|
Wildfires In Russia
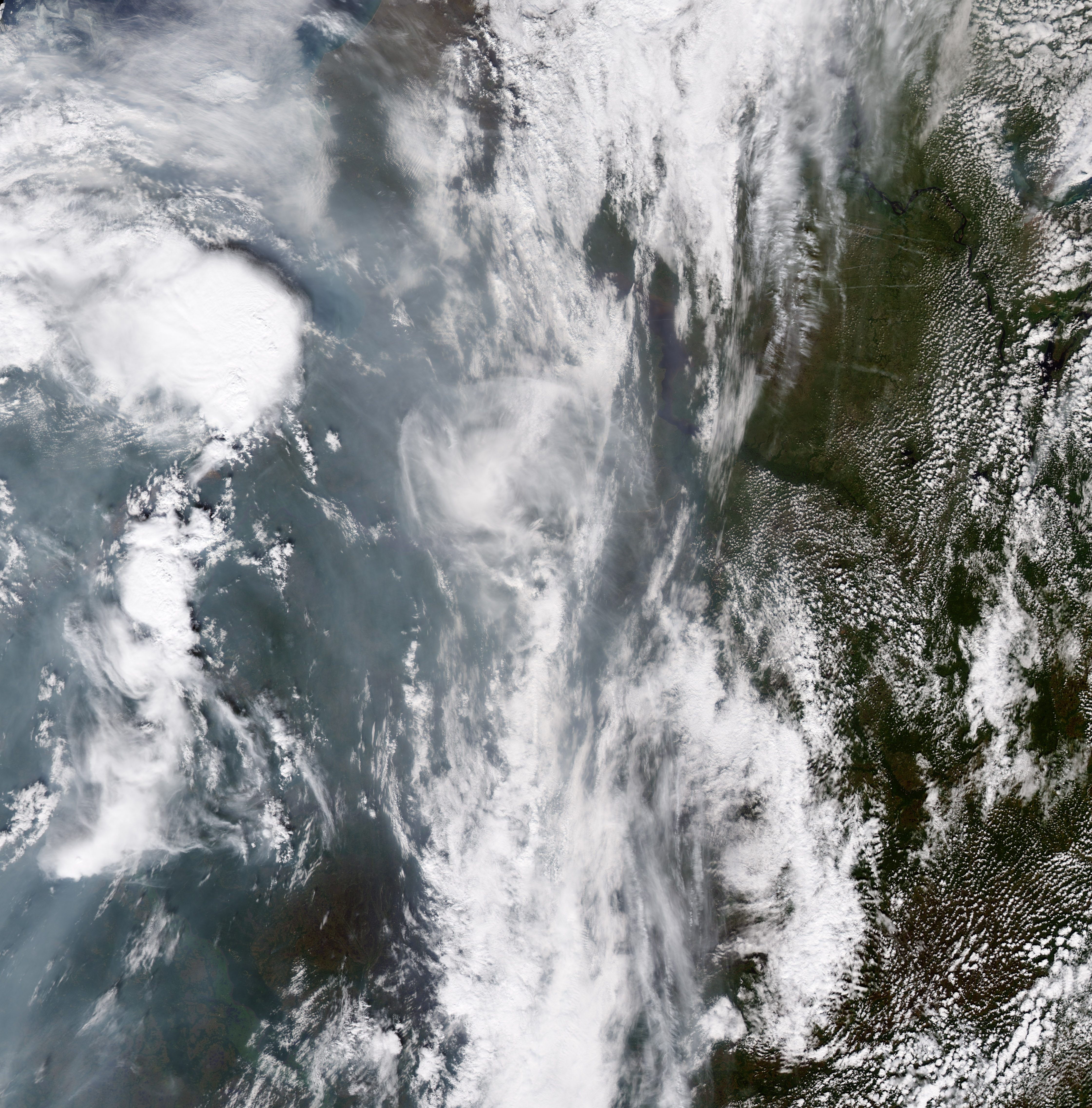
From June 2021, the taiga forests in Siberia and the Far East region of Russia were hit by unprecedented wildfires, following record-breaking heat and drought. For the first time in recorded history, wildfire smoke reached the North Pole. Events Siberia In Yakutia, according to the Republic of Sakha's emergencies ministry, more than 250 fires were burning across roughly 5720 square kilometers of land on July 5. NASA's Aqua satellite also captured images of large fires raging in Kamchatka. In the city of Yakutsk, toxic smoke produced by the fires blanketed the city, reducing air quality to levels described as an "airpocalypse". Fires and smokes forced the Kolyma highway to be closed. A state of emergency was declared, and military planes and helicopters were used to douse the fires and to seed clouds to bring down rainfall. Boats along the River Lena were suspended. Aisen Nikolayev, head of the republic, said the fires were mainly an effect of climate change, and that there had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiga
Taiga or tayga ( ; , ), also known as boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces, and larches. The taiga, or boreal forest, is the world's largest land biome. In North America, it covers most of inland Canada, Alaska, and parts of the northern contiguous United States. In Eurasia, it covers most of Sweden, Finland, much of Russia from Karelia in the west to the Pacific Ocean (including much of Siberia), much of Norway and Estonia, some of the Scottish Highlands, some lowland/coastal areas of Iceland, and areas of northern Kazakhstan, northern Mongolia, and northern Japan (on the island of Hokkaido). The principal tree species, depending on the length of the growing season and summer temperatures, vary across the world. The taiga of North America is mostly spruce; Scandinavian and Finnish taiga consists of a mix of spruce, pines and birch; Russian taiga has spruces, pines and larches depending on the reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by population density, most sparsely populated sovereign state. Mongolia is the world's largest landlocked country that does not border an Endorheic basin, inland sea, and much of its area is covered by grassy steppe, with mountains to the north and west and the Gobi Desert to the south. Ulaanbaatar, the capital and List of cities in Mongolia, largest city, is home to roughly half of the country's population. The territory of modern-day Mongolia has been ruled by various nomadic empires, including the Xiongnu, the Xianbei, the Rouran, the First Turkic Khaganate, the Second Turkic Khaganate, the Uyghur Khaganate and others. In 1206, Genghis Khan founded the Mongol Empire, which became the largest List of largest empires, contiguous land empire i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2010 Russian Wildfires
The 2010 Russian wildfires were several hundred wildfires that broke out across Russia, primarily in the west in summer 2010. They started burning in late July and lasted until early September 2010. The fires were associated with record-high temperatures, which were attributed to climate change—the summer had been the hottest recorded in Russian history—and drought. Russian President Dmitry Medvedev declared a state of emergency in seven regions, and 28 other regions were under a state of emergency due to crop failures caused by the drought. The fires cost roughly $15 billion in damages. A combination of the smoke from the fires, producing heavy smog blanketing large urban regions and the record-breaking heat wave put stress on the Russian healthcare system. Munich Re estimated that in all, 56,000 people died from the effects of the smog and the heat wave. The 2010 wildfires were the worst on record to that time. Prelude During 2010 Russia experienced dry, hot weather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2015 Russian Wildfires
From 12 to 16 April 2015, a series of wildfires spread across southern Siberia, Russia. In the Republic of Khakassia, 29 people were killed and 6,000 left homeless. Further east in Zabaykalsky Krai, four people died in wildfires near Chita. Damage was also reported in Inner Mongolia. Wildfires The series of wildfires began on Sunday morning, 12 April in Khakassia as intentional fires set to clear grass for agriculture were caught by strong winds and got out of control. Warm, dry weather help spread the fires, which quickly spread into the region's forests; daytime temperatures had reached 25 °C and spreading waves of flames soared to 3 meters in height. Russian television said the fires could be seen from space on satellite imagery. At 1 p.m. local time (6:00 GMT), a state of emergency was declared. Fire control planes and helicopters were dispatched by the Ministry of Emergency Situations, but the fires were not completely extinguished until around 6:00 a.m. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2018 Russian Wildfires
Dry, warm conditions in the spring set the stage for fires in Siberia in May 2018. History In mid-July 2018, smoke from the fires could be seen by satellites reaching North America. ''The Siberian Times'' reported were burning. On July 24, the U.S. National Weather Service said smoke had crossed the Canada-U.S. border and reached Bellingham, Washington. Siberian fires were partly blamed by Environment Canada which issued an air quality statement on July 25 for Prince George, BC. On July 29, the Puget Sound Clean Air Agency stated the Puget Sound region would experience "moderate air quality at times with some upper level smoke making for pretty sunsets. This smoke comes from distant fires, mostly originating from Siberia." See also * 2024 Russian wildfires * 2021 Russian wildfires * 2019 Russian wildfires * 2015 Russian wildfires * 2010 Russian wildfires * 1987 Black Dragon fire * List of wildfires § Russia * List of heat waves This is a partial list of temperature ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2019 Russian Wildfires
The 2019 Siberian wildfires are the large-scale wildfires that occurred across Russian Siberia between June and September 2019 and were among the most extensive and destructive in the region’s recent history. By the end of the month the size of the fires reached . The wildfires were primarily concentrated in Yakutia (Sakha Republic), Krasnoyarsk Krai, Irkutsk Oblast, and Buryatia. The total burned area and number of fires exceeded the annual average by approximately 1.5 times, ranking among the most severe wildfires recorded in the past two decades. By mid-August, the cumulative area affected by fires had surpassed . The fires produced dense smoke plumes, which spread over major cities across Siberia, the Urals, and Kazakhstan, significantly deteriorating air quality. As of 30 July, there had been no reported deaths or injuries due to the fires. The 2019 Siberia wildfires generated significant publicity, especially among social media users. As a result, a process of review ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2024 Russian Wildfires
In 2024, far-reaching wildfires ignited and spread across large areas of Russian territory, primarily in Siberia and also in southern regions. The wildfires resulted in a burnt area of 8.8 million hectares (21.7 million acres) by July 18, and carbon emissions of 6.8 megatons by July 1, equaling the combined June–July emissions of 2023 in just one month. Wildfires Climate researchers and experts stated that increases in global temperature have led to the increased prevalence of wildfire conditions across Russian forests by causing increased heat, drier conditions, and decreased soil moisture. Wildfires first began to prominently appear in March 2024, burning nearly 65,000 hectares across the Far East in Khabarovsk, Amur Oblast, Buryatia, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Sverdlovsk Oblast, Zabaykalsky Krai, and the Jewish Autonomous Oblast. The Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) first detected major wildfires in the Arctic regions of Russia in early June, and reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peatlands
A peatland is a type of wetland whose soils consist of Soil organic matter, organic matter from decaying plants, forming layers of peat. Peatlands arise because of incomplete decomposition of organic matter, usually litter from vegetation, due to Waterlogging (agriculture), water-logging and subsequent anoxic waters, anoxia. Peatlands are unusual landforms that derive mostly from biological rather than physical processes, and can take on characteristic shapes and surface patterning. The formation of peatlands is primarily controlled by climatic conditions such as precipitation and temperature, although terrain relief is a major factor as waterlogging occurs more easily on flatter ground and in basins. Peat formation typically initiates as a paludification of a mineral soil forests, terrestrialisation of lakes, or primary peat formation on bare soils on previously glaciated areas. A peatland that is actively forming peat is called a ''mire''. All types of mires share the common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
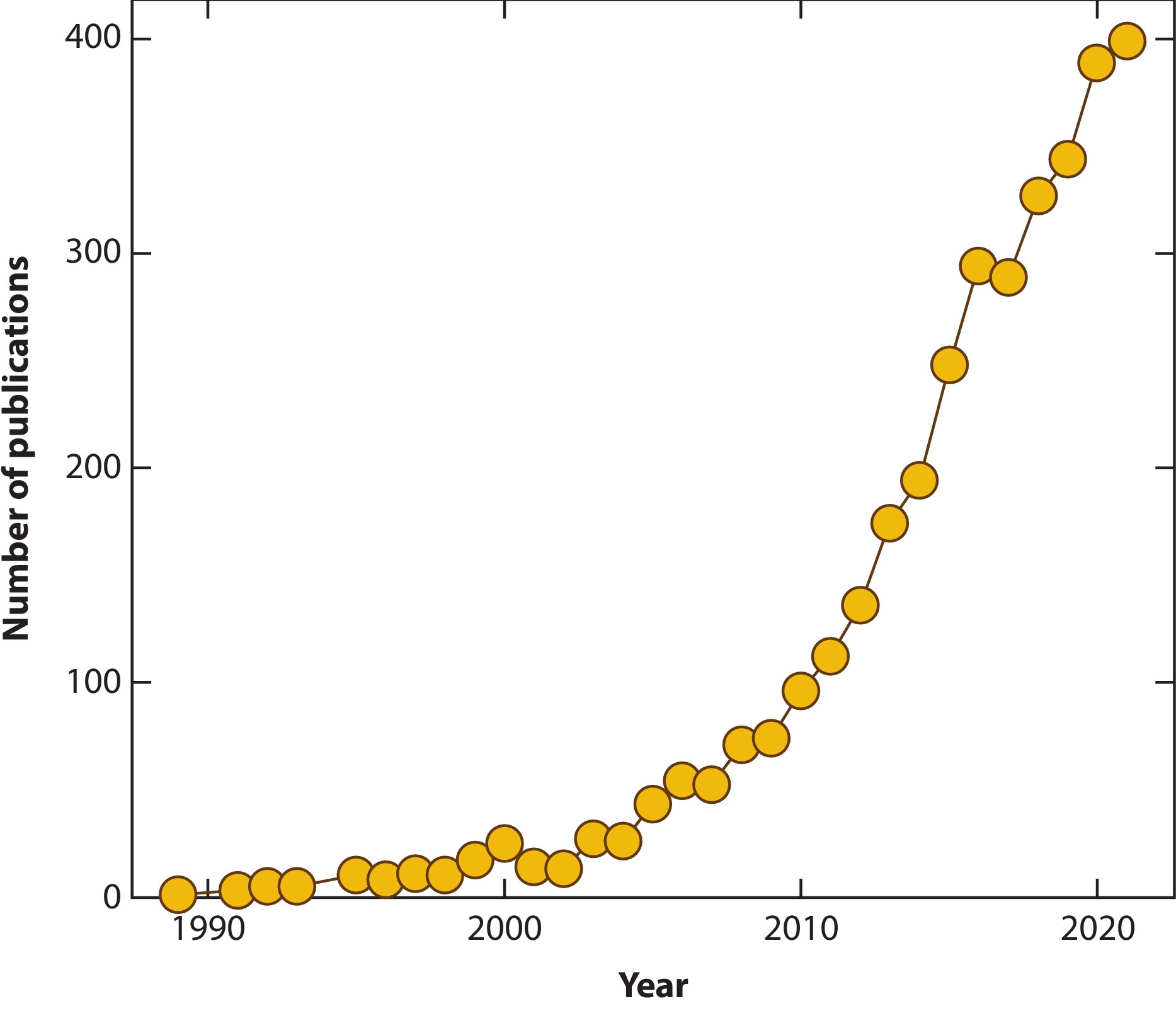
Permafrost Carbon Cycle
The permafrost carbon cycle or Arctic carbon cycle is a sub-cycle of the larger global carbon cycle. Permafrost is defined as subsurface material that remains below 0o C (32o F) for at least two consecutive years. Because permafrost soils remain frozen for long periods of time, they store large amounts of carbon and other nutrients within their frozen framework during that time. Permafrost represents a large carbon reservoir, one which was often neglected in the initial research determining global terrestrial carbon reservoirs. Since the start of the 2000s, however, far more attention has been paid to the subject, with an enormous growth both in general attention and in the scientific research output. The permafrost carbon cycle deals with the transfer of carbon from permafrost soils to terrestrial vegetation and microbes, to Atmosphere of Earth, the atmosphere, back to vegetation, and, finally, back to permafrost soils through burial and sedimentation due to cryogenic processe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 In Climate Change
This article documents events, research findings, scientific and technological advances, and human actions to measure, predict, climate change mitigation, mitigate, and climate change adaptation, adapt to the Effects of climate change, effects of climate change, global warming and climate change—during the year 2021. Summaries * 26 February: The United Nations Synthesis Report on ''Nationally Determined Contributions under the Paris Agreement'' stated that "estimated reductions referred to in paragraphs (on greenhouse gas emissions) fall far short of what is required, demonstrating the need for Parties to further strengthen their mitigation commitments under the Paris Agreement". * 21 June: the World Meteorological Organization wrote that "2021 is a make-or-break year for climate action, with the window to prevent the worst impacts of climate change—which include ever more frequent more intense droughts, floods and storms—closing rapidly." * 28 July: a follow-on to the 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |