|
Cattle Age Determination
The age of cattle is determined chiefly by examination of the teeth, and less perfectly by the horn rings or the length of the tail brush; due to bang-tailing, which is the act of cutting the long hairs at the tip of the tail short to identify the animal after management practices, the last method is the least reliable. Teeth method Cattle are placed in a cattle crush in order to restrain them prior inspecting the mouth and amount of teeth that each animal has. The temporary teeth are in part erupted at birth, and all the incisors are erupted in twenty days; the first, second and third pairs of temporary molars are erupted in thirty days; the teeth have grown large enough to touch each other by the sixth month. Temporary incisors or "milk" teeth are smaller than the permanent incisors. Cattle have thirty-two teeth, including six incisors or biting teeth and two canines in the front on the bottom jaw. The canine teeth are not pointed but look like incisors. The incisor teeth m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mouthing Cattle
In sign language, mouthing is the production of visual syllables with the mouth while signing. That is, signers sometimes say or mouth a word in a spoken language at the same time as producing the sign for it. Mouthing is one of the many ways in which the face and mouth is used while signing. Although not present in all sign languages, and not in all signers, where it does occur it may be an essential (that is, phonemic) element of a sign, distinguishing signs which would otherwise be homophones; in other cases a sign may seem to be flat and incomplete without mouthing even if it is unambiguous. Other signs use a combination of mouth movements and hand movements to indicate the sign; for example, the ASL sign for includes a mouth gesture where the mouth is slightly open. Mouthing often originates from oralist education, where sign and speech are used together. Thus mouthing may preserve an often abbreviated rendition of the spoken translation of a sign. In educated Ugandan Sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Household Cyclopedia
The ''Household Cyclopedia'' was an American guide to housekeeping Housekeeping is the management and routine support activities of running an organised physical institution occupied or used by people, like a house, ship, hospital or factory, such as tidying, cleaning, cooking, routine maintenance, shopping, ... published in 1881. External links ''Household Cyclopedia'' of 1881 1881 non-fiction books Home economics American encyclopedias {{encyclopedia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ear Tag
An ear tag is a plastic or metal object used for identification of domestic livestock and other animals. If the ear tag uses Radio Frequency Identification Device ( RFID) technology it is referred to as an electronic ear tag. Electronic ear tags conform to international standards ISO 11784 and ISO 11785 working at 134.2 kHz, as well as ISO/IEC 18000-6C operating in the UHF spectrum. There are other non-standard systems such as Destron working at 125 kHz. Although there are many shapes of ear tags, the main types in current use are as follows: * Flag-shaped ear tag: two discs joined through the ear, one or both bearing a wide, flat plastic surface on which identification details are written or printed in large, easily legible script. * Button-shaped ear tag: two discs joined through the ear. * Plastic clip ear tag: a moulded plastic strip, folded over the edge of the ear and joined through it. * Metal ear tag: an aluminium, steel or brass rectangle with sharp points, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tattoo
A tattoo is a form of body modification made by inserting tattoo ink, dyes, and/or pigments, either indelible or temporary, into the dermis layer of the skin to form a design. Tattoo artists create these designs using several tattooing processes and techniques, including hand-tapped traditional tattoos and modern tattoo machines. The history of tattooing goes back to Neolithic times, practiced across the globe by many cultures, and the symbolism and impact of tattoos varies in different places and cultures. Tattoos may be decorative (with no specific meaning), symbolic (with a specific meaning to the wearer), or pictorial (a depiction of a specific person or item). Many tattoos serve as rites of passage, marks of status and rank, symbols of religious and spiritual devotion, decorations for bravery, marks of fertility, pledges of love, amulets and talismans, protection, and as punishment, like the marks of outcasts, slaves and convicts. Extensive decorative tattooing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae; they increase in size going towards the lumbar vertebrae, with the lower ones being much larger than the upper. They are distinguished by the presence of facets on the sides of the bodies for articulation with the heads of the ribs, as well as facets on the transverse processes of all, except the eleventh and twelfth, for articulation with the tubercles of the ribs. By convention, the human thoracic vertebrae are numbered T1–T12, with the first one (T1) located closest to the skull and the others going down the spine toward the lumbar region. General characteristics These are the general characteristics of the second through eighth thoracic vertebrae. The first and ninth through twelfth vertebrae contain certa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meat Packing Industry
The meat-packing industry (also spelled meatpacking industry or meat packing industry) handles the slaughtering, processing, packaging, and distribution of meat from animals such as cattle, pigs, sheep and other livestock. Poultry is generally not included. This greater part of the entire meat industry is primarily focused on producing meat for human consumption, but it also yields a variety of by-products including hides, dried blood, protein meals such as meat & bone meal, and, through the process of rendering, fats (such as tallow). In the United States and some other countries, the facility where the meat packing is done is called a ''slaughterhouse'', ''packinghouse'' or a ''meat-packing plant''; in New Zealand, where most of the products are exported, it is called a ''freezing works''. An abattoir is a place where animals are slaughtered for food. The meat-packing industry grew with the construction of the railroads and methods of refrigeration for meat preservation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetlock
Fetlock is the common name in horses, large animals, and sometimes dogs for the metacarpophalangeal and metatarsophalangeal joints (MCPJ and MTPJ). Although it somewhat resembles the human ankle in appearance, the joint is homologous to the ball of the foot. In anatomical terms, the hoof corresponds to the toe, rather than the whole foot. Etymology and related terminology The word literally means "foot-lock" and refers to the small tuft of hair situated on the rear of the fetlock joint. "Feather" refers to the particularly long, luxuriant hair growth over the lower leg and fetlock that is characteristic of certain breeds. Formation A fetlock (a MCPJ or a MTPJ) is formed by the junction of the third metacarpal (in the forelimb) or metatarsal (in the hindlimb) bones, either of which are commonly called the cannon bones, proximad and the proximal phalanx distad, commonly called the pastern bone. Paired proximal sesamoid bones form the joint with the palmar or plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
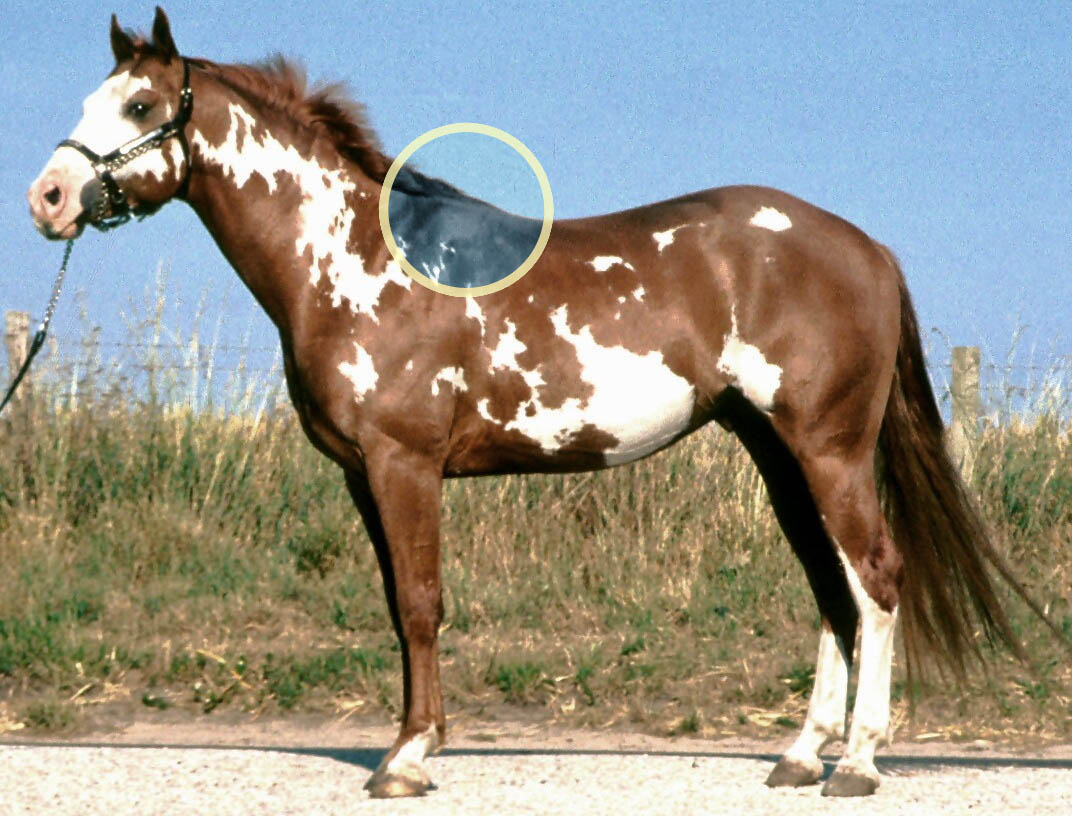
Withers
The withers is the ridge between the shoulder blades of an animal, typically a quadruped. In many species, it is the tallest point of the body. In horses and dogs, it is the standard place to measure the animal's height. In contrast, cattle are often measured to the top of the hips. The term (pronounced ) derives from Old English ''wither'' (“against”), because it is the part of a draft animal that pushes against a load. Horses The withers in horses are formed by the dorsal spinal processes of roughly the 3rd through 11th thoracic vertebrae, which are unusually long in this area. Most horses have 18 thoracic vertebrae. The processes at the withers can be more than long. Since they do not move relative to the ground as the horse's head does, the withers are used as the measuring point for the height of a horse. Horses are sometimes measured in hands – one hand is . Horse heights are extremely variable, from small pony breeds to large draft breeds. The height at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New South Wales
) , nickname = , image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of New South Wales , established_title2 = Establishment , established_date2 = 26 January 1788 , established_title3 = Responsible government , established_date3 = 6 June 1856 , established_title4 = Federation of Australia, Federation , established_date4 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Wales , demonym = , capital = Sydney , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = Local government areas of New South Wales, 128 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarchy of Australia, Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor of New South Wales, Governor , leader_name2 = Margaret Beazley , leader_title3 = Premier of New South Wales, Premie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molar (tooth)
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies from individual to individual. Race can also affect the age at which this occurs, with statistical variations between groups. In some cases, it may not even erupt at all. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, and O. Zolina, 2021Water Cycle Changes In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1055–1210, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.010. This means that a drought is "a moisture deficit relative to the average water availability at a given location and season". A drought can last for days, months or years. Drought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |