|
Tops
Total Operations Processing System (TOPS) is a computer system for managing railway locomotives and rolling stock, known for many years of use in the United Kingdom. TOPS was originally developed between the Southern Pacific Railroad (SP), Stanford University and IBM as a replacement for paper-based systems for managing rail logistics. A jointly-owned consultancy company, ''TOPS On-Line Inc.'', was established in 1960 with the goal of implementing TOPS, as well as selling it to third parties. Development was protracted, requiring around 660 man-years of effort to produce a releasable build. During mid-1968, the first phase of the system was introduced on the SP, and quickly proved its advantages over the traditional methods practiced prior to its availability. In addition to SP, TOPS was widely adopted throughout North America and beyond. While it was at one point in widespread use across many of the United States railroads, the system has been perhaps most prominently use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-Automatic Ground Environment
The Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) was a system of mainframe computer, large computers and associated computer network, networking equipment that coordinated data from many radar sites and processed it to produce a single unified image of the airspace over a wide area. SAGE directed and controlled the NORAD response to a possible Soviet air attack, operating in this role from the late 1950s into the 1980s. Its enormous computers and huge displays remain a part of Cold War lore, and after decommissioning were common props in movies such as ''Dr. Strangelove'' and Colossus: The Forbin Project, ''Colossus'', and on science fiction TV series such as ''The Time Tunnel''. The processing power behind SAGE was supplied by the largest discrete component-based computer ever built, the AN/FSQ-7 Combat Direction Central, AN/FSQ-7, manufactured by IBM. Each SAGE Direction Center (DC) housed an FSQ-7 which occupied an entire floor, approximately not including supporting equipment. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
483004 Shanklin 1
__NOTOC__ Year 483 ( CDLXXXIII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known in the Roman Empire as the Year of the Consulship of Aginantius without colleague (or, less frequently, year 1236 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 483 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Byzantine general Illus (''magister officiorum''), and Verina (widow of the late emperor Leo I), attempt to overthrow Emperor Zeno and place another general named Leontius on the throne. Europe * The Ostrogoths are given status as ''foederati''; they control a large part of Macedonia and Thrace (Balkans). By topic Religion * March 10 – Pope Simplicius dies at Rome after a 15-year reign, and is succeeded by Felix III as the 48th pope; Rome is without a pope for 10 days in the interim. Felix III is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of The United Kingdom
His Majesty's Government, abbreviated to HM Government or otherwise UK Government, is the central government, central executive authority of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.Overview of the UK system of government : Directgov – Government, citizens and rights Archived direct.gov.uk webpage. Retrieved on 29 August 2014. The government is led by the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, prime minister (Keir Starmer since 5 July 2024) who appoints all the other British Government frontbench, ministers. The country has had a Labour Party (UK), Labour government since 2024 United Kingdom general election, 2024. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
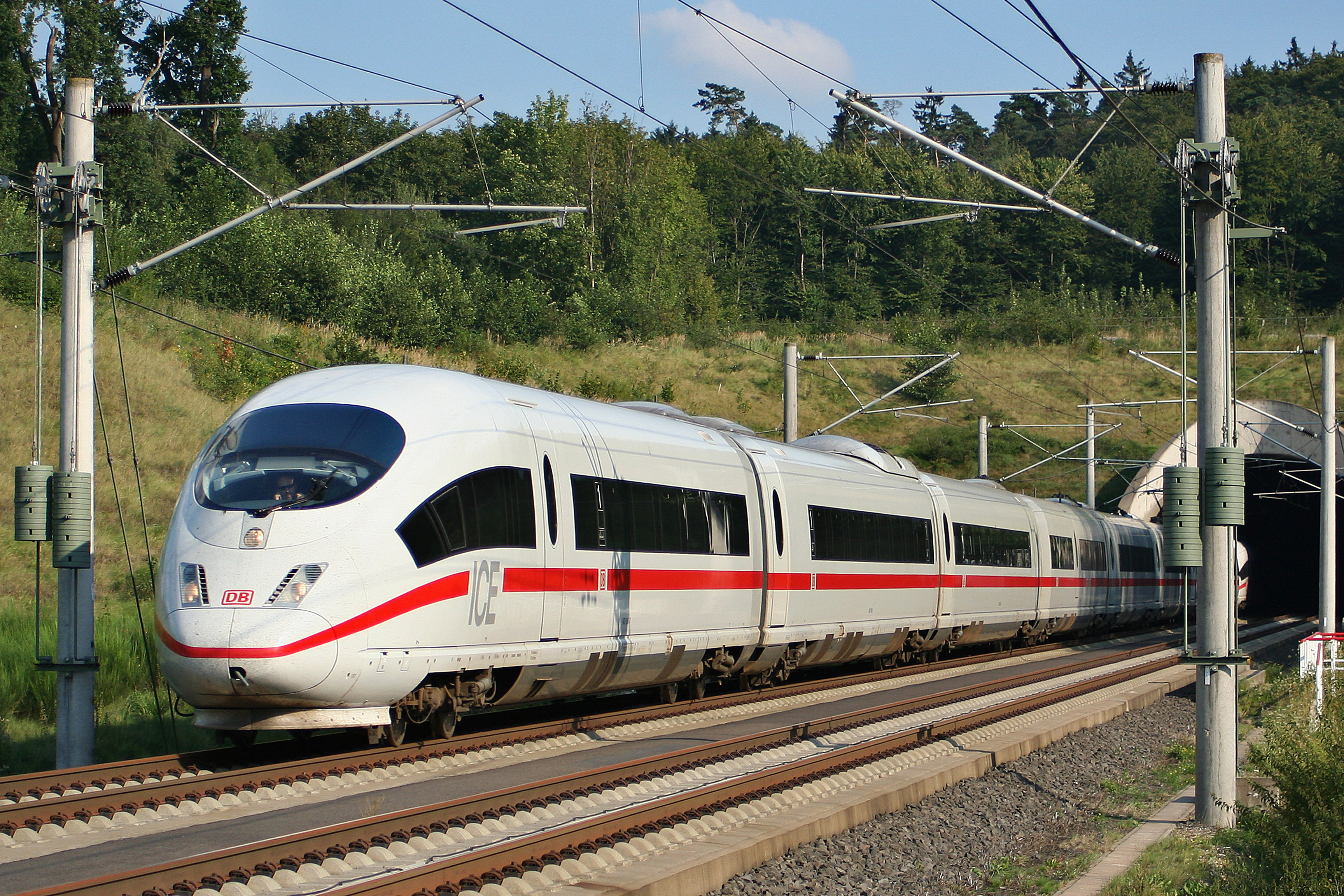
Electric Locomotive
An electric locomotive is a locomotive powered by electricity from overhead lines, a third rail or on-board energy storage such as a Battery (electricity), battery or a supercapacitor. Locomotives with on-board fuelled prime mover (locomotive), prime movers, such as diesel engines or gas turbines, are classed as Diesel–electric powertrain, diesel–electric or turbine–electric powertrain, gas turbine–electric and not as electric locomotives, because the electric generator/motor combination serves only as a Transmission (mechanics), power transmission system. Electric locomotives benefit from the high efficiency of electric motors, often above 90% (not including the inefficiency of generating the electricity). Additional efficiency can be gained from regenerative braking, which allows kinetic energy to be recovered during braking to put power back on the line. Newer electric locomotives use AC motor-inverter drive systems that provide for regenerative braking. Electric loco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 158
The British Rail Class 158 ''Sprinter (British Rail), Express Sprinter'' is a diesel multiple unit (DMU) passenger train. It is a member of the Sprinter (British Rail), Sprinter series of regional trains, produced as a replacement for British Rail's List of British Rail diesel multiple unit classes#First generation, first generation of DMUs; of the other members, the British Rail Class 159, Class 159 is almost identical to the Class 158, having been converted from Class 158 to Class 159 in two batches to operate express services from West of England Main Line, London Waterloo to the West of England. The Class 158 was constructed between 1989 and 1992 by British Rail Engineering Limited (BREL) at its Derby Litchurch Lane Works. The majority were built as two-car sets; some three-car sets were also produced. During September 1990, the first Express Sprinters were operated by ScotRail (British Rail), ScotRail; the type was promptly introduced to secondary routes across the Midland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 41 (HST)
The British Rail Class 41 were two powercars built in 1972 by British Rail Engineering Limited's Crewe Works to operate with the prototype InterCity 125, High Speed Train (HST) with British Rail Mark 3, Mark 3 carriages. History Two power cars were built in 1972 by British Rail Engineering Limited's Crewe Works, numbered 41001 and 41002. They initially conducted tests on the East Coast Main Line with the set based at Neville Hill TMD. Having accumulated more than , including setting a diesel train speed record of between Northallerton railway station, Northallerton and Thirsk railway station, Thirsk in June 1973, they moved to the Great Western Main Line in 1974. On 5 May 1975, both entered revenue service on Great Western services between Paddington railway station, London Paddington and Bristol Temple Meads railway station, Bristol Temple Meads / Weston-super-Mare railway station, Weston-super-Mare. After the British Rail Class 252, Class 252 re-classification they were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 43 (HST)
The British Rail Class 43 (HST) is the TOPS classification used for the InterCity 125 ''High Speed Train'' (formerly Classes 253 and 254) Diesel locomotive#Diesel-electric, diesel-electric power cars, built by British Rail Engineering Limited from 1975 to 1982, and in service in the UK since 1976. The class is officially the Railway speed record#Fuel-electric, fastest diesel locomotive in the world, with an absolute maximum speed of , and a regular service speed of . The record run was led by 43102 (43302) and trailed by 43159. History and background In the early 1970s, the British Railways Board made the decision to replace its main-line express diesel traction. Financial limitations were tight, so mass electrification was not possible. As a result, a new generation of high-speed diesel trains had to be developed. Experience with the high-speed locomotives had shown that a low axle weight was essential to avoid damage to the track at sustained high speed, and that high-sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Unit
A multiple-unit train (or multiple unit (MU)) is a self-propelled train composed of one or more Coach (rail), carriages joined, and where one or more of the carriages have the means of propulsion built in. By contrast, a locomotive-hauled train has all of the carriages unpowered. An implication of this is that all the powered carriages needs to be controllable by a single engineer or driver, which is a case of the broader concept of multiple-unit train control. In other words, all "multiple units" employ some variation of multiple-unit train control. In the broader context "unit" means any powered rail vehicle, including locomotives (that does not carry cargo) and powered cargo-carrying carriages. In the context of this article, "unit" refers specifically to the latter only (whether the cargo is passengers or some other cargo). What follows is that if coupled to another multiple unit, all MUs can still be controlled by the single driver, with multiple-unit train control. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 31-4 Dataplate
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. * British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** British Isles, an island group ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** British Empire, a historical global colonial empire ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) * British Raj, colonial India under the British Empire * British Hong Kong, colonial H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Locomotive
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover (locomotive), power source is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is conveyed to the driving wheels. The most common are diesel–electric locomotives and diesel–hydraulic. Early internal combustion engine, internal combustion locomotives and railcars used kerosene and gasoline as their fuel. Rudolf Diesel patented his first compression-ignition engine in 1898, and steady improvements to the design of diesel engines reduced their physical size and improved their power-to-weight ratios to a point where one could be mounted in a locomotive. Internal combustion engines only operate efficiently within a limited power band, and while low-power gasoline engines could be coupled to mechanical transmission (mechanics), transmissions, the more powerful diesel engines required the development of new forms of transmiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotives Of British Railways
The steam locomotives of British Railways were used by British Railways over the period 1948–1968. The vast majority of these were inherited from its four constituent companies, the "Big Four British railway companies, Big Four". In addition, BR built 2,537 steam locomotives in the period 1948–1960, 1,538 to Transport Act 1947, pre-nationalisation designs and 999 to its own standard designs. These locomotives had short working lives, some as little as five years, because of 1955 Modernisation plan, the decision to end the use of steam traction by 1968, against a design life of over 30 years and a theoretical final withdrawal date of between 1990 and 2000. Background British Railways was created on 1 January 1948 principally by the merger of the "Big Four British railway companies, Big Four" grouped railway companies: the Great Western Railway (GWR), the London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS), the London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) and the Southern Railway (UK), South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Union
A trade union (British English) or labor union (American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers whose purpose is to maintain or improve the conditions of their employment, such as attaining better wages and Employee benefits, benefits, improving Work (human activity), working conditions, improving safety standards, establishing complaint procedures, developing rules governing status of employees (rules governing promotions, just-cause conditions for termination) and protecting and increasing the bargaining power of workers. Trade unions typically fund their head office and legal team functions through regularly imposed fees called ''union dues''. The union representatives in the workforce are usually made up of workplace volunteers who are often appointed by members through internal democratic elections. The trade union, through an elected leadership and bargaining committee, bargains with the employer on behalf of its members, known as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |