|
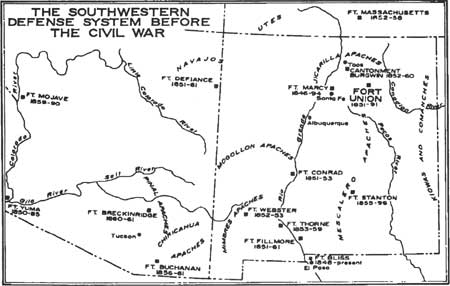
Chiricahua
Chiricahua ( ) is a band of Apache Native Americans. Based in the Southern Plains and Southwestern United States, the Chiricahua (Tsokanende ) are related to other Apache groups: Ndendahe (Mogollon, Carrizaleño), Tchihende (Mimbreño), Sehende (Mescalero), Lipan, Salinero, Plains, and Western Apache. Chiricahua historically shared a common area, language, customs, and intertwined family relations with their fellow Apaches. At the time of European contact, they had a territory of 15 million acres (61,000 km2) in Southwestern New Mexico and Southeastern Arizona in the United States and in Northern Sonora and Chihuahua in Mexico. Today Chiricahua are enrolled in three federally recognized tribes in the United States: the Fort Sill Apache Tribe, located near Apache, Oklahoma, with a small reservation outside Deming, New Mexico; the Mescalero Apache Tribe of the Mescalero Reservation near Ruidoso, New Mexico; and the San Carlos Apache Tribe in southeastern Arizona. Name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apache
The Apache () are a group of culturally related Native American tribes in the Southwestern United States, which include the Chiricahua, Jicarilla, Lipan, Mescalero, Mimbreño, Ndendahe (Bedonkohe or Mogollon and Nednhi or Carrizaleño and Janero), Salinero, Plains (Kataka or Semat or "Kiowa-Apache") and Western Apache ( Aravaipa, Pinaleño, Coyotero, Tonto). Distant cousins of the Apache are the Navajo, with whom they share the Southern Athabaskan languages. There are Apache communities in Oklahoma and Texas, and reservations in Arizona and New Mexico. Apache people have moved throughout the United States and elsewhere, including urban centers. The Apache Nations are politically autonomous, speak several different languages, and have distinct cultures. Historically, the Apache homelands have consisted of high mountains, sheltered and watered valleys, deep canyons, deserts, and the southern Great Plains, including areas in what is now Eastern Arizona, Northern Mexico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiricahua Apache Language
Chiricahua (also known as Chiricahua Apache) is a Southern Athabaskan language spoken by the Chiricahua people in Chihuahua and Sonora, México and in Oklahoma and New Mexico. It is related to Navajo and Western Apache and has been described in great detail by the anthropological linguist Harry Hoijer (1904–1976), especially in Hoijer & Opler (1938) and Hoijer (1946). Hoijer & Opler's ''Chiricahua and Mescalero Apache Texts'', including a grammatical sketch and traditional religious and secular stories, has been converted into an online "book" available from the University of Virginia. Virginia Klinekole, the first female president of the Mescalero Apache Tribe, was known for her efforts to preserve the language. There is at least one language-immersion school for children in Mescalero. Phonology Consonants Chiricahua has 31 consonants: Vowels Chiricahua has 16 vowels: Chiricahua has phonemic oral, nasal, short, and long Long may refer to: Measurement * Long, chara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Sill Apache Tribe
The Fort Sill Apache Tribe is the federally recognized Native American tribe of Chiricahua Warm Springs Apache in Oklahoma. Government The Fort Sill Apache Tribe is headquartered in Apache, Oklahoma. Tribal member enrollment, which requires a minimum blood quantum (equivalent to one great-great-grandparent), stands at 650. The tribe continues to maintain close connections to the Chiricahua Apache who were moved to the Mescalero Apache Reservation in the late 19th century. Lori Gooday Ware is the elected tribal chairperson; the position has a two-year term, as do the elected tribal council positions. Lands The tribal jurisdictional area, as opposed to a reservation, spans Caddo, Comanche, and Grady Counties in Oklahoma. A private landholder returned four acres of sacred land in Cochise County, Arizona to the tribe, and it is included in their trust lands. In 2011, the tribe won the right to establish a reservation in New Mexico. They now control near Deming, New Mexico. Eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mescalero
Mescalero or Mescalero Apache ( apm, Naa'dahéńdé) is an Apache tribe of Southern Athabaskan–speaking Native Americans. The tribe is federally recognized as the Mescalero Apache Tribe of the Mescalero Apache Reservation, located in south-central New Mexico. In the 19th century, the Mescalero opened their reservation to other Apache tribes, such as the Mimbreno (Chíhéńde, Warm Springs Apaches) and the Chiricahua (Shá'i'á-ńde or Chidikáágu). Some Lipan Apache (Tú 'édì-néńde and Tú ntsaa-ńde) also joined the reservation. Their descendants are enrolled in the Mescalero Apache Tribe. Reservation Originally established on May 27, 1873, by executive order of President Ulysses S. Grant, the reservation was first located near Fort Stanton (Zhúuníidu). The present reservation was established in 1883. It has a land area of 1,862.463 km² (719.101 sq mi), almost entirely in Otero County. The 463,000-acre reservation lies on the eastern flank of the Sacr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mescalero Apache Tribe Of The Mescalero Reservation
Mescalero or Mescalero Apache ( apm, Naa'dahéńdé) is an Apache tribe of Southern Athabaskan–speaking Native Americans. The tribe is federally recognized as the Mescalero Apache Tribe of the Mescalero Apache Reservation, located in south-central New Mexico. In the 19th century, the Mescalero opened their reservation to other Apache tribes, such as the Mimbreno (Chíhéńde, Warm Springs Apaches) and the Chiricahua (Shá'i'á-ńde or Chidikáágu). Some Lipan Apache (Tú 'édì-néńde and Tú ntsaa-ńde) also joined the reservation. Their descendants are enrolled in the Mescalero Apache Tribe. Reservation Originally established on May 27, 1873, by executive order of President Ulysses S. Grant, the reservation was first located near Fort Stanton (Zhúuníidu). The present reservation was established in 1883. It has a land area of 1,862.463 km² (719.101 sq mi), almost entirely in Otero County. The 463,000-acre reservation lies on the eastern flank of the Sacra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mescalero Apache
Mescalero or Mescalero Apache ( apm, Naa'dahéńdé) is an Apache tribe of Southern Athabaskan–speaking Native Americans. The tribe is federally recognized as the Mescalero Apache Tribe of the Mescalero Apache Reservation, located in south-central New Mexico. In the 19th century, the Mescalero opened their reservation to other Apache tribes, such as the Mimbreno (Chíhéńde, Warm Springs Apaches) and the Chiricahua (Shá'i'á-ńde or Chidikáágu). Some Lipan Apache (Tú 'édì-néńde and Tú ntsaa-ńde) also joined the reservation. Their descendants are enrolled in the Mescalero Apache Tribe. Reservation Originally established on May 27, 1873, by executive order of President Ulysses S. Grant, the reservation was first located near Fort Stanton (Zhúuníidu). The present reservation was established in 1883. It has a land area of 1,862.463 km² (719.101 sq mi), almost entirely in Otero County. The 463,000-acre reservation lies on the eastern flank of the Sacr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Carlos Apache
The San Carlos Apache Indian Reservation ( Western Apache: Tsékʼáádn), in southeastern Arizona, United States, was established in 1872 as a reservation for the Chiricahua Apache tribe as well as surrounding Yavapai and Apache bands removed from their original homelands under a strategy devised by General George Crook of setting the various Apache tribes against one another. Once nicknamed "Hell's Forty Acres" during the late 19th century due to poor health and environmental conditions, today's San Carlos Apaches successfully operate a Chamber of Commerce, the Apache Gold and Apache Sky Casinos, a Language Preservation program, a Culture Center, and a Tribal College. History On December 14, 1872, President U.S. Grant established the San Carlos Apache Reservation. The government gave various religious groups responsibility for managing the new reservations, and the Dutch Reformed Church was in charge of the San Carlos Apache Indian Reservation. The church chose John Clum, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Carlos Apache Tribe
The San Carlos Apache Indian Reservation (Western Apache: Tsékʼáádn), in southeastern Arizona, United States, was established in 1872 as a reservation for the Chiricahua Apache tribe as well as surrounding Yavapai and Apache bands removed from their original homelands under a strategy devised by General George Crook of setting the various Apache tribes against one another. Once nicknamed "Hell's Forty Acres" during the late 19th century due to poor health and environmental conditions, today's San Carlos Apaches successfully operate a Chamber of Commerce, the Apache Gold and Apache Sky Casinos, a Language Preservation program, a Culture Center, and a Tribal College. History On December 14, 1872, President U.S. Grant established the San Carlos Apache Reservation. The government gave various religious groups responsibility for managing the new reservations, and the Dutch Reformed Church was in charge of the San Carlos Apache Indian Reservation. The church chose John Clum, who tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jicarilla
Jicarilla Apache (, Jicarilla language: Jicarilla Dindéi), one of several loosely organized autonomous bands of the Eastern Apache, refers to the members of the Jicarilla Apache Nation currently living in New Mexico and speaking a Southern Athabaskan language. The term ''jicarilla'' comes from Mexican Spanish meaning "little basket", referring to the small sealed baskets they used as drinking vessels. To neighboring Apache bands, such as the Mescalero and Lipan, they were known as ''Kinya-Inde'' ("People who live in fixed houses"). The Jicarilla called themselves also ''Haisndayin'' translated as "people who came from below". because they believed themselves to be the sole descendants of the first people to emerge from the underworld, the abode of Ancestral Man and Ancestral Woman, who produced the first people. The Jicarilla believed ''Hascin'', their chief deity, was responsible for the creation of Ancestral Man and Ancestral Woman and also for the creation of the animals and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Apache
The Western Apache live primarily in east central Arizona, in the United States. Most live within reservations. The Fort Apache Indian Reservation, San Carlos Apache Indian Reservation, Yavapai-Apache Nation, Tonto Apache, and the Fort McDowell Yavapai Nation are home to the majority of Western Apache and are the bases of their federally recognized tribes. In addition, there are numerous bands. The Western Apache bands call themselves ''Ndee (Indé)'' (“The People”). Because of dialectical differences, the Pinaleño/Pinal and Arivaipa/Aravaipa bands of the San Carlos Apache pronounce the word as ''Innee'' or Nnēē:. Language and culture The various dialects of Western Apache language, Western Apache (which they refer to as ''Ndee biyati' / Nnee biyati'') are a form of Apachean, a branch of the Southern Athabaskan language family. The Navajo speak a related Apachean language, but the peoples separated several hundred years ago and are considered culturally distinct. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jicarilla Apache
Jicarilla Apache (, Jicarilla language: Jicarilla Dindéi), one of several loosely organized autonomous bands of the Eastern Apache, refers to the members of the Jicarilla Apache Nation currently living in New Mexico and speaking a Southern Athabaskan language. The term ''jicarilla'' comes from Mexican Spanish meaning "little basket", referring to the small sealed baskets they used as drinking vessels. To neighboring Apache bands, such as the Mescalero and Lipan, they were known as ''Kinya-Inde'' ("People who live in fixed houses"). The Jicarilla called themselves also ''Haisndayin'' translated as "people who came from below". because they believed themselves to be the sole descendants of the first people to emerge from the underworld, the abode of Ancestral Man and Ancestral Woman, who produced the first people. The Jicarilla believed ''Hascin'', their chief deity, was responsible for the creation of Ancestral Man and Ancestral Woman and also for the creation of the animals and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Americans In The United States
Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the mainland United States ( Indigenous peoples of Hawaii, Alaska and territories of the United States are generally known by other terms). There are 574 federally recognized tribes living within the US, about half of which are associated with Indian reservations. As defined by the United States Census, "Native Americans" are Indigenous tribes that are originally from the contiguous United States, along with Alaska Natives. Indigenous peoples of the United States who are not listed as American Indian or Alaska Native include Native Hawaiians, Samoan Americans, and the Chamorro people. The US Census groups these peoples as " Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islanders". European colonization of the Americas, which began in 1492, resulted in a precipitous decline in Native American population because of new diseases, wars, ethni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)