|
Würzburg
Würzburg (; Main-Franconian: ) is, after Nuremberg and Fürth, the Franconia#Towns and cities, third-largest city in Franconia located in the north of Bavaria. Würzburg is the administrative seat of the Regierungsbezirk Lower Franconia. It spans the banks of the Main (river), Main river. Würzburg is situated approximately 110 km west-northwest of Nuremberg and 120 km east-southeast of Frankfurt, Frankfurt am Main. The population as of 2019 is approximately 130,000 residents. Würzburg is famous for its partly rebuilt and reconstructed old town and its Würzburger Residenz, a palace that is a List of World Heritage Sites in Germany, UNESCO World Heritage Site. The regional dialect is East Franconian German. History Early and medieval history A Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Urnfield culture) refuge castle, the Celtic Segodunum, and later a Roman Empire, Roman fort, stood on the hill known as the Leistenberg, the site of the present Fortress Marienberg. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Würzburg Residence
The Würzburg Residence (German: ''Würzburger Residenz'') is a palace in Würzburg, Germany. Johann Lukas von Hildebrandt and Maximilian von Welsch, representatives of the Austrian/Southern German Baroque style, were involved in the construction, as well as Robert de Cotte and Germain Boffrand, who were followers of the French style. Balthasar Neumann, court architect of the Bishop of Würzburg, was the principal architect of the Residence, which was commissioned by the Prince-Bishop of Würzburg Johann Philipp Franz von Schönborn and his brother Friedrich Carl von Schönborn in 1720, and completed in 1744. The Venetian painter Giovanni Battista Tiepolo, assisted by his son, Domenico, painted frescoes in the building. Interiors considered masterworks of Baroque/Rococo or Neoclassical architecture and art include the grand staircase, the chapel, and the Imperial Hall. The building was reportedly called the "largest parsonage in Europe" by Napoleon. It was heavily dama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Würzburg Soviet Republic
The Würzburg Soviet Republic (German: ) was an unrecognized, short-lived state organized under council communism in Würzburg, Germany in April 1919. It had little support among the local citizenry or political parties and was quickly put down by a unit of the Bavarian Army. Background On 3 November 1918, at the beginning of the November Revolution that overthrew Germany's Hohenzollern monarchy in the final days of World War I, Fritz Endres, a member of the state parliament of Würzburg and later minister of state, publicly called for the establishment of a republic. On 8 November the royal House of Wittelsbach was toppled in Munich and the socialist People's State of Bavaria proclaimed by Kurt Eisner of the Independent Social Democratic Party (USPD). The next day, the annexation of Würzburg to the People's State was announced in front of thousands of people on the square facing the Würzburg Residence. Later, a Workers' and Soldiers' Council was formed, supported mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince-Bishopric Of Würzburg
The Prince-Bishopric of Würzburg () was an Hochstift, ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire located in Lower Franconia, west of the Prince-Bishopric of Bamberg. Würzburg had been a diocese since 743. As established by the Concordat of 1448, bishops in Germany were chosen by the canons of the cathedral chapter and their election was later confirmed by the pope. Following a common practice in Germany, the prince-bishops of Würzburg were frequently elected to other ecclesiastical principalities as well. The last few prince-bishops resided at the Würzburg Residence, which is one of the grandest Baroque architecture, Baroque palaces in Europe. As a consequence of the 1801 Treaty of Lunéville, Würzburg, along with the other ecclesiastical states of Germany, was German mediatization, secularized in 1803 and absorbed into the Electorate of Bavaria. In the same year Ferdinand III, Grand Duke of Tuscany, Ferdinand III, former Grand Duchy of Tuscany, Grand Duke of Tuscan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Würzburg Cathedral
Würzburg Cathedral () is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Würzburg in Bavaria, Germany, dedicated to Saint Kilian. It is the seat of the Bishop of Würzburg and has served as the burial place for the Prince-Bishops of Würzburg for hundreds of years. With an overall length of 103 metres, it is the fourth largest Romanesque church building in Germany, and a masterpiece of German architecture from the Salian period. Notable later additions include work by Tilman Riemenschneider and Balthasar Neumann. The cathedral was heavily damaged by British bombs in March 1945 but rebuilt post-World War II. History A cathedral and an attached monastery existed in Würzburg as early as the 8th Century, presumably built by the city's first bishop, Burchard. On July 8, 752, Burchard transferred the relics of Kilian and his companions Totnan and Colman to the cathedral. The skulls of these three saints are still kept in the High Altar of the cathedral. The cathedral was destroyed by fire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marienberg Fortress
Marienberg Fortress (German: ''Festung Marienberg'') is a prominent landmark on the left bank of the Main river in Würzburg, in the Franconia region of Bavaria, Germany. It is a symbol of Würzburg and served as a home of the local prince-bishops for nearly five centuries. It has been a fort since ancient times, although most of the current structures were built in Renaissance and Baroque styles between the 16th and 18th centuries. After Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden conquered the area in 1631 during the Thirty Years' War, the castle was reconstructed as a Baroque residence. After it ceased to serve as residence of the Bishops of Würzburg, the fortress saw repeated action in the wars of the late 18th and 19th centuries. It was severely damaged by British bombs in March 1945 and only fully rebuilt in 1990. Today, it houses two museums. Geography The fortress is located on a prominent spur of the Marienberg, which rises about 100 metres over the Main river on the opposite side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
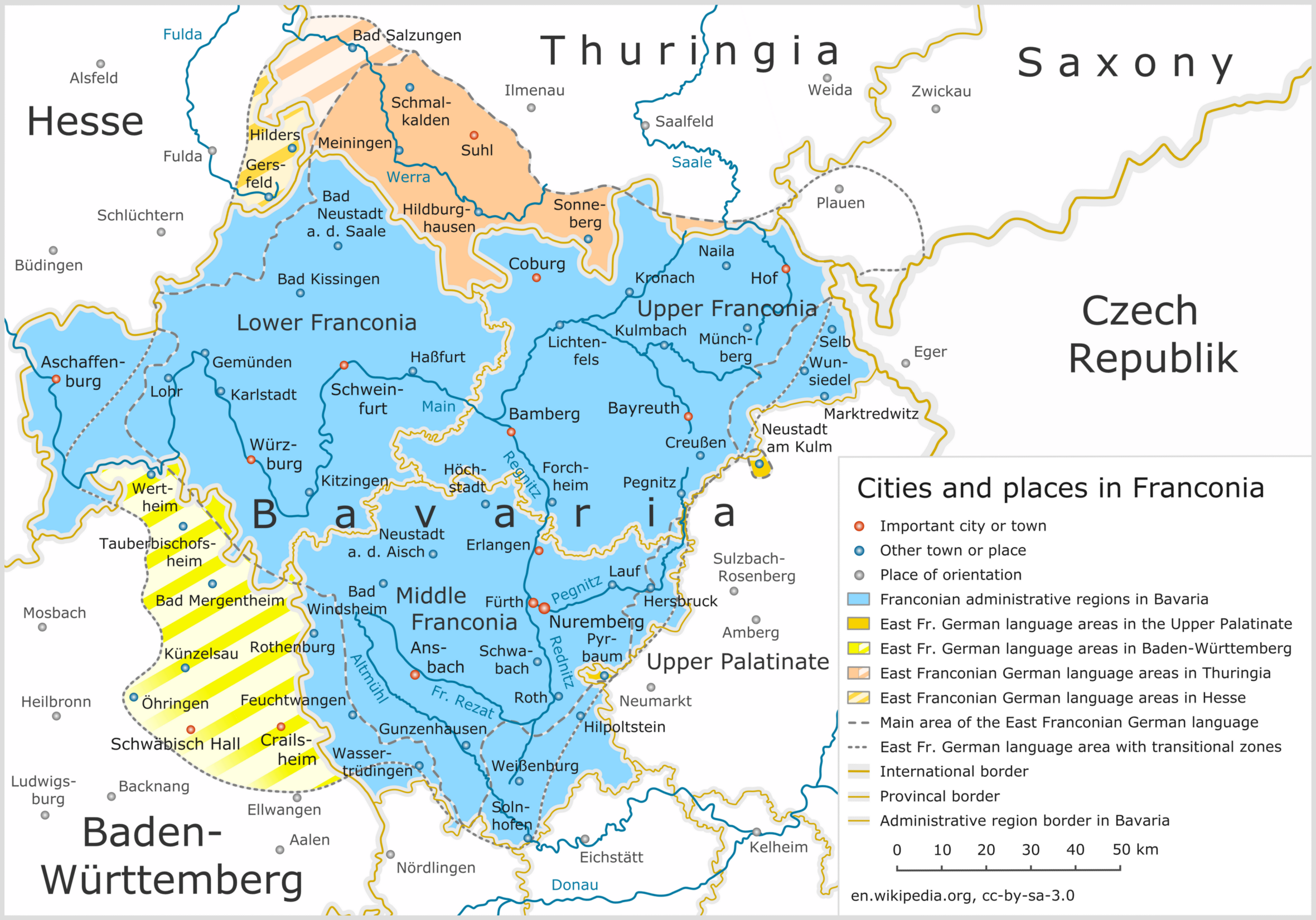
Franconia
Franconia ( ; ; ) is a geographical region of Germany, characterised by its culture and East Franconian dialect (). Franconia is made up of the three (governmental districts) of Lower Franconia, Lower, Middle Franconia, Middle and Upper Franconia in Bavaria, the adjacent, East Franconian, Franconian-speaking South Thuringia, south of the Thuringian Forest—which constitutes the language boundary between Franconian and Thuringian—and the eastern parts of Heilbronn-Franconia in Baden-Württemberg. Those parts of the Vogtland lying in Saxony (largest city: Plauen) are sometimes regarded as Franconian as well, because the Vogtlandian dialects are mostly East Franconian. The inhabitants of Saxon Vogtland, however, mostly do not consider themselves Franconian. On the other hand, the inhabitants of the Hessian dialect, Hessian-speaking parts of Lower Franconia west of the Spessart (largest city: Aschaffenburg) do consider themselves Franconian, although not speaking the dialect. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Würzburg
The Grand Duchy of Würzburg () was a German grand duchy centered on Würzburg existing in the early 19th century. History As a consequence of the 1801 Treaty of Lunéville, the Bishopric of Würzburg was secularized in 1803 and granted to the Electorate of Bavaria. In the same year Ferdinand III, former Grand Duke of Tuscany, was compensated with the Electorate of Salzburg. In the Peace of Pressburg on 26 December 1805, Ferdinand lost Salzburg to the Austrian Empire but was compensated with the Würzburg territory, Bavaria having relinquished it in return for Tyrol. Ferdinand's state was briefly known as the Electorate of Würzburg (''Kurfürstentum Würzburg''), but it was elevated to the status of a Grand Duchy after the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire on 6 August 1806. It joined the Confederation of the Rhine on 30 September 1806. In 1810 it acquired Schweinfurt. After Napoleon's defeat at the Battle of Leipzig, Ferdinand dissolved his alliance with the First French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Franconia
Lower Franconia (, ) is one of seven districts of Bavaria, Germany. The districts of Lower, Middle and Upper Franconia make up the region of Franconia. It consists of nine districts and 308 municipalities (including three cities). History After the founding of the Kingdom of Bavaria the state was totally reorganised and, in 1808, divided into 15 administrative government regions (German: , singular ), in Bavaria called (singular: ). They were created in the fashion of the French departements, quite even in size and population, and named after their main rivers. In the following years, due to territorial changes (e. g. loss of Tyrol, addition of the Palatinate), the number of Kreise was reduced to 8. One of these was the Untermainkreis (Lower Main District). In 1837 king Ludwig I of Bavaria renamed the Kreise after historical territorial names and tribes of the area. This also involved some border changes or territorial swaps. Thus the name Untermainkreis changed to Lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main (river)
The Main () is the longest tributary of the Rhine, one of the major List of rivers of Europe, European rivers. It rises as the White Main in the Fichtel Mountains of northeastern Bavaria and flows west through central Germany for to meet the Rhine below Rüsselsheim, Hesse. The cities of Mainz and Wiesbaden are close to the confluence. The largest cities on the Main are Frankfurt am Main, Offenbach am Main and Würzburg. It is the longest river lying entirely in Germany (if the Weser-Werra are considered separate). Geography The Main flows through the north and north-west of the States of Germany, state of Bavaria and then across southern Hesse; against the latter it demarcates a third state, Baden-Württemberg, east and west of Wertheim am Main, the northernmost town of that state. The upper end of its drainage basin, basin opposes that of the Danube where the watershed is recognised by natural biologists, sea salinity studies (and hydrology science more broadly) as the Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Franconian German
East Franconian ( ), usually referred to as Franconian (' ) in German, is a dialect spoken in Franconia, the northern part of the federal state of Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, Bamberg, Coburg, Würzburg, Hof, Bayreuth, Meiningen, Bad Mergentheim, and Crailsheim. The major subgroups are ' (spoken in Lower Franconia and southern Thuringia), ' (spoken in Upper and Middle Franconia) and ' (spoken in some parts of Middle Franconia and Hohenlohe). Until the wholesale expulsion of Germans from Bohemia, the dialect was also spoken around Saaz (today: Žatec). In the transitional area between Rhine Franconian in the northwest and the Austro-Bavarian dialects in the southeast, East Franconian has elements of Central German and Upper German. The same goes only for South Franconian German in adjacent Baden-Württemberg Baden-Württemberg ( ; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a states of Germany, German state () in Southwest Germany, east of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main-Franconian
East Franconian ( ), usually referred to as Franconian (' ) in German, is a dialect spoken in Franconia, the northern part of the federal state of Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, Bamberg, Coburg, Würzburg, Hof, Bayreuth, Meiningen, Bad Mergentheim, and Crailsheim. The major subgroups are ' (spoken in Lower Franconia and southern Thuringia), ' (spoken in Upper Franconia, Upper and Middle Franconia) and ' (spoken in some parts of Middle Franconia and Hohenlohe (district), Hohenlohe). Until the wholesale expulsion of Germans from Bohemia, the dialect was also spoken around Žatec, Saaz (today: Žatec). In the transitional area between Rhine Franconian dialects, Rhine Franconian in the northwest and the Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian dialects in the southeast, East Franconian has elements of Central German and Upper German. The same goes only for South Franconian German in adjacent Baden-Württemberg. East Franconian is one of the German dialects with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |