|
Zinc Compounds
Zinc compounds are chemical compounds containing the element zinc which is a member of the group 12 element, group 12 of the periodic table. The oxidation state of zinc in most compounds is the group oxidation state of +2. Zinc may be classified as a post-transition main group element with zinc(II). Zinc compounds are noteworthy for their nondescript appearance and behavior: they are generally colorless (unlike compounds of other elements with oxidation number +2, which are colored), do not readily engage in redox reactions, and generally adopt symmetrical structures. General characteristics In its compounds, Zn2+ ions have an electronic configuration [Ar] 3d10. As such, Zn2+ tends to have a symmetrical coordination geometry in both its complexes and compounds. In both ZnO and ZnS, (zincblende) zinc is bound tetrahedrally bound to four ligands (oxide and sulfide, respectively). Many coordination complex, complexes, such as ZnCl42−, are tetrahedral. Tetrahedrally coordinated zin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken or new bonds formed or both. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossils of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name comes from Latin ''calx'' " lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharmaceuticals for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid. The first category of acids are the proton donors, or Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acids. In the special case of aqueous solutions, proton donors form the hydronium ion H3O+ and are known as Acid–base reaction#Arrhenius theory, Arrhenius acids. Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted, Brønsted and Martin Lowry, Lowry generalized the Arrhenius theory to include non-aqueous solvents. A Brønsted–Lowry or Arrhenius acid usually contains a hydrogen atom bonded to a chemical structure that is still energetically favorable after loss of H+. Aqueous Arrhenius acids have characteristic properties that provide a practical description of an acid. Acids form aqueous solutions with a sour taste, can turn blue litmus red, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passivation (chemistry)
In physical chemistry and engineering, passivation is coating a material so that it becomes "passive", that is, less readily affected or corroded by the environment. Passivation involves creation of an outer layer of shield material that is applied as a microcoating, created by chemical reaction with the base material, or allowed to build by spontaneous oxidation in the air. As a technique, passivation is the use of a light coat of a protective material, such as metal oxide, to create a shield against corrosion. Passivation of silicon is used during fabrication of microelectronic devices. Undesired passivation of electrodes, called "fouling", increases the circuit resistance so it interferes with some electrochemical applications such as electrocoagulation for wastewater treatment, amperometric chemical sensing, and electrochemical synthesis. When exposed to air, many metals naturally form a hard, relatively inert surface layer, usually an oxide (termed the "native oxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redox Potential
Redox potential (also known as oxidation / reduction potential, ''ORP'', ''pe'', ''E_'', or E_) is a measure of the tendency of a chemical species to acquire electrons from or lose electrons to an electrode and thereby be reduced or oxidised respectively. Redox potential is expressed in volts (V). Each species has its own intrinsic redox potential; for example, the more positive the reduction potential (reduction potential is more often used due to general formalism in electrochemistry), the greater the species' affinity for electrons and tendency to be reduced. Measurement and interpretation In aqueous solutions, redox potential is a measure of the tendency of the solution to either gain or lose electrons in a reaction. A solution with a higher (more positive) reduction potential than some other molecule will have a tendency to gain electrons from this molecule (i.e. to be reduced by oxidizing this other molecule) and a solution with a lower (more negative) reduction potential w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reducing Agent
In chemistry, a reducing agent (also known as a reductant, reducer, or electron donor) is a chemical species that "donates" an electron to an (called the , , , or ). Examples of substances that are common reducing agents include hydrogen, carbon monoxide, the alkali metals, formic acid, oxalic acid, and sulfite compounds. In their pre-reaction states, reducers have extra electrons (that is, they are by themselves reduced) and oxidizers lack electrons (that is, they are by themselves oxidized). This is commonly expressed in terms of their oxidation states. An agent's oxidation state describes its degree of loss of electrons, where the higher the oxidation state then the fewer electrons it has. So initially, prior to the reaction, a reducing agent is typically in one of its lower possible oxidation states; its oxidation state increases during the reaction while that of the oxidizer decreases. Thus in a redox reaction, the agent whose oxidation state increases, that "loses/Electron d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamagnetic
Diamagnetism is the property of materials that are repelled by a magnetic field; an applied magnetic field creates an induced magnetic field in them in the opposite direction, causing a repulsive force. In contrast, paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials are attracted by a magnetic field. Diamagnetism is a quantum mechanical effect that occurs in all materials; when it is the only contribution to the magnetism, the material is called diamagnetic. In paramagnetic and ferromagnetic substances, the weak diamagnetic force is overcome by the attractive force of magnetic dipoles in the material. The magnetic permeability of diamagnetic materials is less than the permeability of vacuum, ''μ''0. In most materials, diamagnetism is a weak effect which can be detected only by sensitive laboratory instruments, but a superconductor acts as a strong diamagnet because it entirely expels any magnetic field from its interior (the Meissner effect). Diamagnetism was first discovered whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frenkel Defect
In crystallography, a Frenkel defect is a type of point defect in crystalline solids, named after its discoverer Yakov Frenkel. The defect forms when an atom or smaller ion (usually cation) leaves its place in the structure, creating a vacancy and becomes an interstitial by lodging in a nearby location. In elemental systems, they are primarily generated during particle irradiation, as their formation enthalpy is typically much higher than for other point defects, such as vacancies, and thus their equilibrium concentration according to the Boltzmann distribution is below the detection limit. In ionic crystals, which usually possess low coordination number or a considerable disparity in the sizes of the ions, this defect can be generated also spontaneously, where the smaller ion (usually the cation) is dislocated. Similar to a Schottky defect the Frenkel defect is a stoichiometric defect (does not change the over all stoichiometry of the compound). In ionic compounds, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-transfer Complex
In chemistry, charge-transfer (CT) complex, or electron donor-acceptor complex, describes a type of supramolecular assembly of two or more molecules or ions. The assembly consists of two molecules that self-attract through electrostatic forces, i.e., one has at least partial negative charge and the partner has partial positive charge, referred to respectively as the electron acceptor and electron donor. In some cases, the degree of charge transfer is "complete", such that the CT complex can be classified as a salt. In other cases, the charge-transfer association is weak, and the interaction can be disrupted easily by polar solvents. Examples Electron donor-acceptor complexes A number of organic compounds form charge-transfer complex, which are often described as electron-donor-acceptor complexes (EDA complexes). Typical acceptors are nitrobenzenes or tetracyanoethylene (TCNE). The strength of their interaction with electron donors correlates with the ionization potential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
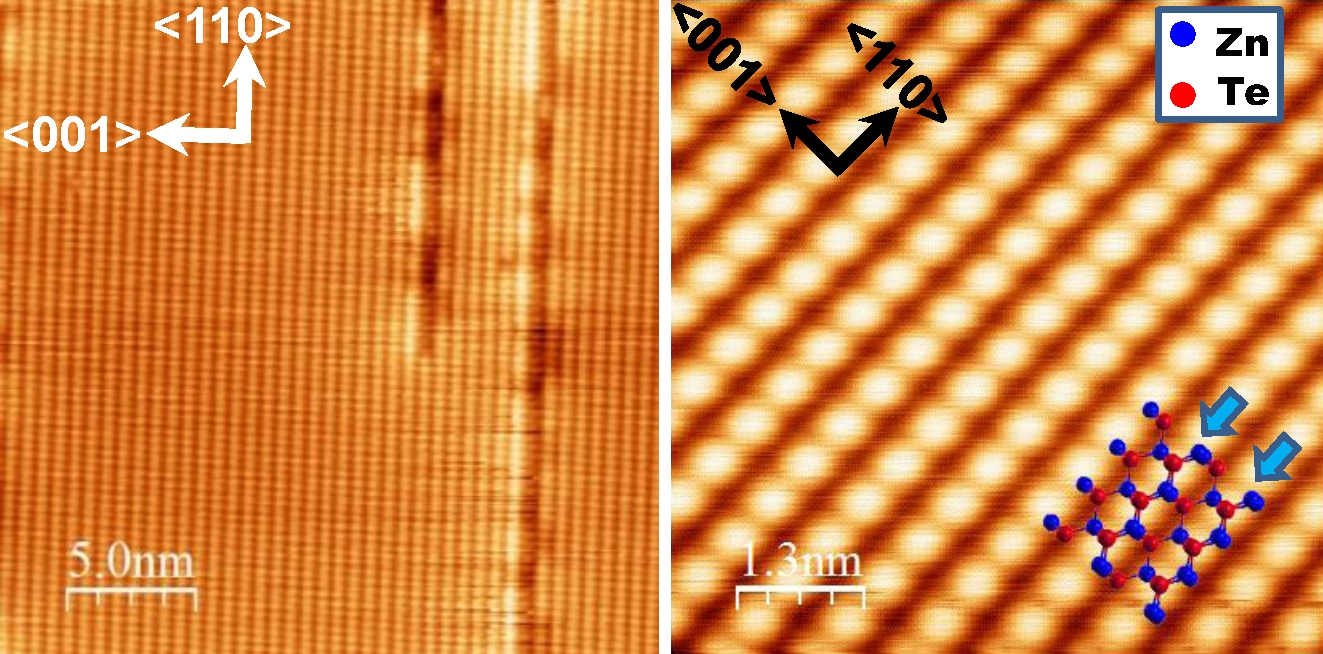
Zinc Telluride
Zinc telluride is a binary chemical compound with the formula ZnTe. This solid is a semiconductor material with a direct band gap of 2.26 eV. It is usually a p-type semiconductor. Its crystal structure is cubic, like that for sphalerite and diamond. Properties ZnTe has the appearance of grey or brownish-red powder, or ruby-red crystals when refined by sublimation. Zinc telluride typically has a cubic (sphalerite, or "zincblende") crystal structure, but can be also prepared as rocksalt crystals or in hexagonal crystals (wurtzite structure). Irradiated by a strong optical beam burns in presence of oxygen. Its lattice constant is 0.6101 nm, allowing it to be grown with or on aluminium antimonide, gallium antimonide, indium arsenide, and lead selenide. With some lattice mismatch, it can also be grown on other substrates such as GaAs, and it can be grown in thin-film polycrystalline (or nanocrystalline) form on substrates such as glass, for example, in the manufacture of thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Selenide
Zinc selenide is the inorganic compound with the formula ZnSe. It is a lemon-yellow solid although most samples have a duller color due to the effects of oxidation. It is an intrinsic semiconductor with a band gap of about 2.70 eV at , equivalent to a wavelength of 459 nm. ZnSe occurs as the rare mineral stilleite, named after Hans Stille. Synthesis and properties ZnSe is available in both hexagonal (wurtzite) and cubic (zincblende) polymorphs. In both cases, the Zn2+ and Se2− sites are tetrahedral. The difference in the structures related to close packing motifs, hexagonal vs cubic. Cubic ZnSe is produced by treatment of an aqueous solution of zinc sulfate with hydrogen selenide: : Heating the cubic form gives hexagonal ZnSe. An alternative synthesis involves heating a mixture of zinc oxide, zinc sulfide, and selenium: : It is a wide-bandgap semiconductor of the II-VI semiconductor group (since zinc and selenium belong to the 12th and 16th groups of the periodic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis acids and bases, Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent bond, covalent to ionic bond, ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acids and bases, Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity (chemistry), reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |