|
Supertasks
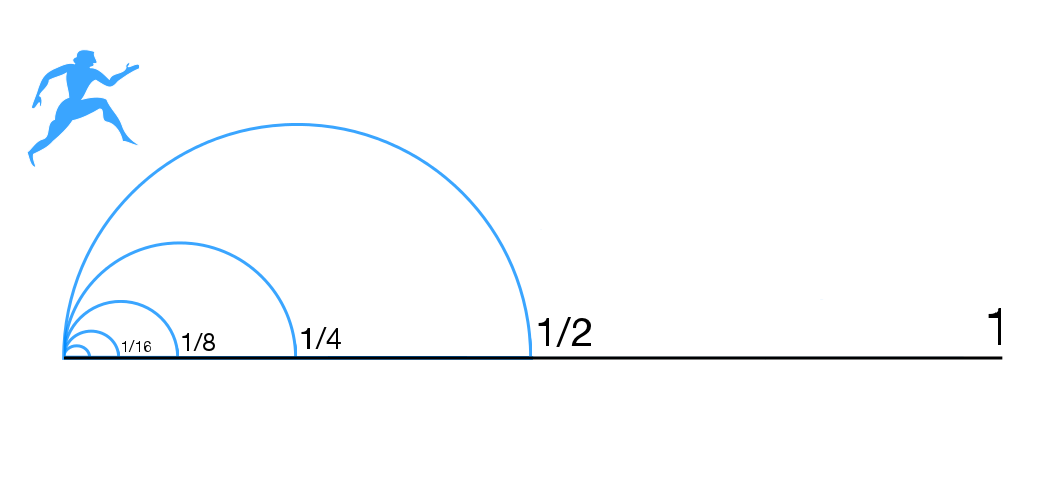
In philosophy, a supertask is a countably infinite sequence of operations that occur sequentially within a finite interval of time. Supertasks are called hypertasks when the number of operations becomes uncountably infinite. A hypertask that includes one task for each ordinal number is called an ultratask. The term "supertask" was coined by the philosopher James F. Thomson, who devised Thomson's lamp. The term "hypertask" derives from Clark and Read in their paper of that name. History Zeno Motion The origin of the interest in supertasks is normally attributed to Zeno of Elea. Zeno claimed that motion was impossible. He argued as follows: suppose our burgeoning "mover", Achilles say, wishes to move from A to B. To achieve this he must traverse half the distance from A to B. To get from the midpoint of AB to B, Achilles must traverse half ''this'' distance, and so on and so forth. However many times he performs one of these "traversing" tasks, there is another one left for him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomson's Lamp
Thomson's lamp is a philosophical puzzle based on infinites. It was devised in 1954 by British philosopher James F. Thomson, who used it to analyze the possibility of a supertask, which is the completion of an infinite number of tasks. Consider a lamp with a toggle switch. Flicking the switch once turns the lamp on. Another flick will turn the lamp off. Now suppose that there is a being who is able to perform the following task: starting a timer, he turns the lamp on. At the end of one minute, he turns it off. At the end of another half minute, he turns it on again. At the end of another quarter of a minute, he turns it off. At the next eighth of a minute, he turns it on again, and he continues thus, flicking the switch each time after waiting exactly one-half the time he waited before flicking it previously. The sum of this infinite series of time intervals is exactly two minutes. The following question is then considered: Is the lamp on or off at two minutes? Thomson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeno's Paradoxes
Zeno's paradoxes are a series of philosophical arguments presented by the ancient Greek philosopher Zeno of Elea (c. 490–430 BC), primarily known through the works of Plato, Aristotle, and later commentators like Simplicius of Cilicia. Zeno devised these paradoxes to support his teacher Parmenides's philosophy of monism, which posits that despite people's sensory experiences, reality is singular and unchanging. The paradoxes famously challenge the notions of plurality (the existence of many things), motion, space, and time by suggesting they lead to logical contradictions. Zeno's work, primarily known from second-hand accounts since his original texts are lost, comprises forty "paradoxes of plurality," which argue against the coherence of believing in multiple existences, and several arguments against motion and change. Of these, only a few are definitively known today, including the renowned "Achilles Paradox", which illustrates the problematic concept of infinite divisibi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational and critical inquiry that reflects on its methods and assumptions. Historically, many of the individual sciences, such as physics and psychology, formed part of philosophy. However, they are considered separate academic disciplines in the modern sense of the term. Influential traditions in the history of philosophy include Western philosophy, Western, Islamic philosophy, Arabic–Persian, Indian philosophy, Indian, and Chinese philosophy. Western philosophy originated in Ancient Greece and covers a wide area of philosophical subfields. A central topic in Arabic–Persian philosophy is the relation between reason and revelation. Indian philosophy combines the Spirituality, spiritual problem of how to reach Enlightenment in Buddhism, enlighten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church–Turing Thesis
In Computability theory (computation), computability theory, the Church–Turing thesis (also known as computability thesis, the Turing–Church thesis, the Church–Turing conjecture, Church's thesis, Church's conjecture, and Turing's thesis) is a wiktionary:thesis, thesis about the nature of computable functions. It states that a function (mathematics), function on the natural numbers can be calculated by an effective method if and only if it is computable by a Turing machine. The thesis is named after American mathematician Alonzo Church and the British mathematician Alan Turing. Before the precise definition of computable function, mathematicians often used the informal term ''effectively calculable'' to describe functions that are computable by paper-and-pencil methods. In the 1930s, several independent attempts were made to formal system, formalize the notion of computability: * In 1933, Kurt Gödel, with Jacques Herbrand, formalized the definition of the class of general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalam Cosmological Argument
The Kalam cosmological argument is a modern formulation of the cosmological argument for the existence of God. It is named after the ''Kalam'' (medieval Islamic scholasticism) from which many of its key ideas originated. Philosopher and theologian William Lane Craig was principally responsible for revitalising these ideas for modern academic discourse through his book '' The Kalām Cosmological Argument'' (1979), as well as other publications. The argument's central thesis is the metaphysical impossibility of a temporally past-infinite universe and of actual infinities existing in the real world, traced by Craig to 11th-century Persian Muslim scholastic philosopher Al-Ghazali. This feature distinguishes it from other cosmological arguments, such as Aquinas's Second Way, which rests on the impossibility of a causally ordered infinite regress, and those of Leibniz and Samuel Clarke, which refer to the principle of sufficient reason. Reichenbach, 2004 Since Craig's original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Chalmers
David John Chalmers (; born 20 April 1966) is an Australian philosopher and cognitive scientist, specializing in philosophy of mind and philosophy of language. He is a professor of philosophy and neural science at New York University, as well as co-director of NYU's Center for Mind, Brain and Consciousness (along with Ned Block). In 2006, he was elected a Fellow of the Australian Academy of the Humanities. In 2013, he was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts & Sciences. Chalmers is best known for formulating the hard problem of consciousness, and for popularizing the philosophical zombie thought experiment. Chalmers and David Bourget co-founded PhilPapers; a database of journal articles for philosophers. Early life and education David Chalmers was born in Sydney, New South Wales, and subsequently grew up in Adelaide, South Australia, where he attended Unley High School. As a child, he experienced synesthesia. He began coding and playing computer games ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Benardete
José Amado Benardete (1928 - 2016) was an American philosopher and Emeritus Professor of Philosophy at Syracuse University. He was the son of Maír José Benardete and the brother of Seth Benardete and Diego Benardete, professor of mathematics at the University of Hartford. He is known for his works on metaphysics and infinity. Books * ''Greatness of Soul in Hume, Aristotle and Hobbes'' (Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2013) * ''Metaphysics: The Logical Approach'' (Oxford University Press, 1989) * Infinity: An Essay in Metaphysics' (Oxford University Press, 1964) References External linksPersonal Website 1928 births 2016 deaths American people of Turkish-Jewish descent American philosophy academics Jewish philosophers Syracuse University faculty University of Virginia alumni American metaphysicians 20th-century American philosophers Place of birth missing Place of death missing Date of birth missing Date of death missing {{US-philosopher-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minds And Machines
''Minds and Machines'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal covering artificial intelligence, philosophy, and cognitive science. The journal was established in 1991 with James Henry Fetzer as founding editor-in-chief. It was published by Kluwer Academic Publishers but was taken over by Springer in 2021 (Springer Science+Business Media). The journal affiliates with the Society for Machines and Mentality, a special interest group within the International Association for Computing and Philosophy. The current editor-in-chief is Mariarosaria Taddeo (University of Oxford). Editors Previous editors-in-chief of the journal have been James H. Fetzer (1991–2000), James H. Moor (2001–2010), and Gregory Wheeler (2011–2016). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed by the following services: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2016 impact factor of 0.514. Article categories The journal publishes articles in the categories Resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustavo E
Gustavo is the Latinate form of a Germanic male given name with respective prevalence in Portuguese, Spanish, and Italian. It is derived from Gustav /ˈɡʊstɑːv/, also spelled Gustaf, a Swedish name, likely from Slavic Gostislav. People with the name Drama, film and television * Gustavo Alatriste, Mexican actor, director, and producer of films, married to Silvia Pinal * Gustavo Aguerre (born 1953), Argentine artist, curator, writer, and theatre designer * Gustavo Sorola, American actor, podcast host, and co-founder of the American company, Rooster Teeth Engineering, religion and science * Gustavo Colonnetti (1886–1968), Italian mathematician and engineer * Gustavo Gutiérrez Merino (1928-2024), Peruvian theologian and Dominican priest regarded as the founder of Liberation Theology at the University of Notre Dame * Gustavo Tamayo, Colombian ophthalmologist * Gustavo Marín, Chilean-French economist and sociologist * Gustavo Scuseria (born 1956), Robert A. Welch Profe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Hole
A black hole is a massive, compact astronomical object so dense that its gravity prevents anything from escaping, even light. Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will form a black hole. The boundary (topology), boundary of no escape is called the event horizon. A black hole has a great effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, but has no locally detectable features according to general relativity. In many ways, a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light. Quantum field theory in curved spacetime predicts that event horizons emit Hawking radiation, with thermal radiation, the same spectrum as a black body of a temperature inversely proportional to its mass. This temperature is of the Orders of magnitude (temperature), order of billionths of a kelvin for stellar black holes, making it essentially impossible to observe directly. Objects whose gravitational fields are too strong for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Dilation
Time dilation is the difference in elapsed time as measured by two clocks, either because of a relative velocity between them (special relativity), or a difference in gravitational potential between their locations (general relativity). When unspecified, "time dilation" usually refers to the effect due to velocity. The dilation compares "wristwatch" clock readings between events measured in different inertial frames and is not observed by visual comparison of clocks across moving frames. These predictions of the theory of relativity have been repeatedly confirmed by experiment, and they are of practical concern, for instance in the operation of satellite navigation systems such as GPS and Galileo. Invisibility Time dilation is a relationship between clock readings. Visually observed clock readings involve delays due to the propagation speed of light from the clock to the observer. Thus there is no direct way to observe time dilation. As an example of time dilation, two expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Grünbaum
Adolf Grünbaum (; ; May 15, 1923 – November 15, 2018) was a German-American philosopher of science and a critic of both psychoanalysis and Karl Popper's philosophy of science. He was the first Andrew Mellon Professor of Philosophy at the University of Pittsburgh from 1960 until his death, and also served as co-chairman of its Center for Philosophy of Science (from 1978), research professor of psychiatry (from 1979), and primary research professor in the department of history and philosophy of science (from 2006). His works include '' Philosophical Problems of Space and Time'' (1963), '' The Foundations of Psychoanalysis'' (1984), and ''Validation in the Clinical Theory of Psychoanalysis'' (1993). Life and career Being Jewish, Adolf Grünbaum's family left Nazi Germany in 1938 and emigrated to the United States. Grünbaum received a B.A. with twofold High Distinction in philosophy and in mathematics from Wesleyan University, Middletown, Connecticut, in 1943. During the Seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |