|
Welfare In Russia
Welfare may refer to: Philosophy *Well-being (happiness, prosperity, or flourishing) of a person or group * Utility in utilitarianism * Value in value theory Economics * Utility, a general term for individual well-being in economics and decision theory ** Decision utilities, utilities as revealed by human behavior under the assumption of rationality ** Economic surplus, the total economic benefit or gains from trade provided for society * Social welfare function, a function that aggregates individual welfares to create an overall social welfare ** Social choice theory, the study of welfare aggregation * Welfare economics, the study of social well-being Government-run public aid * Welfare spending, government intervention meant to provide a minimal level of well-being and social support for all citizens * Welfare state, the concept of a government playing a key role in individual economic and social well-being Other uses * ''Welfare'' (film), a 1975 film by Frederick Wiseman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Well-being
Well-being is what is Intrinsic value (ethics), ultimately good for a person. Also called "welfare" and "quality of life", it is a measure of how well life is going for someone. It is a central goal of many individual and societal endeavors. Subjective well-being refers to how a person feels about and evaluates their life. Objective well-being encompasses factors that can be assessed from an external perspective, such as health, income, and security. Individual well-being concerns the quality of life of a particular person, whereas community well-being measures how well a group of people functions and thrives. Various types of well-being are categorized based on the domain of life to which they belong, such as physical, psychological, emotional, social, and economic well-being. Theories of well-being aim to identify the Essence, essential features of well-being. Hedonism argues that the balance of pleasure over pain is the only factor. Desire theories assert that the satisfact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welfare Economics
Welfare economics is a field of economics that applies microeconomic techniques to evaluate the overall well-being (welfare) of a society. The principles of welfare economics are often used to inform public economics, which focuses on the ways in which government intervention can improve social welfare. Additionally, welfare economics serves as the theoretical foundation for several instruments of public economics, such as cost–benefit analysis. The intersection of welfare economics and behavioral economics has given rise to the subfield of behavioral welfare economics. Two fundamental theorems are associated with welfare economics. The first states that competitive markets, under certain assumptions, lead to Pareto efficient outcomes. This idea is sometimes referred to as Adam Smith's invisible hand. The second theorem states that with further restrictions, any Pareto efficient outcome can be achieved through a competitive market equilibrium, provided that a social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corporate Welfare
Corporate welfare refers to government financial assistance, Subsidy, subsidies, tax breaks, or other favorable policies provided to private businesses or specific industries, ostensibly to promote economic growth, job creation, or other public benefits. This support can take various forms, including tax credits, tax deductions, tax exemptions, government contracts, preferential regulatory treatment, debt write-offs, public-private partnerships, bailout programs, discount schemes, deferrals, low-interest loans or loan guarantees, direct subsidies or public grants. The definition of corporate welfare spending, welfare is sometimes restricted to direct Subsidy, government subsidies of major corporations, excluding Tax avoidance, tax loopholes and all manner of Regulation, regulatory and trade decisions. Origin of term The term "corporate welfare" was reportedly coined in 1956 by Ralph Nader. Alternative adages "Socialism for the rich, capitalism for the poor" Believed to ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Welfare
Animal welfare is the quality of life and overall well-being of animals. Formal standards of animal welfare vary between contexts, but are debated mostly by animal welfare groups, legislators, and academics. Animal welfare science uses measures such as longevity, disease, immunosuppression, ethology, behavior, physiology, and reproduction, although there is debate about which of these best indicate animal welfare. Respect for animal welfare is often based on the belief that nonhuman animals are Sentience, sentient and that consideration should be given to their well-being or suffering, especially when they are under the care of humans. These concerns can include how animals are Animal slaughter, slaughtered for food, how they are used in Animal testing, scientific research, how they are kept (as pets, in zoos, farms, circuses, etc.), and how human activities affect the welfare and survival of wild species. There are two forms of criticism of the concept of animal welfare, comin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Welfare
Three ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS ''Welfare''. A fourth was planned but never completed: * was a King's ship mentioned in 1350. * was a captain's John Strong ship, commanding which he made a first landing on Falkland Islands The Falkland Islands (; ), commonly referred to as The Falklands, is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and from Cape Dub ... in 1690. * HMS ''Welfare'' was to have been an Admiralty modified W-class destroyer. She was laid down in 1918 but cancelled later that year. * was an launched in 1943 and broken up in 1957. {{DEFAULTSORT:Welfare, Hms Royal Navy ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welfare (film)
''Welfare'' is a 1975 film directed by Frederick Wiseman. Summary It examines the welfare system in the United States The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ..., from the viewpoint of both officials and claimants. Reception and legacy ''Welfare'' is considered by film critics to be Wiseman's masterpiece. References External links Official website* Richard Brody's take on Frederick Wiseman's 1975 documentary at The New Yorker {{Frederick Wiseman 1975 films 1975 documentary films American documentary films Films directed by Frederick Wiseman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welfare State
A welfare state is a form of government in which the State (polity), state (or a well-established network of social institutions) protects and promotes the economic and social well-being of its citizens, based upon the principles of equal opportunity, equitable distribution of wealth, and public responsibility for citizens unable to avail themselves of the minimal provisions for a good life. There is substantial variability in the form and trajectory of the welfare state across countries and regions. All welfare states entail some degree of Public–private partnership, private–public partnerships wherein the administration and delivery of at least some welfare programs occur through private entities. Welfare state services are also provided at varying territorial levels of government. The contemporary capitalist welfare state has been described as a type of mixed economy in the sense of state interventionism, as opposed to a mixture of planning and markets, since economic p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
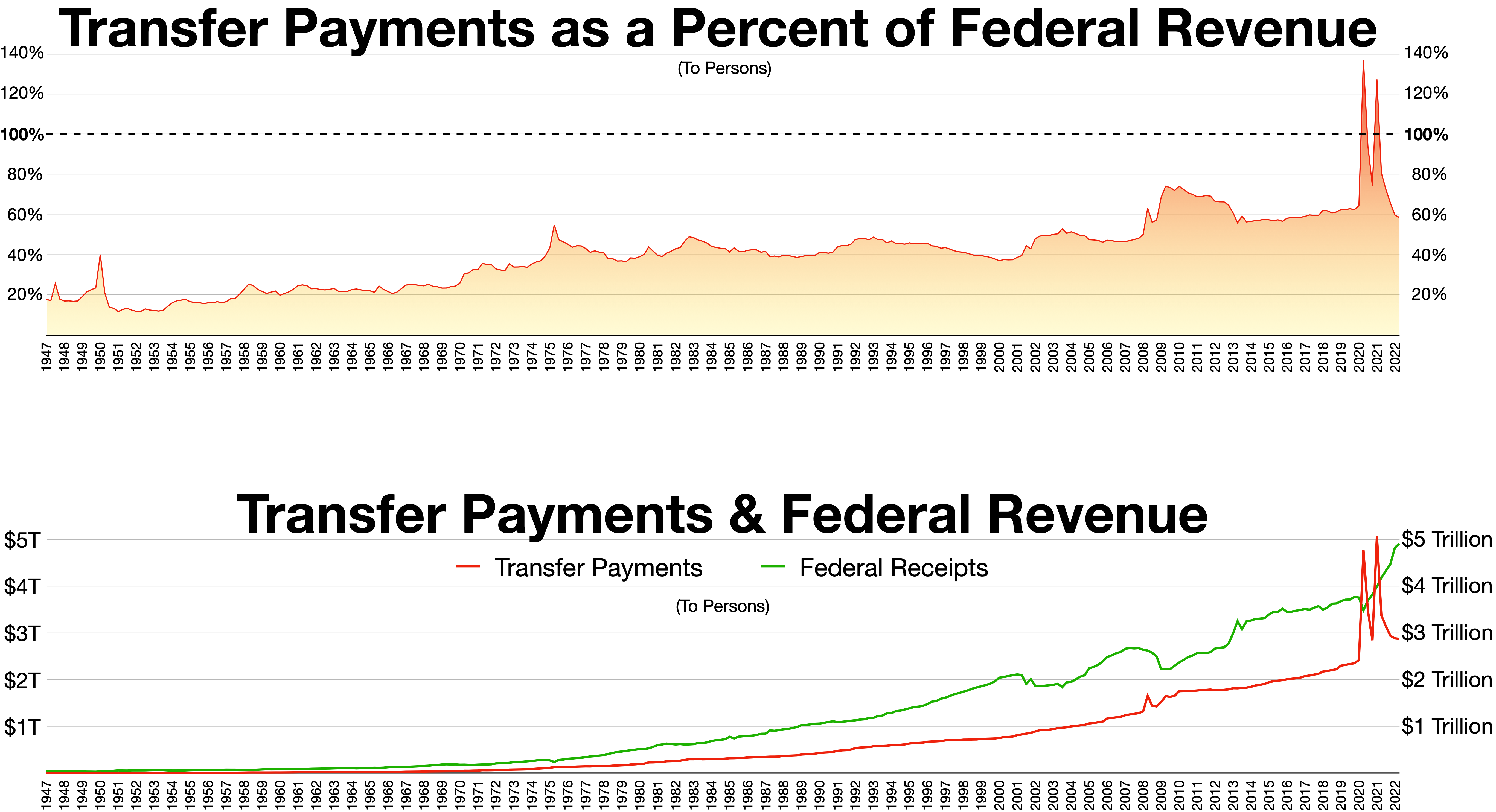
Welfare Spending
Welfare spending is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifically to social insurance programs which provide support only to those who have previously contributed (e.g. pensions), as opposed to ''social assistance'' programs which provide support on the basis of need alone (e.g. most disability benefits). The International Labour Organization defines social security as covering support for those in old age, support for the maintenance of children, medical treatment, parental and sick leave, unemployment and disability benefits, and support for sufferers of occupational injury. More broadly, welfare may also encompass efforts to provide a basic level of well-being through subsidized ''social services'' such as healthcare, education, infrastructure, vocational training, and public housing.''The New Fontana Diction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Choice Theory
Social choice theory is a branch of welfare economics that extends the Decision theory, theory of rational choice to collective decision-making. Social choice studies the behavior of different mathematical procedures (social welfare function, social welfare functions) used to combine individual preferences into a coherent whole.Amartya Sen (2008). "Social Choice". ''The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics'', 2nd EditionAbstract & TOC./ref> It contrasts with political science in that it is a Normative economics, normative field that studies how a society can make good decisions, whereas political science is a Positive economics, descriptive field that observes how societies actually do make decisions. While social choice began as a branch of economics and decision theory, it has since received substantial contributions from mathematics, philosophy, political science, and game theory. Real-world examples of social choice rules include constitution, constitutions and Parliamentary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utilitarianism
In ethical philosophy, utilitarianism is a family of normative ethical theories that prescribe actions that maximize happiness and well-being for the affected individuals. In other words, utilitarian ideas encourage actions that lead to the greatest good for the greatest number. Although different varieties of utilitarianism admit different characterizations, the basic idea that underpins them all is, in some sense, to maximize utility, which is often defined in terms of well-being or related concepts. For instance, Jeremy Bentham, the founder of utilitarianism, described ''utility'' as the capacity of actions or objects to produce benefits, such as pleasure, happiness, and good, or to prevent harm, such as pain and unhappiness, to those affected. Utilitarianism is a version of consequentialism, which states that the consequences of any action are the only standard of right and wrong. Unlike other forms of consequentialism, such as egoism and altruism, egalitarian util ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Welfare Function
In welfare economics and social choice theory, a social welfare function—also called a social ordering, ranking, utility, or choice function—is a function that ranks a set of social states by their desirability. Each person's preferences are combined in some way to determine which outcome is considered better by society as a whole. It can be seen as mathematically formalizing Rousseau's idea of a general will. Social choice functions are studied by economists as a way to identify socially-optimal decisions, giving a procedure to rigorously define which of two outcomes should be considered better for society as a whole (e.g. to compare two different possible income distributions). They are also used by democratic governments to choose between several options in elections, based on the preferences of voters; in this context, a social choice function is typically referred to as an electoral system. The notion of social utility is analogous to the notion of a utility fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gains From Trade
In economics, gains from trade are the net benefits to economic agents from being allowed an increase in voluntary trading with each other. In technical terms, they are the increase of consumer surplus plus producer surplus from lower tariffs or otherwise liberalizing trade. Dynamics Gains from trade are commonly described as resulting from: * specialization in production from division of labor, economies of scale, scope, and agglomeration and relative availability of factor resources in types of output by farms, businesses, location and economies * a resulting increase in total output possibilities * trade through markets from sale of one type of output for other, more highly valued goods. Market incentives, such as reflected in prices of outputs and inputs, are theorized to attract factors of production, including labor, into activities according to comparative advantage, that is, for which they each have a low opportunity cost. The factor owners then use th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |