|
Cherax Tenuimanus
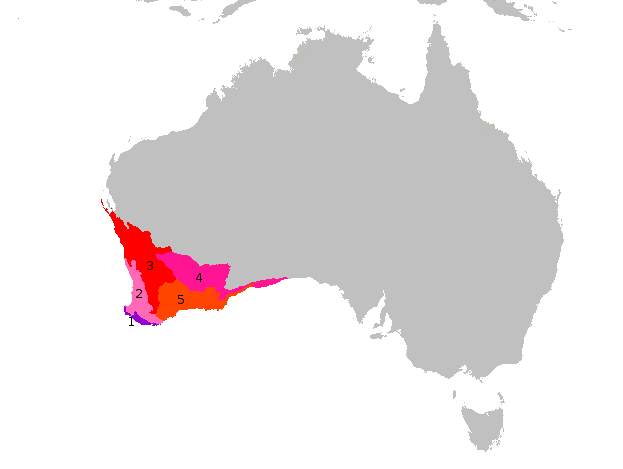
''Cherax tenuimanus'', known as the hairy marron or Margaret River marron, is one of two species of crayfish in Southwestern Australia known as marron. It occupies a narrow range within the southwestern biogeographical region of Margaret River. It is currently listed as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biol ..., because of the threat from the wider ranged smooth marron, '' Cherax cainii'', which was introduced to its habitat. Recent studies have shown that adding mannanoligosaccharide (Bio-Mos) to the diet of ''Cherax tenuimanus'' can increase their immunity and rate of survival. Description The hairy marron ranges in color from olive green to brown to black, with females sometimes having red or purple patches on their und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marron
Marron is a name given to two closely related species of crayfish in Western Australia. Formerly considered a single species, it is now recognised as comprising two species, the critically endangered '' Cherax tenuimanus'', and the species that is outcompeting it, '' C. cainii''. Marron are considered a luxury product and are the subject of a developing aquaculture industry in Western Australia and other Australian states. Total Australian production of farmed marron was 30 tons in 1996. In Western Australia, recreational fishing for marron is tightly controlled, with a limited season, permits are required, and minimum sizes are enforced. Marron have been introduced to Kangaroo Island in South Australia South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ..., where they have been co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crayfish
Crayfish are freshwater crustaceans belonging to the clade Astacidea, which also contains lobsters. In some locations, they are also known as crawfish, craydids, crawdaddies, crawdads, freshwater lobsters, mountain lobsters, rock lobsters, mudbugs, baybugs or yabbies. Taxonomically, they are members of the superfamilies Astacoidea and Parastacoidea. They breathe through feather-like gills. Some species are found in brooks and streams, where fresh water is running, while others thrive in swamps, ditches, and paddy fields. Most crayfish cannot tolerate polluted water, although some species, such as '' Procambarus clarkii'', are hardier. Crayfish feed on animals and plants, either living or decomposing, and detritus. The term "crayfish" is applied to saltwater species in some countries. Terminology The name "crayfish" comes from the Old French word ' ( Modern French '). The word has been modified to "crayfish" by association with "fish" (folk etymology). The largely Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwestern Australia
Southwest Australia is a biogeographic region in Western Australia. It includes the Mediterranean-climate area of southwestern Australia, which is home to a diverse and distinctive flora and fauna. The region is also known as the Southwest Australia Global Diversity Hotspot, as well as Kwongan. Geography The region includes the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregions of Western Australia. The region covers 356,717 km2, consisting of a broad coastal plain 20-120 kilometres wide, transitioning to gently undulating uplands made up of weathered granite, gneiss and laterite. Bluff Knoll in the Stirling Range is the highest peak in the region, at 1,099 metres (3,606 ft) elevation. Desert and xeric shrublands lie to the north and east across the centre of Australia, separating Southwest Australia from the other Mediterranean and humid-climate regions of the continent. Climate The region has a wet-winter, dry-summer Mediterranean climate, one of five such r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaret River, Western Australia
Margaret River is a town in the South West of Western Australia, located in the valley of the eponymous Margaret River, south of Perth, the state capital. Its Local Government Area is the Shire of Augusta-Margaret River. Margaret River's coast to the west of the town is a renowned surfing location, with worldwide fame for its surf breaks including, but not limited to, Main Break, The Box, and "Rivadog" a.k.a breakline, or joey's nose. Colloquially, the area is referred to as "Margs" or "maggot creek". The surrounding area is the Margaret River Wine Region and is known for its wine production and tourism, attracting an estimated 500,000 visitors annually. In earlier days the area was better known for hardwood timber and agricultural production of the finest herbs in the southwest. Also wine. History The town is named after the river, which is presumed to be named after Margaret Whicher, cousin of John Garrett Bussell (founder of Busselton) in 1831. The name is first sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biological species. It uses a set of precise criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and subspecies. These criteria are relevant to all species and all regions of the world. With its strong scientific base, the IUCN Red List is recognized as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity. A series of Regional Red Lists are produced by countries or organizations, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit. The aim of the IUCN Red List is to convey the urgency of conservation issues to the public and policy makers, as well as help the international community to reduce species extinction. According to IUCN the formally stated goals of the Red List are to provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherax Cainii
''Cherax cainii'', known as the smooth marron, is one of two species of crayfish that are endemic in Southwestern Australia known as marron. It occupies a range extending from around Hutt River in the north west to around Esperance in the south east of Western Australia. The species is also now found in variety of artificial and natural fresh water bodies of Queensland, South Australia, Victoria and New South Wales ) , nickname = , image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , es ... in Australia. It has also been introduced to other countries including North America, Chile, South Africa, Zambia, Japan and New Zealand as a part of commercial aquaculture schemes. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q20086290 Parastacidae Crustaceans described in 2002 Arthropods of Western Australia Endemic fauna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parastacidae
The Parastacidae are the family of freshwater crayfish found in the Southern Hemisphere. The family is a classic Gondwana-distributed taxon, with extant members in South America, Madagascar, Australia, New Zealand, and New Guinea, and extinct taxa also in Antarctica. Distribution Three genera are found in Chile, ''Virilastacus'', ''Samastacus'' and '' Parastacus'', the last of which also occurs disjunctly in southern Brazil and Uruguay. There are no crayfish native to continental Africa, but seven species on Madagascar, all of the genus ''Astacoides''. Australasia is particularly rich in crayfish. The small genus '' Paranephrops'' is endemic to New Zealand. The genera '' Astacopsis'' is endemic to Tasmania, while a further two are found on either side of the Bass Strait – '' Geocharax'' and '' Engaeus''. The greatest diversity, however, is found on the Australian mainland. Three genera are endemic and have restricted distributions ('' Engaewa'', '' Gramastacus'' and '' Ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustaceans Described In 1912
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropods Of Western Australia
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. Their nervous system is "ladder- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |