|
Virulence Factors
Virulence factors (preferably known as pathogenicity factors or effectors in botany) are cellular structures, molecules and regulatory systems that enable microbial pathogens (bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa) to achieve the following: * colonization of a niche in the host (this includes movement towards and attachment to host cells) * immunoevasion, evasion of the host's immune response * immunosuppression, inhibition of the host's immune response (this includes leukocidin-mediated cell death) * entry into and exit out of cells (if the pathogen is an intracellular one) * obtain nutrition from the host Specific pathogens possess a wide array of virulence factors. Some are chromosomally encoded and intrinsic to the bacteria (e.g. capsules and endotoxin), whereas others are obtained from mobile genetic elements like plasmids and bacteriophages (e.g. some exotoxins). Virulence factors encoded on mobile genetic elements spread through horizontal gene transfer, and can convert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botany
Botany, also called plant science, is the branch of natural science and biology studying plants, especially Plant anatomy, their anatomy, Plant taxonomy, taxonomy, and Plant ecology, ecology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who specialises in this field. "Plant" and "botany" may be defined more narrowly to include only land plants and their study, which is also known as phytology. Phytologists or botanists (in the strict sense) study approximately 410,000 species of Embryophyte, land plants, including some 391,000 species of vascular plants (of which approximately 369,000 are flowering plants) and approximately 20,000 bryophytes. Botany originated as history of herbalism#Prehistory, prehistoric herbalism to identify and later cultivate plants that were edible, poisonous, and medicinal, making it one of the first endeavours of human investigation. Medieval physic gardens, often attached to Monastery, monasteries, contained plants possibly having medicinal benefit. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles
Outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) are vesicle (biology and chemistry), vesicles released from the bacterial outer membrane, outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria. While Gram-positive bacteria release vesicles as well, those vesicles fall under the broader category of bacterial membrane vesicles (MVs). OMVs were the first MVs to be discovered, and are distinguished from outer inner membrane vesicles (OIMVs), which are gram-negative bacterial vesicles containing portions of both the outer and inner bacterial membrane. Outer membrane vesicles were first discovered and characterized using Transmission electron microscopy, transmission-electron microscopy by Indian people, Indian Scientist Prof. Smriti Narayan Chatterjee and J. Das in 1966-67. OMVs are ascribed the functionality to provide a manner to communicate among themselves, with other microorganisms in their environment and with the host. These vesicles are involved in membrane vesicle trafficking, trafficking bacterial cell si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell (biology), cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a Multicellular organism, multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. The two main cells that do this are the Macrophages and the Neutrophils of the immune system. Where phagocytosis is used as a means of feeding and provides the organism part or all of its nourishment, it is called phagotrophy and is distinguished from osmotrophy, which is nutrition taking place by absorption. History The history of phag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neisseria Meningitidis
''Neisseria meningitidis'', often referred to as the meningococcus, is a Gram-negative bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life-threatening sepsis. The bacterium is referred to as a coccus because it is round, and more specifically a diplococcus because of its tendency to form pairs. About 10% of adults are carriers of the bacteria in their nasopharynx. As an exclusively human pathogen, it causes developmental impairment and death in about 10% of cases. It causes the only form of bacterial meningitis known to occur epidemically, mainly in Africa and Asia. It occurs worldwide in both epidemic and endemic form. ''N. meningitidis'' is spread through saliva and respiratory secretions during coughing, sneezing, kissing, chewing on toys and through sharing a source of fresh water. It has also been reported to be Sexually transmitted infection, transmitted through oral sex and cause urethritis in men. It infects its hos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
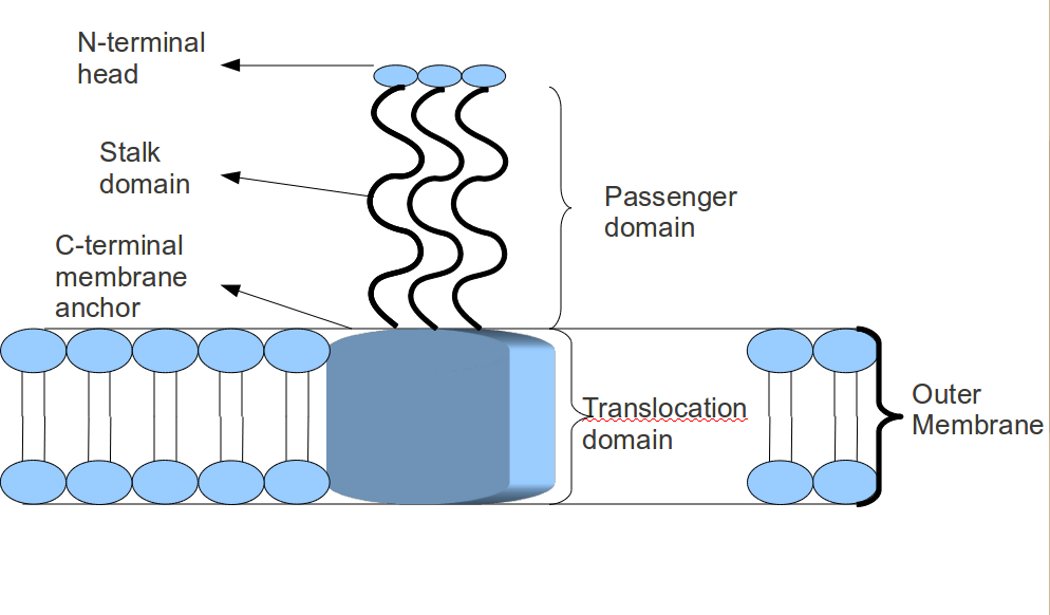
Trimeric Autotransporter Adhesins (TAA)
In molecular biology, trimeric autotransporter adhesins (TAAs), are proteins found on the bacterial outer membrane, outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Bacteria use TAAs in order to infect their host (biology), host cell (biology), cells via a process called cell adhesion. TAAs also go by another name, Oligomeric protein, oligomeric Coiled coil, coiled-coil adhesins, which is shortened to OCAs. In essence, they are virulence factors, factors that make the bacteria harmful and infective to the host organism. TAAs are just one of many methods bacteria use to infect their hosts, infection resulting in diseases such as pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis. Most bacteria infect their host through a method named the secretion pathway. TAAs are part of the secretion pathway, to be more specific the secretion#Type V secretion system (T5SS), type Vc secretion system. Trimeric autotransporter adhesins have a unique structure. The structure they hold is crucial to their function. They a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)