|
Two-dimensional Nanomaterials
In materials science, the term single-layer materials or 2D materials refers to crystalline solids consisting of a single layer of atoms. These materials are promising for some applications but remain the focus of research. Single-layer materials derived from single elements generally carry the -ene suffix in their names, e.g. graphene. Single-layer materials that are compounds of two or more elements have -ane or -ide suffixes. 2D materials can generally be categorized as either 2D allotropes of various elements or as compounds (consisting of two or more covalently bonding elements). It is predicted that there are hundreds of stable single-layer materials. The atomic structure and calculated basic properties of these and many other potentially synthesisable single-layer materials, can be found in computational databases. 2D materials can be produced using mainly two approaches: top-down exfoliation and bottom-up synthesis. The exfoliation methods include sonication, mechanical, hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Materials Science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field of researching and discovering materials. Materials engineering is an engineering field of finding uses for materials in other fields and industries. The intellectual origins of materials science stem from the Age of Enlightenment, when researchers began to use analytical thinking from chemistry, physics, and engineering to understand ancient, phenomenological observations in metallurgy and mineralogy. Materials science still incorporates elements of physics, chemistry, and engineering. As such, the field was long considered by academic institutions as a sub-field of these related fields. Beginning in the 1940s, materials science began to be more widely recognized as a specific and distinct field of science and engineering, and major technical universities around the world created dedicated schools for its study. Materials scientists emphasize understanding how the history of a material (''processing'') influences its struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphyne
Graphyne is an allotrope of carbon. Although it has been studied in theoretical models, it is very difficult to synthesize and only small amounts of uncertain purity have been created. Its structure is one-atom-thick Planar crystallographic group, planar sheets of sp and Sp2 bond, sp2-bonded carbon atoms arranged in crystal lattice. It can be seen as a lattice of benzene rings connected by acetylene bonds. The material is called graphyne-''n'' when benzene rings are connected by ''n'' sequential acetylene molecules, and graphdiyne for a particular case of ''n'' = 2 (diacetylene links). Depending on the content of acetylene groups, graphyne can be considered a mixed hybridization, sp''k'', where k can be 1 or 2, and thus differs from the hybridization of graphene (considered pure sp2) and diamond (pure sp3). First-principles calculations showed that periodic graphyne structures and their boron nitride analogues are stable. The calculations used Phonon scattering, phonon dispers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 118 picometers (for C2H2) is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (132 pm, for C2H4) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Communications
''ChemComm'' (or ''Chemical Communications''), formerly known as ''Journal of the Chemical Society D: Chemical Communications'' (1969–1971), ''Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications'' (1972–1995), is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Royal Society of Chemistry. It covers all aspects of chemistry. In January 2012, the journal moved to publishing 100 issues per year. The current chair of the editorial board is Douglas Stephan (University of Toronto, Canada), while the executive editor is Richard Kelly. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: * Chemical Abstracts * Science Citation Index * Current Contents/Physical, Chemical & Earth Sciences * Scopus * Index Medicus/MEDLINE/PubMed According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor of 4.3. See also * '' New Journal of Chemistry'' * ''Chemical Society Reviews ''Chemical Society Reviews'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diacetylene
Diacetylene (also known as butadiyne) is the organic compound with the formula or . It is the simplest compound containing two triple bonds. It is first in the series of polyynes, which are of theoretical but not of practical interest. Occurrence Diacetylene has been identified in the atmosphere of Titan and in the protoplanetary nebula CRL 618 by its characteristic vibrational spectrum. It is proposed to arise by a reaction between acetylene and the ethynyl radical (), which is produced when acetylene undergoes photolysis. This radical can in turn attack the triple bond in acetylene and react efficiently even at low temperatures. Diacetylene has also been detected on the Moon. Preparation This compound may be made by the dehydrohalogenation of 1,4-dichloro-2-butyne by potassium hydroxide (in alcoholic medium) at ~70°C: : The bis(trimethylsilyl)-protected derivative may be prepared by the Hay coupling of (trimethylsilyl)acetylene: : See also * Acetylene * Diiodobutadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revue Roumaine De Chimie
A revue is a type of multi-act popular theatrical entertainment that combines music, dance, and sketches. The revue has its roots in 19th century popular entertainment and melodrama but grew into a substantial cultural presence of its own during its golden years from 1916 to 1932. Though most famous for their visual spectacle, revues frequently satirized contemporary figures, news or literature. Similar to the related subforms of operetta and musical theatre, the revue art form brings together music, dance and sketches to create a compelling show. In contrast to these, however, revue does not have an overarching storyline. Rather, a general theme serves as the motto for a loosely related series of acts that alternate between solo performances and dance ensembles. Owing to high ticket prices, ribald publicity campaigns and the occasional use of prurient material, the revue was typically patronized by audience members who earned more and felt even less restricted by middle-class s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron Nitride
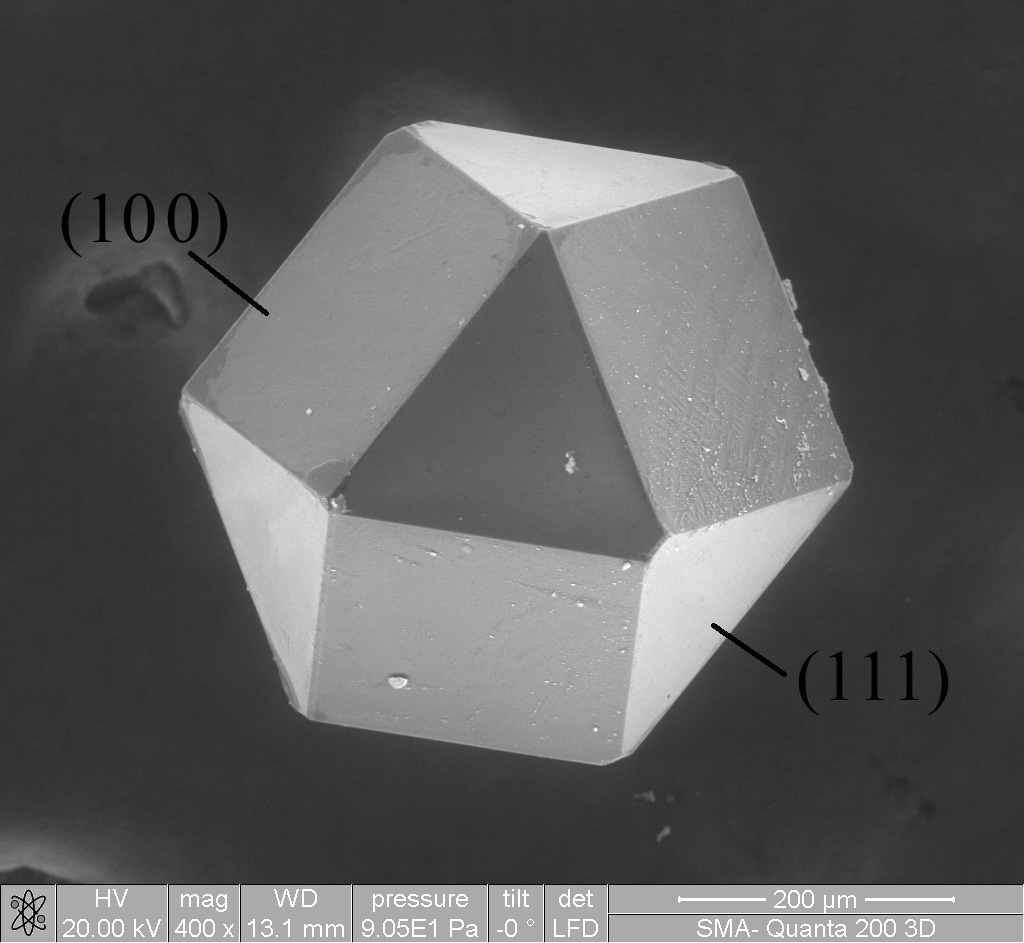
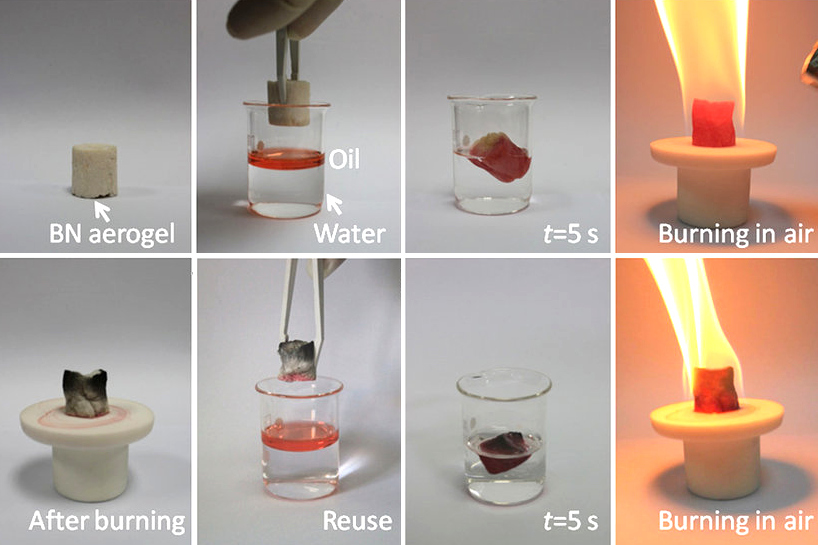
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula B N. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexagonal form corresponding to graphite is the most stable and soft among BN polymorphs, and is therefore used as a lubricant and an additive to cosmetic products. The cubic ( zincblende aka sphalerite structure) variety analogous to diamond is called c-BN; it is softer than diamond, but its thermal and chemical stability is superior. The rare wurtzite BN modification is similar to lonsdaleite but slightly softer than the cubic form. Because of excellent thermal and chemical stability, boron nitride ceramics are used in high-temperature equipment and metal casting. Boron nitride has potential use in nanotechnology. History Boron nitride was discovered by chemistry teacher of the Liverpool Institute in 1842 via reduction of boric acid with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ab Initio
( ) is a Latin term meaning "from the beginning" and is derived from the Latin ("from") + , ablative singular of ("beginning"). Etymology , from Latin, literally "from the beginning", from ablative case of "entrance", "beginning", related to verb "to go into", "enter upon", "begin". Uses ''Ab initio'' (abbreviation: ''ab init.'') is used in several contexts, including the following: Law In law, ''ab initio'' refers to something being the case from the start or from the instant of the act rather than from when the court declared it so. For instance, the term "void ''ab initio''" means "to be treated as invalid from the outset." E.g., in many jurisdictions, if a person signs a contract under duress, that contract is treated as being "void ''ab initio''". Typically, documents or acts which are void ''ab initio'' cannot be fixed and if a jurisdiction, a document, or an act is so declared at law to be void ''ab initio'', the parties are returned to their respective positions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonon Scattering
Phonons can scatter through several mechanisms as they travel through the material. These scattering mechanisms are: Umklapp phonon-phonon scattering, phonon-impurity scattering, phonon-electron scattering, and phonon-boundary scattering. Each scattering mechanism can be characterised by a relaxation rate 1/\tau which is the inverse of the corresponding relaxation time. All scattering processes can be taken into account using Matthiessen's rule. Then the combined relaxation time \tau_ can be written as: :\frac = \frac+\frac+\frac+\frac The parameters \tau_, \tau_, \tau_, \tau_\text are due to Umklapp scattering, mass-difference impurity scattering, boundary scattering and phonon-electron scattering, respectively. Phonon-phonon scattering For phonon-phonon scattering, effects by normal processes (processes which conserve the phonon wave vector - N processes) are ignored in favor of Umklapp processes (U processes). Since normal processes vary linearly with \omega and umklapp proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of electricity, and insoluble in water. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the Chemical stability, chemically stable form of carbon at Standard temperature and pressure, room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest Scratch hardness, hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of lattice defect, defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) can color ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physica Status Solidi B
''Physica Status Solidi'', often stylized ''physica status solidi'' or ''pss'', is a family of international peer-reviewed, scientific journals, publishing research on all aspects of solid state physics, and materials science. It is owned and published by Wiley–VCH. These journals publish over 2000 articles per year, making it one of the largest international publications in condensed matter physics. The current editor in chief is Stefan Hildebrandt at the Editorial Office based in Berlin. This office also manages the peer-review process. History ''Physica Status Solidi'' was founded by Karl Wolfgang Böer (then at Humboldt University of Berlin) in East Berlin and published its first issue in July 1961. Shortly after the journal was founded, the construction of the Berlin Wall in August 1961 exacerbated the distances between scientists from the Eastern and Western blocs. Throughout the Cold War ''Physica Status Solidi'' maintained political independence and English as public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon (journal)
''Carbon'' is a scientific journal published by Elsevier Elsevier ( ) is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as ''The Lancet'', ''Cell (journal), Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, .... According to the journal's website, "Carbon publishes papers that deal with original research on carbonaceous solids with an emphasis on graphene-based materials. These materials include, but are not limited to, carbon nanotubes, carbon fibers and filaments, graphites, activated carbons, pyrolytic carbons, glass-like carbons, carbon blacks, and chars." The Editor-in-Chief is Mauricio Terrones of Penn State University (USA) and the Senior Editor is Gareth Neighbour of the Open University (UK) and these are supported by an editorial board of 14 carbon scientists. External links * Elsevier academic journals Chemistry journals Materials science journals English-language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |