|
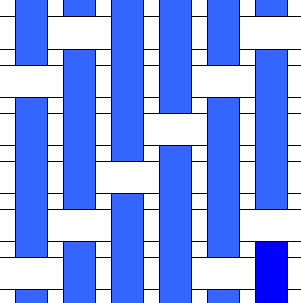
Woven Fabrics
Woven fabric is any textile formed by weaving. Woven fabrics, often created on a loom, are made of many threads woven in a warp and weft. Technically, a woven fabric is any fabric made by interlacing two or more threads at right angles to one another. Woven fabrics can be made of natural fibers, synthetic fibers, or a mixture of both, such as cotton and polyester. Woven fabrics are used for clothing, garments, decorations, furniture, carpets and other uses. Production process Yarn preparation Fibers are spun into yarns and prepared with specific properties tailored for either the warp (longitudinal yarns) or the weft (transverse yarns). Warping The warp yarns are arranged on a beam to prepare for weaving. The warp threads are held taut and parallel, and as such must be strong and durable. Weaving During weaving, the weft yarn passes over and under the warp yarns in various patterns. The primary types of weaves are plain weave, Twill, twill weave, and Satin, satin weave. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
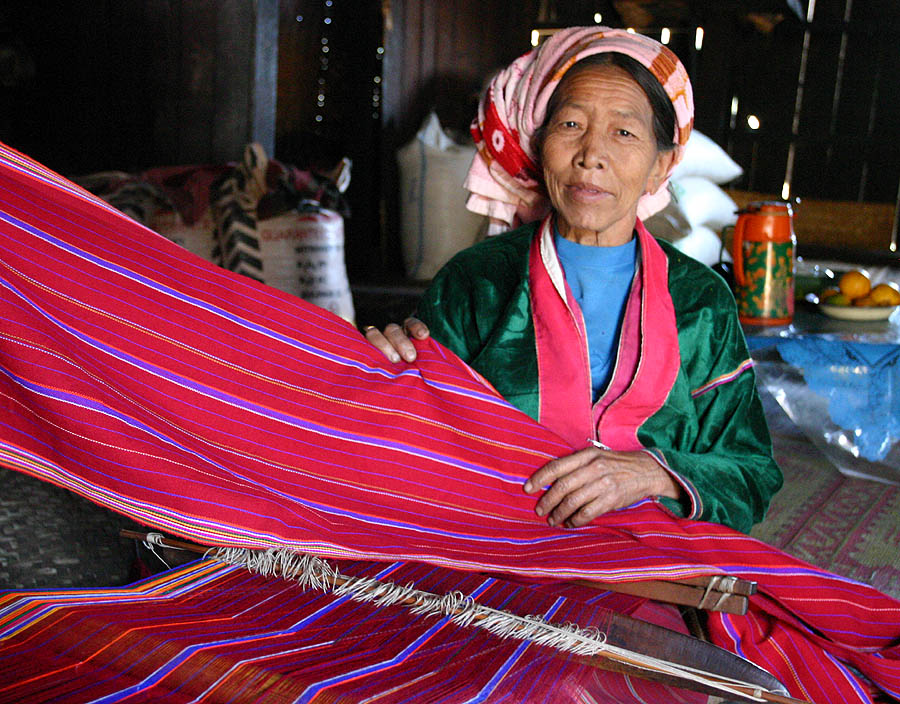
Palaung Woman Kalaw Shan Myanmar
Palaung or De'ang or Taang may refer to: *Palaung people, a people of Shan State, Myanmar **Palaung language, their Mon-Khmer language *Delaware Air National Guard {{dab Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twill
Twill is a type of textile Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, and different types of #Fabric, fabric. ... weave with a pattern of parallel, diagonal ribs. It is one of three fundamental types of weave, along with plain weave and satin. It is made by passing the weft thread over one or more warp threads then under two or more warp threads and so on, with a "step", or offset, between rows to create the characteristic diagonal pattern. Due to this structure, twill generally drapes well. Classification Twill weaves can be classified from four points of view: # According to the stepping: #* ''Warp-way'': 3/1 warp way twill, etc. #* ''Weft-way'': 2/3 weft way twill, etc. # According to the direction of twill lines on the face of the fabric: #* ''S-twill'', or ''left-hand twill weave'': 2/1 S, etc. #* ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knitted Fabric
Knitted fabric is a textile that results from knitting, the process of inter-looping of yarns or inter-meshing of loops. Its properties are distinct from woven fabric in that it is more flexible and can be more readily constructed into smaller pieces, making it ideal for socks and hats. Weft-knit and warp-knit fabric There are two basic varieties of knit fabric: weft-knit and warp-knit fabric. Warp-knitted fabrics such as tricot and milanese are resistant to runs, and are commonly used in lingerie. Weft-knit fabrics are easier to make and more common. When cut, they will unravel (run) unless repaired. Warp-knit fabrics are resistant to runs and relatively easy to sew. Raschel lace—the most common type of machine made lace—is a warp knit fabric but using many more guide-bars (12+) than the usual machines which mostly have three or four bars. (14+) Structure of knitted fabrics Courses and wales In weaving, threads are always straight, running parallel either lengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knitted Fabric
Knitted fabric is a textile that results from knitting, the process of inter-looping of yarns or inter-meshing of loops. Its properties are distinct from woven fabric in that it is more flexible and can be more readily constructed into smaller pieces, making it ideal for socks and hats. Weft-knit and warp-knit fabric There are two basic varieties of knit fabric: weft-knit and warp-knit fabric. Warp-knitted fabrics such as tricot and milanese are resistant to runs, and are commonly used in lingerie. Weft-knit fabrics are easier to make and more common. When cut, they will unravel (run) unless repaired. Warp-knit fabrics are resistant to runs and relatively easy to sew. Raschel lace—the most common type of machine made lace—is a warp knit fabric but using many more guide-bars (12+) than the usual machines which mostly have three or four bars. (14+) Structure of knitted fabrics Courses and wales In weaving, threads are always straight, running parallel either lengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinking Shears
Pinking shears are scissors with saw-toothed blades instead of straight blades. They produce a zigzag pattern instead of a straight edge. Before pinking scissors were invented, a pinking punch or pinking iron was used to punch out a decorative hem on a garment. The punch would be hammered by a mallet against a hard surface and the punch would cut through the fabric. In 1874, Eliza P. Welch patented an improved design for a pinking iron, which featured a pair of handles. The pinking shears design that is most well known was patented by Louise Austin in 1893. In 1934, Samuel Briskman patented a pinking shear design (Felix Wyner and Edward Schulz are listed as the inventors). In 1952, Benjamin Luscalzo was granted a patent for pinking shears that would keep the blades aligned to prevent wear. Pinking shears are used for cutting woven cloth. Cloth edges that are unfinished will easily fray, the weave becoming undone and threads pulling out easily. The sawtooth pattern does not pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bias (textile)
For woven textiles, grain refers to the orientation of the weft and warp threads. The three named grains are straight grain, cross grain, and the bias grain. In sewing, a pattern piece can be cut from fabric in any orientation, and the chosen grain or orientation will affect the way the fabric hangs and stretches and thus the fit of a garment. Generally speaking a piece is said to be cut on a particular grain when the longest part of the pattern or the main seams of the finished piece are aligned with that grain. Non-woven materials such as felt, interfacing or leather do not have a grain. Straight grain The straight grain is oriented parallel with the warp threads and the selvedge. The straight grain typically has less stretch than the cross grain since the warp threads will be pulled tighter than the weft during weaving. Most garments are cut with the straight grain oriented top to bottom.Howard, Pamela. "For woven fabrics, it's important to go with the grain". Threads (Taunton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satin
A satin weave is a type of Textile, fabric weave that produces a characteristically glossy, smooth or lustrous material, typically with a glossy top surface and a dull back; it is not durable, as it tends to snag. It is one of three fundamental types of textile Weaving, weaves alongside plain weave and Twill, twill weave. The satin weave is characterised by four or more fill or Warp and weft, weft yarns floating over a Warp and weft, warp yarn, and four warp yarns floating over a single weft yarn. Floats are missed interfacings, for example where the warp yarn lies on top of the weft in a warp-faced satin. These floats explain the high lustre and even sheen, as unlike in other weaves, light is not scattered as much when hitting the fibres, resulting in a stronger reflection. Satin is usually a warp-faced weaving technique in which warp yarns are "floated" over weft yarns, although there are also weft-faced satins. If a fabric is formed with a satin weave using Staple (textile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plain Weave
Plain weave (also called tabby weave, linen weave or taffeta weave) is the most basic of three fundamental types of textile weaving, weaves (along with satin weave and twill). It is strong and hard-wearing, and is used for fashion and furnishing fabrics. Fabrics with a plain weave are generally strong, durable, and have a smooth surface. They are often used for a variety of applications, including clothing, home textiles, and industrial fabrics. In plain weave cloth, the warp (weaving), warp and weft threads cross at right angles, aligned so they form a simple criss-cross pattern. Each weft thread crosses the warp threads by going over one, then under the next, and so on. The next weft thread goes under the warp threads that its neighbor went over, and vice versa. * Balanced plain weaves are fabrics in which the warp and weft are made of threads of the same weight (size) and the same number of Units of textile measurement#Ends per inch, ends per inch as Units of textile meas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textile
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, and different types of #Fabric, fabric. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and Nonwoven, non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to Bulletproof vest, bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and Medical gown, doctor's gowns. Textiles are divided into two groups: consumer textiles for domestic purposes and technical textiles. In consumer textiles, Aesthetics (textile), aesthetics and Textile performance#Comfort, comfort are the most important factors, while in techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabric Yarn Fiber
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, and different types of fabric. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and doctor's gowns. Textiles are divided into two groups: consumer textiles for domestic purposes and technical textiles. In consumer textiles, aesthetics and comfort are the most important factors, while in technical textiles, functional properties are the priority. The durability of textiles is an important property, with common cotton or blend garments (such as t-shirts) able to las ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |