dimensional quadratic form in the plane, any closed one-dimensional figure, or any of the above plus all the enclosed points. If the enclosed points are included in the base, the cone is a solid object; otherwise it is a two-dimensional object in three-dimensional space. In the case of a solid object, the boundary formed by these lines or partial lines is called the ''lateral surface''; if the lateral surface is unbounded, it is a conical surface. In the case of line segments, the cone does not extend beyond the base, while in the case of half-lines, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial CT Scanning
Industrial computed tomography (CT) scanning is any computer-aided tomographic process, usually X-ray computed tomography, that uses irradiation to produce three-dimensional internal and external representations of a scanned object. Industrial CT scanning has been used in many areas of industry for internal inspection of components. Some of the key uses for industrial CT scanning have been flaw detection, failure analysis, metrology, assembly analysis and reverse engineering applications. Just as in medical imaging, industrial imaging includes both nontomographic radiography (industrial radiography) and computed tomographic radiography (computed tomography). Types of scanners ''Line beam scanning'' is the traditional process of industrial CT scanning.Hofmann, J., Flisch, A., Obrist, A., Adaptive CT scanning-mesh based optimisation methods for industrial X-ray computer tomography applications. NDT&E International (37), 2004, pp. 271–278. X-rays are produced and the beam is coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomographic Reconstruction
Tomographic reconstruction is a type of multidimensional inverse problem where the challenge is to yield an estimate of a specific system from a finite number of projections. The mathematical basis for tomographic imaging was laid down by Johann Radon. A notable example of applications is the reconstruction of computed tomography (CT) where cross-sectional images of patients are obtained in non-invasive manner. Recent developments have seen the Radon transform and its inverse used for tasks related to realistic object insertion required for testing and evaluating computed tomography use in airport security. This article applies in general to reconstruction methods for all kinds of tomography, but some of the terms and physical descriptions refer directly to the reconstruction of X-ray computed tomography. Introducing formula The projection of an object, resulting from the tomographic measurement process at a given angle \theta, is made up of a set of line integrals (see F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |