|
Stephen, King Of England
Stephen (1092 or 1096 – 25 October 1154), often referred to as Stephen of Blois, was King of England from 22 December 1135 to his death in 1154. He was Count of Boulogne ''jure uxoris'' from 1125 until 1147 and Duke of Normandy from 1135 until 1144. His reign was marked by the Anarchy, a civil war with his cousin and rival, the Empress Matilda, whose son, Henry II, succeeded Stephen as the first of the Angevin kings of England. Stephen was born in the County of Blois in central France as the fourth son of Stephen-Henry, Count of Blois, and Adela, daughter of William the Conqueror. His father died as a crusader while Stephen was still young, and he was brought up by his mother. Placed into the court of his uncle Henry I of England, Stephen rose in prominence and was granted extensive lands. He married Matilda of Boulogne, inheriting additional estates in Kent and Boulogne that made the couple one of the wealthiest in England. Stephen narrowly escaped drowning with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthew Paris
Matthew Paris, also known as Matthew of Paris (; 1200 – 1259), was an English people, English Benedictine monk, English historians in the Middle Ages, chronicler, artist in illuminated manuscripts, and cartographer who was based at St Albans Cathedral, St Albans Abbey in Hertfordshire. He authored a number of historical works, many of which he scribed and illuminated himself, typically in drawings partly coloured with watercolour washes, sometimes called "tinted drawings". Some were written in Latin, others in Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman or Old French, French verse. He is sometimes confused with the nonexistent Matthew of Westminster. His is a renowned Medieval work, in many cases being a key source for mid-13th century Europe, partially due to his verbose insertion of personal opinions into his narrative and his use of sources such as records, letters, and conversations with witnesses to events including the English king Henry III of England, Henry III, earl Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
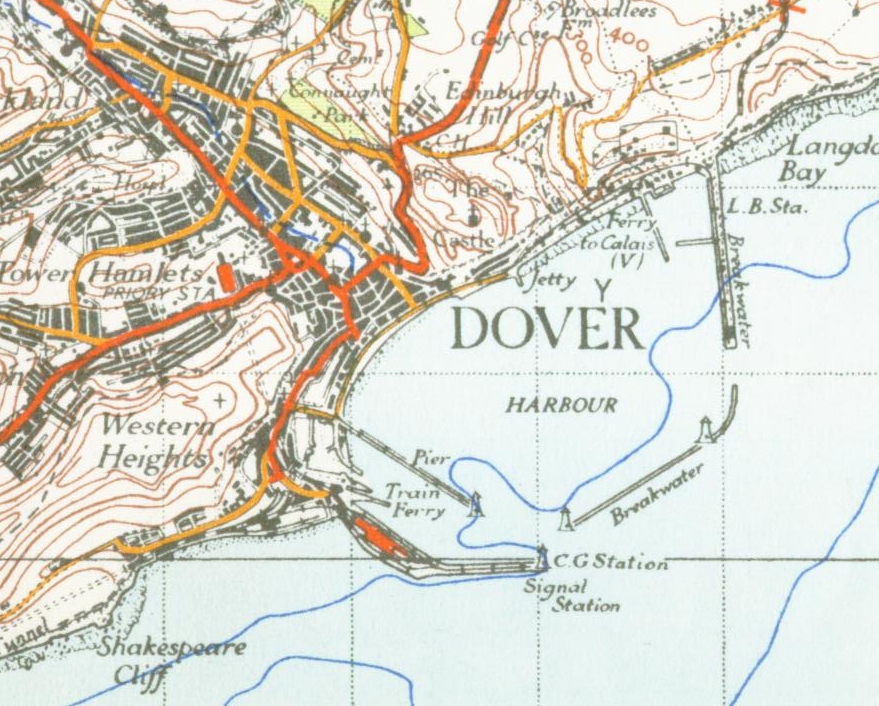
Dover
Dover ( ) is a town and major ferry port in Kent, southeast England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies southeast of Canterbury and east of Maidstone. The town is the administrative centre of the Dover District and home of the Port of Dover. Archaeological finds have revealed that the area has always been a focus for peoples entering and leaving Great Britain, Britain. The name derives from the River Dour that flows through it. In recent times the town has undergone transformations with a high-speed rail link to London, new retail in town with St James' area opened in 2018, and a revamped promenade and beachfront. This followed in 2019, with a new 500m Pier to the west of the Harbour, and new Marina unveiled as part of a £330m investment in the area. It has also been a point of destination for many English Channel migrant crossings (2018-present), illegal migrant crossings. The Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kent
Kent is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Essex across the Thames Estuary to the north, the Strait of Dover to the south-east, East Sussex to the south-west, Surrey to the west, and Greater London to the north-west. The county town is Maidstone. The county has an area of and had population of 1,875,893 in 2022, making it the Ceremonial counties of England#Lieutenancy areas since 1997, fifth most populous county in England. The north of the county contains a conurbation which includes the towns of Chatham, Kent, Chatham, Gillingham, Kent, Gillingham, and Rochester, Kent, Rochester. Other large towns are Maidstone and Ashford, Kent, Ashford, and the City of Canterbury, borough of Canterbury holds City status in the United Kingdom, city status. For local government purposes Kent consists of a non-metropolitan county, with twelve districts, and the unitary authority area of Medway. The county historically included south-ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matilda Of Boulogne
Matilda I of Boulogne ( – 3 May 1152) was Countess of Boulogne in her own right from 1125 and Queen of England from the accession of her husband, King Stephen, in 1135 until her death in 1152. She supported Stephen in his struggle for the English throne against their mutual cousin Empress Matilda. She played an unusually active role for a woman of the period when her husband was captured, and proved herself an effective general who managed to force the Empress to release Stephen. Under the agreement that settled the civil war, the Queen's children did not inherit the English throne but her three surviving children ruled Boulogne in turn as Eustace IV, William I, and Marie I. Background Matilda was born in Boulogne, France. Her father was Count Eustace III of Boulogne. Her mother, Mary, was the daughter of King Malcolm III of Scotland and Saint Margaret of Scotland. Through her maternal grandmother, Matilda was descended from the Anglo-Saxon kings of England. Coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William The Conqueror
William the Conqueror (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), sometimes called William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England (as William I), reigning from 1066 until his death. A descendant of Rollo, he was Duke of Normandy (as William II) from 1035 onward. By 1060, following a long struggle, his hold on Normandy was secure. In 1066, following the death of Edward the Confessor, William invaded England, leading a Franco-Norman army to victory over the Anglo-Saxon forces of Harold Godwinson at the Battle of Hastings, and suppressed subsequent English revolts in what has become known as the Norman Conquest. The rest of his life was marked by struggles to consolidate his hold over England and his continental lands, and by difficulties with his eldest son, Robert Curthose. William was the son of the unmarried Duke Robert I of Normandy and his mistress Herleva. His Legitimacy (family law), illegitimate status and youth caused some difficulties for h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen-Henry, Count Of Blois
Stephen Henry (in French, ''Étienne Henri'', in Old French, ''Estienne Henri''; – 19 May 1102) was the count of Blois and County of Chartres, Chartres. He led an army during the First Crusade, was at the siege of Nicaea, surrender of the city of Nicaea, and directed the siege of Antioch. Returning home without fulfilling his crusader vows, Stephen joined the crusade of 1101. Making his way to Jerusalem, he fought in the Second Battle of Ramla, where he was captured and later executed. Life Stephen was the son of Theobald III, count of Blois, and Gersent of Le Mans. He is first mentioned as approaching William the Conqueror to ask for and receive the hand of his daughter Adela of Normandy. In 1089, upon the death of his father, Stephen became the Count of Blois and Chartres, although Theobald had given him the administration of those holdings in 1074. Stephen was one of the leaders of the First Crusade, leading one of the major armies of the crusade and often writing ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France In The Middle Ages
The Kingdom of France in the Middle Ages (roughly, from the 10th century to the middle of the 15th century) was marked by the fragmentation of the Carolingian Empire and West Francia (843–987); the expansion of royal control by the House of Capet (987–1328), including their struggles with the virtually independent principalities (duchies and counties, such as the Normandy#Norman expansion, Norman and County of Anjou, Angevin regions), and the creation and extension of administrative/state control (notably under Philip II of France, Philip II Augustus and Louis IX of France, Louis IX) in the 13th century; and the rise of the House of Valois (1328–1589), including the protracted dynastic crisis against the House of Plantagenet and their Angevin Empire, culminating in the Hundred Years' War (1337–1453) (compounded by the catastrophic Black Death in 1348), which laid the seeds for a more centralized and expanded state in the Early modern France, early modern period and the cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
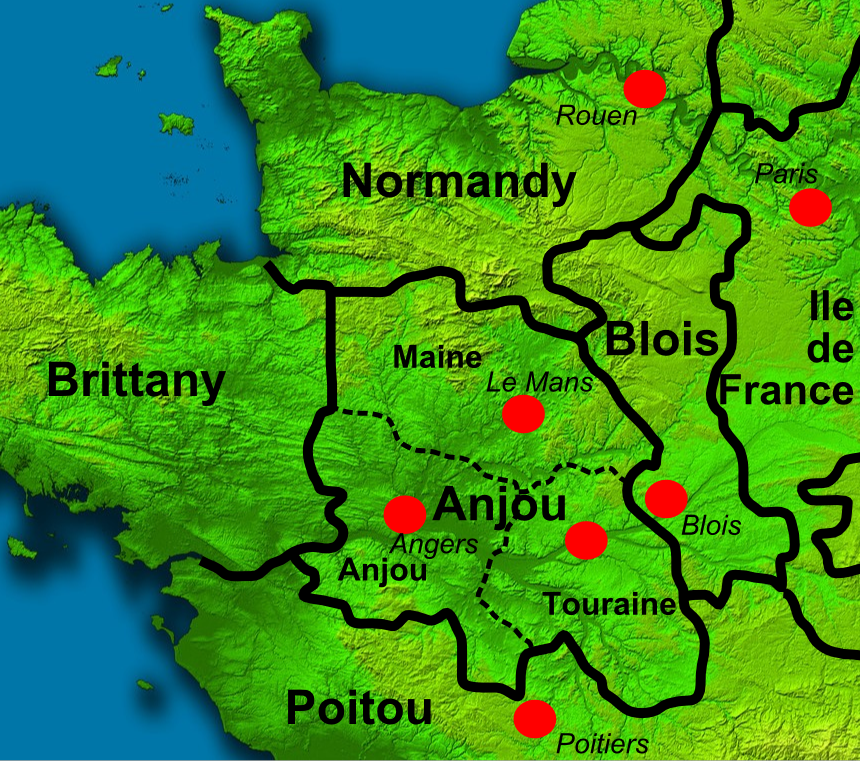
County Of Blois
The County of Blois was a feudal principality centred on Blois, south of Paris, France. It was created just after king Clovis I conquered Roman Gaul around AD 500. Between the 8th and the 13th centuries, it was amongst the most powerful vassal counties within the Kingdom of France, after having succeeded in surrounding the Capetian dynasty's lands of France since Blois annexed the Champagne. Since its creation up to 1498, the county was directed by counts, often with various more or less prestigious titles of nobility, or sometimes delegating their task to viscounts. The county existed until its definitive attachment to the Kingdom's lands in 1660, when Gaston, Duke of Orléans and last count of Blois, died. History Ancient times From the 1st to the 5th centuries, Bloisian depended on the Carnutes '' oppidum'' of ''Autrium'' (corresponding to current city of Chartres), in the Roman province of Gallia Lugdunensis Senonia. At that time, Blois was actually a little gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angevin Kings Of England
The Angevins (; "of/from Anjou") were a royal house of Anglo-French origin that ruled England and Ireland and in France in the 12th and early 13th centuries; its monarchs were Henry II, Richard I and John. Henry II won control of a vast assemblage of lands in western Europe that would last for 80 years and would retrospectively be referred to as the Angevin Empire. As a political entity this was structurally different from the preceding Norman and subsequent Plantagenet realms. Geoffrey of Anjou became Duke of Normandy in 1144 and died in 1151. In 1152, his heir, Henry, added Aquitaine by virtue of his marriage to Eleanor of Aquitaine. Henry also inherited the claim of his mother, Empress Matilda, the daughter of King Henry I of England and Matilda of Scotland (who was also the remaining descendant of the royal House of Wessex), to the English throne, to which Henry II succeeded in 1154 following the death of Matilda's cousin Stephen. In 1189, Henry was succeeded by h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Anarchy
The Anarchy was a civil war in England and Duchy of Normandy, Normandy between 1138 and 1153, which resulted in a widespread breakdown in law and order. The conflict was a war of succession precipitated by the accidental death of William Adelin (the only legitimate son of Henry I of England, Henry I), who drowned in the White Ship disaster, ''White Ship'' disaster of 1120. Henry sought to be succeeded by his daughter, known as Empress Matilda, but was only partially successful in convincing the nobility to support her. On Henry's death in 1135, his nephew Stephen of Blois seized the throne with the help of Stephen's brother Henry of Blois, who was the bishop of Winchester. He was crowned as Stephen, King of England, King Stephen, and his early reign saw fierce fighting with disloyal English barons, rebellious Welsh leaders, and Scottish invaders. Following a major rebellion in the southwest of England, Matilda invaded in 1139 with the help of her half-brother Robert, 1st Earl o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Normandy
In the Middle Ages, the duke of Normandy was the ruler of the Duchy of Normandy in north-western France. The duchy arose out of a grant of land to the Viking leader Rollo by the French king Charles the Simple in 911. In 924 and again in 933, Normandy was expanded by royal grant. Rollo's male-line descendants continued to rule it until 1135, and cognatic descendants ruled it until 1204. In 1202 the French king Philip II declared Normandy a forfeited fief and by 1204 his army had conquered it. It remained a French royal province thereafter, still called the Duchy of Normandy, but only occasionally granted to a duke of the royal house as an appanage. Despite both the 13th century loss of mainland Normandy, the renunciation of the title by Henry III of England in the Treaty of Paris (1259), and the extinction of the duchy itself in modern-day France, the monarch of the United Kingdom is regardless still often informally referred to by the title "Duke of Normandy." This is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jure Uxoris
''Jure uxoris'' (a Latin phrase meaning "by right of (his) wife"), citing . describes a title of nobility used by a man because his wife holds the office or title '' suo jure'' ("in her own right"). Similarly, the husband of an heiress could become the legal possessor of her lands. For example, married women in England and Wales were legally prohibited from owning real estate until the Married Women's Property Act 1882. Middle Ages During the feudal era, the husband's control over his wife's real property, including titles, was substantial. On marriage, the husband gained the right to possess his wife's land during the marriage, including any acquired after the marriage. Whilst he did not gain the formal legal title to the lands, he was able to spend the rents and profits of the land and sell his right, even if the wife protested. The concept of ''jure uxoris'' was standard in the Middle Ages even for queens regnant. In the Kingdom of Jerusalem, Fulk V of Anjou, Guy of Lusig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |