|
UIC Classification
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements, sometimes known as the German classification''The Railway Data File''. Leicester: Silverdale, 2000. p. 52. . or German system,Kalla-Bishop P.M. & Greggio, Luciano, ''Steam Locomotives'', Crescent, 1985, p. 226. describes the wheel arrangement of locomotives, multiple units and trams. It is used in much of the world, notable exceptions being the United Kingdom and North America. The classification system is managed by the International Union of Railways (UIC). Structure The UIC uses the following structure: ; Upper-case letters : Indicate driving axles, starting at A for a single axle. B thus indicates two and C indicates three consecutive pairs of driving wheels. ; Lower-case "o" : Related to driving axles (minimum 2, "B"), indicates they are individually driven by separate traction motors. ; Numbers : Consecutive non-driving axles, starting with 1 for a single axle. ; Prime symbol " ′ " : The axles indicated by a sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheel Arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement or wheel configuration is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed under a locomotive. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and connections, with the adopted notations varying by country. Within a given country, different notations may also be employed for different kinds of locomotives, such as steam, electric, and diesel powered. Especially in steam days, wheel arrangement was an important attribute of a locomotive because there were many different types of layout adopted, each wheel being optimised for a different use (often with only some being actually "driven"). Modern diesel and electric locomotives are much more uniform, usually with all axles driven. Major notation schemes The main notations are the Whyte notation (based on counting the wheels), the AAR wheel arrangement notation (based on counting either the axles or the bogies), and the UIC classifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0-4-4-0
In the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotive wheel arrangement, an 0-4-4-0 is a locomotive with no leading wheels, two sets of four driving wheels, and no trailing wheels. The arrangement is chosen to give the articulation of a locomotive with only the short rigid wheelbase of an , but with its weight spread across eight wheels, and with all the weight carried on the driving wheels; effectively a flexible . Articulated examples were constructed as Mallet, Meyer, BMAG and Double Fairlie locomotives and also as geared locomotives such as Shay, Heisler, and Climax types. A similar configuration was used on some Garratt locomotives, but it is referred to as . In the electric and diesel eras, the Bo-Bo is comparable and closest to the Meyer arrangement of two swivelling bogies. Although rigid duplex locomotives were also constructed with pairs of driving axles and the 0-4-4-0 driven arrangement, these were intended for express passenger service and so we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0-10-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, ten powered and coupled driving wheels on five axles and no trailing wheels. In the United Kingdom, this type is known as a Decapod, a name which is applied to types in the United States. In the United States, the type is known as ten-coupled. Overview The lack of leading and trailing wheels makes this wheel arrangement unstable at speed, and it is a type usually confined to fairly low-speed work, such as switcher, switching (shunting), transfer runs, slow-speed drag freight, or running over mountainous terrain. The Russian E class was the most numerous single class of locomotive in the world, with around 11,000 manufactured. Usage Austria In 1899, Karl Gölsdorf introduced his famous 180.00 class for the Austrian State Railway, an 0-10-0 for mountain regions which had a remarkably low axle load. It employed the Gölsdorf axle system and had the driv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
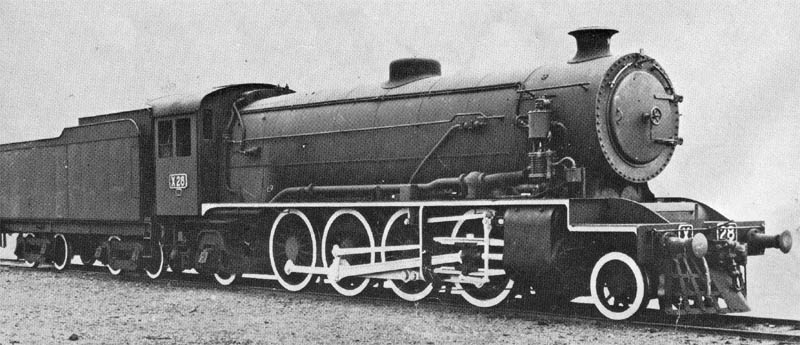
2-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and two trailing wheels on one axle, usually in a trailing truck. This configuration of steam locomotive is most often referred to as a Mikado, frequently shortened to Mike. It was also at times referred to on some railroads in the United States as the McAdoo Mikado and, during World War II, the MacArthur. The notation 2-8-2T indicates a tank locomotive of this wheel arrangement, the "T" suffix indicating a locomotive on which the water is carried in tanks mounted on the engine rather than in an attached tender. Overview The 2-8-2 wheel arrangement allowed the locomotive's firebox to be placed behind instead of above the driving wheels, thereby allowing a larger firebox that could be both wide and deep. This supported a greater rate of combustion and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
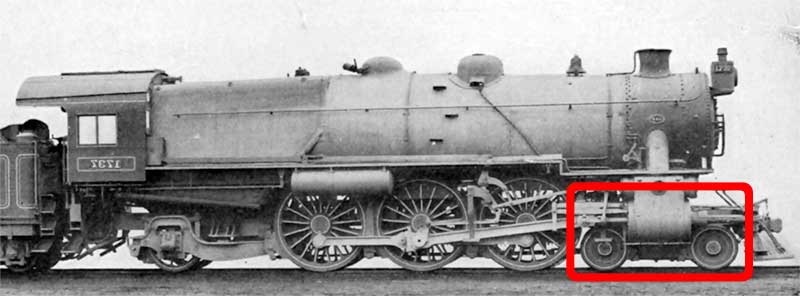
Trailing Wheel
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle (Wheelset (rail transport), wheelset) located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels is usually located in a trailing Bogie, truck. On some large locomotives, a booster engine was mounted on the trailing truck to provide extra tractive effort when starting a heavy train and at low speeds on gradients. Trailing wheels were used in some early locomotives but fell out of favor for a time during the latter 19th century. As demand for more powerful locomotives increased, trailing wheels began to be used to support the crew cab and rear firebox area. Trailing wheels first appeared on American locomotives between 1890 and 1895, but their axle worked in rigid pedestals. It enabled boilers to be lowered, since the top of the main frames was dropped down behind the driving wheels and under the firebox. The firebox could also be longer and wider, increasing the heating su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leading Wheel
The leading wheel or leading axle or pilot wheel of a steam locomotive is an unpowered wheel or axle located in front of the driving wheels. The axle or axles of the leading wheels are normally located on a leading truck. Leading wheels are used to help the locomotive negotiate curves and to support the front portion of the boiler. Overview Many leading bogies do not have simple rotational motion about a vertical pivot. Bogies with a sliding motion controlled by springs was patented by William Adams in 1865. Other designs used swing links to take the weight of the bogie with a centering action. The first use of leading wheels is commonly attributed to John B. Jervis, who employed them in his 1832 design for a locomotive with four leading wheels and two driving wheels (a type that became known as the ''Jervis''). In the Whyte system of describing locomotive wheel arrangements, his locomotive would be classified as a 4-2-0, that is to say, it had four leading wheels, two dri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and no trailing wheels. Locomotives of this type are also referred to as eight coupled. Overview Examples of the 0-8-0 wheel arrangement were constructed both as tender locomotive, tender and tank locomotives. The earliest locomotives were built for mainline haulage, particularly for Freight rail transport, freight, but the configuration was later also often used for large switcher locomotives (shunter locomotives). The wheel arrangement provided a powerful layout with all engine weight as adhesive weight, which maximised the tractive effort and factor of adhesion. The layout was generally too large for smaller and lighter railways, where the more popular wheel arrangement would often be found performing similar duties. Usage Austria Two 0-8-0 locomotives were delivered from Elsässische Maschinenbau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PRR GG1
The Pennsylvania Railroad Class GG1 is a class of streamlined electric locomotives built for the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR), in the northeastern United States. The class was known for its striking art deco shell, its ability to pull trains at up to 100 mph, and its long operating career of almost 50 years. Between 1934 and 1943, General Electric and the PRR's Altoona Works built 139 GG1s. The GG1 entered service with the PRR in 1935 and later ran on successor railroads Penn Central, Conrail, and Amtrak. The last GG1 was retired by New Jersey Transit in 1983. Most have been scrapped, but sixteen are preserved in museums. Technical information Body and mechanical The GG1 was long and weighed . The frame of the locomotive was in two halves joined with a ball joint, allowing the locomotive to negotiate sharper curves. The body rested on the frame and was clad in welded steel plates. The control cabs were near the center of the locomotive on each side of the main oil-co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JNR Class EF58
The is a class of Japanese 2-C+C-2 wheel arrangement DC electric locomotives. 172 locomotives were built between 1946 and 1958. The later years In 1984, 64 out of 172 EF58 locos built were still in service or temporary storage. However, they were withdrawn en masse from Tokaido and Sanyo Main Line freight duties in 1984, and by 1987, immediately prior to privatization of JNR, there were just four members of the class (EF58 61, 89, 122, and 150) remaining in service. Details of the locomotives currently in operational service are as follows. EF58 61 Owned by JR East and based at Tabata Depot in Tokyo, this locomotive was built in 1953 by Hitachi specially for use as the official Imperial Train locomotive, a role it performs to the present day. While other locos had chrome-plated “whiskers” on the cab ends, this loco was built with stainless steel whiskers extending as a thin band along the body sides. The loco remains in its original brown livery, and is maintained in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Pacific 9010
Southern Pacific 9010 is a KM ML 4000 C′C′ diesel-hydraulic locomotive, built in 1964 by German manufacturer Krauss-Maffei for the Southern Pacific Railroad. SP 9010 generated from two V16 Maybach MD870 diesel engines. It is the sole surviving ML 4000 C′C′ built for use in North America, and the sole surviving mainline diesel-hydraulic locomotive in North America. (Several diesel-hydraulic switchers exist in service and in museums). It was painted to Southern Pacific's 1958 standard, the so-called 'bloody nose' colors of Scarlet and Lark Dark Gray, for its entire operating career. It was renumbered to SP 9113 in late 1965, rebuilt extensively at SP's Sacramento General Shops (later Sacramento Locomotive Works) during the latter half of 1966, and was initially retired in 1968. It was revived and rebuilt by Sacramento General Shops into a 'camera car' for the purpose of shooting motion picture background plates for a ground-based full-motion locomotive training simulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Co-Co Locomotive
Co-Co is the wheel arrangement for diesel and electric locomotives with two six-wheeled bogies with all axles powered, with a separate traction motor per axle. The equivalent UIC classification (Europe) for this arrangement is Co′Co′, or C-C for AAR (North America). Use Co-Cos are most suited to freight work as the extra wheels give them good traction. They are also popular because the greater number of axles results in a lower axle load to the track. History The first mainline diesel-electric locomotives were of Bo-Bo arrangement. As they grew in power and weight, from 1937 the EMD E-units used an A1A-A1A layout with six axles to reduce axle load. After WWII, the British LMS ordered two prototype locomotives with some of the first Co-Co arrangements. The first C-C design recorded was a narrow-gauge Hornsby opposed-piston Hornsby-Akroyd-engined locomotive of 1903 for the Chattenden and Upnor Railway. There was a two-speed mechanical transmission with dri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0-6-0
is the Whyte notation designation for steam locomotives with a wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and no trailing wheels. Historically, this was the most common wheel arrangement used on both Tender (rail), tender and tank locomotives in versions with both Cylinder (locomotive), inside and outside cylinders. In the United Kingdom, the Whyte notation of wheel arrangement was also often used for the classification of electric and diesel-electric locomotives with side-rod coupled driving wheels. Under the UIC classification, popular in Europe, this wheel arrangement is written as C if the wheels are coupled with rods or gears, or Co if they are independently driven, the latter usually being electric and diesel-electric locomotives. Overview History The 0-6-0 configuration was the most widely used wheel arrangement for both Tender (rail), tender and tank locomotive, tank steam locomotives. The type was also widely used fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |