|
Voice Technology
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound production in which the vocal folds (vocal cords) are the primary sound source. (Other sound production mechanisms produced from the same general area of the body involve the production of unvoiced consonants, clicks, whistling and whispering.) Generally speaking, the mechanism for generating the human voice can be subdivided into three parts; the lungs, the vocal folds within the larynx (voice box), and the articulators. The lungs, the "pump" must produce adequate airflow and air pressure to vibrate vocal folds. The vocal folds (vocal cords) then vibrate to use airflow from the lungs to create audible pulses that form the laryngeal sound source. The muscles of the larynx adjust the length and tension of the vocal folds to 'fine-tune' pitch an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Voice Spectrogram
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing#Evolution of hairlessness, hairlessness, bipedality, bipedalism, and high Human intelligence, intelligence. Humans have large Human brain, brains, enabling more advanced cognitive skills that facilitate successful adaptation to varied environments, development of sophisticated tools, and formation of complex social structures and civilizations. Humans are Sociality, highly social, with individual humans tending to belong to a Level of analysis, multi-layered network of distinct social groups — from families and peer groups to corporations and State (polity), political states. As such, social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of Value theory, values, norm (sociology), social norms, languages, and traditions (co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whispering
Whispering is an unvoiced mode of phonation in which the vocal cords are abducted so that they do not vibrate; air passes between the arytenoid cartilages to create audible turbulence during speech. Supralaryngeal articulation remains the same as in normal speech. In normal speech, the vocal cords alternate between states of voice and voicelessness. In whispering, only the voicing segments change, so that the vocal cords alternate between whisper and voicelessness (though the acoustic difference between the two states is minimal). Because of this, implementing speech recognition for whispered speech is more difficult, as the characteristic spectral range needed to detect syllables and words is not given through the total absence of tone. More advanced techniques such as neural networks may be used, however, as is done by Amazon Alexa. There is no symbol in the IPA for whispered phonation, since it is not used phonemically in any language. However, a sub-dot under pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anger
Anger, also known as wrath ( ; ) or rage (emotion), rage, is an intense emotional state involving a strong, uncomfortable and non-cooperative response to a perceived provocation, hurt, or threat. A person experiencing anger will often experience physical effects, such as increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and increased levels of epinephrine, adrenaline and norepinephrine, noradrenaline. Some view anger as an emotion that triggers part of the fight-or-flight response, fight or flight response. Anger becomes the predominant feeling behavior, behaviorally, cognition, cognitively, and physiology, physiologically when a person makes the conscious choice to take action to immediately stop the threatening behavior of another outside force. Anger can have many physical and mental consequences. The external expression of anger can be found in facial expressions, body language, physiological responses, and at times public acts of aggression. Facial expressions can range from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emotion
Emotions are physical and mental states brought on by neurophysiology, neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavior, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or suffering, displeasure. There is no scientific consensus on a definition. Emotions are often reciprocal determinism, intertwined with mood (psychology), mood, temperament, personality psychology, personality, disposition, or creativity. Research on emotion has increased over the past two decades, with many fields contributing, including psychology, medicine, history, sociology of emotions, computer science and philosophy. The numerous attempts to explain the origin, functional accounts of emotion, function, and other aspects of emotions have fostered intense research on this topic. Theorizing about the evolutionary origin and possible purpose of emotion dates back to Charles Darwin. Current areas of research include the neuroscience of emotion, using tools like positron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
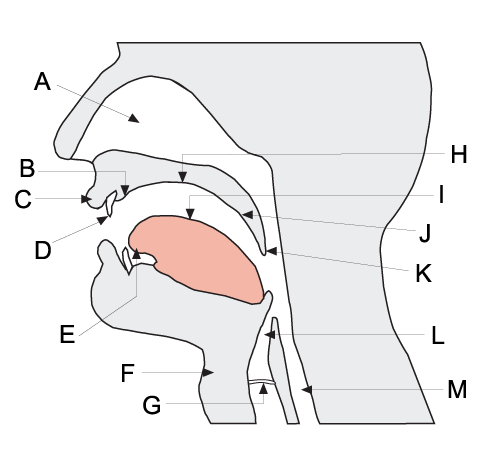
Speech Organ
The field of articulatory phonetics is a subfield of phonetics that studies articulation and ways that humans produce speech. Articulatory phoneticians explain how humans produce speech sounds via the interaction of different physiological structures. Generally, articulatory phonetics is concerned with the transformation of aerodynamic energy into acoustic energy. Aerodynamic energy refers to the airflow through the vocal tract. Its potential form is air pressure; its kinetic form is the actual dynamic airflow. Acoustic energy is variation in the air pressure that can be represented as sound waves, which are then perceived by the human auditory system as sound. Respiratory sounds can be produced by expelling air from the lungs. However, to vary the sound quality in a way useful for speaking, two speech organs normally move towards each other to contact each other to create an obstruction that shapes the air in a particular fashion. The point of maximum obstruction is called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band-pass Filter
A band-pass filter or bandpass filter (BPF) is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects ( attenuates) frequencies outside that range. It is the inverse of a '' band-stop filter''. Description In electronics and signal processing, a filter is usually a two-port circuit or device which removes frequency components of a signal (an alternating voltage or current). A band-pass filter allows through components in a specified band of frequencies, called its ''passband'' but blocks components with frequencies above or below this band. This contrasts with a high-pass filter, which allows through components with frequencies above a specific frequency, and a low-pass filter, which allows through components with frequencies below a specific frequency. In digital signal processing, in which signals represented by digital numbers are processed by computer programs, a band-pass filter is a computer algorithm that performs the same function. The term band ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manner Of Articulation
articulatory phonetics, the manner of articulation is the configuration and interaction of the articulators ( speech organs such as the tongue, lips, and palate) when making a speech sound. One parameter of manner is ''stricture,'' that is, how closely the speech organs approach one another. Others include those involved in the r-like sounds ( taps and trills), and the sibilancy of fricatives. The concept of manner is mainly used in the discussion of consonants, although the movement of the articulators will also greatly alter the resonant properties of the vocal tract, thereby changing the formant structure of speech sounds that is crucial for the identification of vowels. For consonants, the place of articulation and the degree of phonation or voicing are considered separately from manner, as being independent parameters. Homorganic consonants, which have the same place of articulation, may have different manners of articulation. Often nasality and laterality are inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheek
The cheeks () constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. ''Buccal'' means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve. The area between the inside of the cheek and the teeth and gums is called the vestibule or ''buccal'' pouch or ''buccal'' cavity and forms part of the mouth. In other animals, the cheeks may also be referred to as " jowls". Structure Cheeks are fleshy in humans, the skin being suspended by the chin and the jaws, and forming the lateral wall of the human mouth, visibly touching the cheekbone below the eye. The inside of the cheek is lined with a mucous membrane (''buccal'' mucosa, part of the oral mucosa). During mastication (chewing), the cheeks and tongue between them serve to keep the food between the teeth. Clinical significance The cheek is the most common location from which a DNA sample can be taken. (Some saliva is collected from inside the mouth, e.g. using a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soft Palate
The soft palate (also known as the velum, palatal velum, or muscular palate) is, in mammals, the soft biological tissue, tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is part of the palate of the mouth; the other part is the hard palate. The soft palate is distinguished from the hard palate at the front of the mouth in that it does not contain bone. Structure Muscles The five muscles of the soft palate play important roles in swallowing and breathing. The muscles are: # Tensor veli palatini, which is involved in swallowing # Palatoglossus, involved in swallowing # Palatopharyngeus, involved in breathing # Levator veli palatini, involved in swallowing # Musculus uvulae, which moves the palatine uvula, uvula These muscles are innervated by the pharyngeal plexus of vagus nerve, pharyngeal plexus via the vagus nerve, with the exception of the tensor veli palatini. The tensor veli palatini is innervated by the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongue
The tongue is a Muscle, muscular organ (anatomy), organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive system, digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is to enable speech in humans and animal communication, vocalization in other animals. The human tongue is divided into two parts, an oral cavity, oral part at the front and a pharynx, pharyngeal part at the back. The left and right sides are also separated along most of its length by a vertical section of connective tissue, fibrous tissue (the lingual septum) that results in a groove, the median sulcus, on the tongue's surface. There are two groups of glossal muscles. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tone (linguistics)
Tone is the use of pitch (music), pitch in language to distinguish lexical or grammatical meaning—that is, to distinguish or to inflection, inflect words. All oral languages use pitch to express emotional and other para-linguistic information and to convey emphasis, contrast and other such features in what is called intonation (linguistics), intonation, but not all languages use tones to distinguish words or their inflections, analogously to consonants and vowels. Languages that have this feature are called tonal languages; the distinctive tone patterns of such a language are sometimes called tonemes, by analogy with ''phoneme''. Tonal languages are common in East Asia, East and Southeast Asia, Africa, the Americas, and the Pacific islands, Pacific. Tonal languages are different from pitch-accent languages in that tonal languages can have each syllable with an independent tone whilst pitch-accent languages may have one syllable in a word or morpheme that is more prominent t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch (music)
Pitch is a perception, perceptual property that allows sounds to be ordered on a frequency-related scale (music), scale, or more commonly, pitch is the quality that makes it possible to judge sounds as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melody, melodies. Pitch is a major auditory system, auditory attribute of musical tones, along with duration (music), duration, loudness, and timbre. Pitch may be quantified as a frequency, but pitch is not a purely objective physical property; it is a subjective Psychoacoustics, psychoacoustical attribute of sound. Historically, the study of pitch and pitch perception has been a central problem in psychoacoustics, and has been instrumental in forming and testing theories of sound representation, processing, and perception in the auditory system. Perception Pitch and frequency Pitch is an auditory sensation in which a listener assigns musical tones to relative positions on a musical scale based primarily on their percep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |