|
Solar And Heliospheric Observatory
The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) is a European Space Agency (ESA) spacecraft built by a European industrial consortium led by Matra Marconi Space (now Airbus Defence and Space) that was launched on a Lockheed Martin Atlas IIAS launch vehicle on 2 December 1995, to study the Sun. It has also discovered more than 5,000 comets. It began normal operations in May 1996. It is a joint project between the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA. SOHO was part of the International Solar Terrestrial Physics Program (ISTP). Originally planned as a two-year mission, SOHO continues to operate after 29 years in space; the mission has been extended until the end of 2025, subject to review and confirmation by ESA's Science Programme Committee. In addition to its scientific mission, it is a main source of near-real-time solar data for space weather prediction. Along with Aditya-L1, Wind, Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE), and Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR), SOHO is one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Observation
Solar observation is the scientific endeavor of studying the Sun and its behavior and relation to the Earth and the remainder of the Solar System. Deliberate solar observation began thousands of years ago. That initial era of direct observation gave way to telescopes in the 1600s followed by satellites in the twentieth century. Prehistory Stratigraphy, Stratigraphic data suggest that solar cycles have occurred for hundreds of millions of years, if not longer; measuring varves in precambrian sedimentary rock has revealed repeating peaks in layer thickness corresponding to the cycle. It is possible that the early atmosphere on Earth was more sensitive to solar irradiation than today, so that greater glacial melting (and thicker sediment deposits) could have occurred during years with greater sunspot activity. This would presume annual layering; however, alternative explanations (diurnal) have also been proposed. Analysis of tree rings revealed a detailed picture of past solar cycle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Angle And Spectrometric Coronagraph
The Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronagraph (LASCO) on board the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory satellite (SOHO) consists of three solar coronagraphs with nested fields of view: * C1 - a Fabry–Pérot interferometer coronagraph imaging from 1.1 to 3 solar radii, non-functional since the 24 June 1998 SOHO Mission Interruption * C2 - a white light coronagraph imaging from 1.5 to 6 solar radii (orange) * C3 - a white light coronagraph imaging from 3.7 to 30 solar radii (blue) The first principal investigator was Dr. Guenter Brueckner. These coronagraphs monitor the solar corona by using an optical system to create, in effect, an artificial solar eclipse. The white light coronagraphs C2 and C3 produce images of the corona over much of the visible spectrum, while the C1 interferometer produces images of the corona in a number of very narrow visible wavelength bands. Shutter speed LASCO C3, the clear coronagraph picture, has a shutter time of about 19 seconds. LASCO C2, the oran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Corona
In astronomy, a corona (: coronas or coronae) is the outermost layer of a star's Stellar atmosphere, atmosphere. It is a hot but relatively luminosity, dim region of Plasma (physics), plasma populated by intermittent coronal structures such as solar prominence, prominences, coronal loops, and helmet streamers. The Sun's corona lies above the chromosphere and extends millions of kilometres into outer space. Coronal light is typically obscured by diffuse sky radiation and Glare (vision), glare from the solar disk, but can be easily seen by the naked eye during a total solar eclipse or with a specialized coronagraph. Spectroscopic measurements indicate strong ionization in the corona and a plasma temperature in excess of , much hotter than the surface of the Sun, known as the photosphere. is, in turn, derived . History In 1724, French-Italian astronomer Giacomo F. Maraldi recognized that the aura visible during a solar eclipse belongs to the Sun, not to the Moon. In 1809, Span ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Transition Region
The solar transition region is a region of the Sun's atmosphere between the upper chromosphere and corona. It is important because it is the site of several unrelated but important transitions in the physics of the solar atmosphere: * Below, gravity tends to dominate the shape of most features, so that the Sun may often be described in terms of layers and horizontal features (like sunspots); above, dynamic forces dominate the shape of most features, so that the transition region itself is not a well-defined layer at a particular altitude. * Below, most of the helium is not fully ionized, so that it radiates energy very effectively; above, it becomes fully ionized. This has a profound effect on the equilibrium temperature (see below). * Below, the material is opaque to the particular colors associated with spectral lines, so that most spectral lines formed below the transition region are absorption lines in infrared, visible light, and near ultraviolet, while most lines formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosphere
A chromosphere ("sphere of color", from the Ancient Greek words χρῶμα (''khrôma'') 'color' and σφαῖρα (''sphaîra'') 'sphere') is the second layer of a Stellar atmosphere, star's atmosphere, located above the photosphere and below the solar transition region and Stellar corona, corona. The term usually refers to the Sun's chromosphere, but not exclusively, since it also refers to the corresponding layer of a stellar atmosphere. The name was suggested by the English astronomer Norman Lockyer after conducting systematic solar observations in order to distinguish the layer from the white-light emitting photosphere. In the solar atmosphere, Sun's atmosphere, the chromosphere is roughly in height, or slightly more than 1% of the Sun's radius at maximum thickness. It possesses a homogeneous layer at the boundary with the photosphere. Narrow jets of Plasma (physics), plasma, called Solar spicule, spicules, rise from this homogeneous region and through the chromosphere, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining Orientation (geometry), orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rotation (spin axis) is free to assume any orientation by itself. When rotating, the orientation of this axis is unaffected by tilting or rotation of the mounting, due to the angular momentum#Conservation of angular momentum, conservation of angular momentum. Gyroscopes based on other operating principles also exist, such as the microchip-packaged Vibrating structure gyroscope#MEMS gyroscopes, MEMS gyroscopes found in electronic devices (sometimes called gyrometers), solid-state ring laser gyroscope, ring lasers, fibre optic gyroscopes, and the extremely sensitive quantum gyroscope. Applications of gyroscopes include inertial navigation systems, such as in the Hubble Space Telescope, or inside the steel hull of a submer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
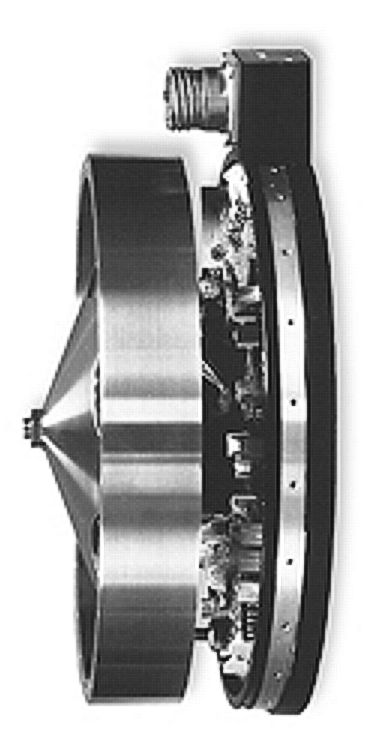
Reaction Wheel
A reaction wheel (RW) is an electric motor attached to a flywheel, which, when its rotation speed is changed, causes a counter-rotation proportionately through conservation of angular momentum. A reaction wheel can rotate only around its center of mass; it is not capable of moving from one place to another ( translational force). Reaction wheels are used primarily by spacecraft for three-axis attitude control, and do not require rockets or external applicators of torque, which reduces the mass fraction needed for fuel. They provide a high pointing accuracy, and are particularly useful when the spacecraft must be rotated by very small amounts, such as keeping a telescope pointed at a star. A reaction wheel is sometimes operated at a constant (or near-constant) rotation speed, to provide a satellite with a large amount of stored angular momentum. Doing so alters the spacecraft's rotational dynamics so that disturbance torques perpendicular to one axis of the satellite (the axis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au or AU) is a unit of length defined to be exactly equal to . Historically, the astronomical unit was conceived as the average Earth-Sun distance (the average of Earth's aphelion and perihelion), before its modern redefinition in 2012. The astronomical unit is used primarily for measuring distances within the Solar System or around other stars. It is also a fundamental component in the definition of another unit of astronomical length, the parsec. One au is approximately equivalent to 499 light-seconds. History of symbol usage A variety of unit symbols and abbreviations have been in use for the astronomical unit. In a 1976 resolution, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) had used the symbol ''A'' to denote a length equal to the astronomical unit. In the astronomical literature, the symbol AU is common. In 2006, the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) had recommended ua as the symbol for the unit, from the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
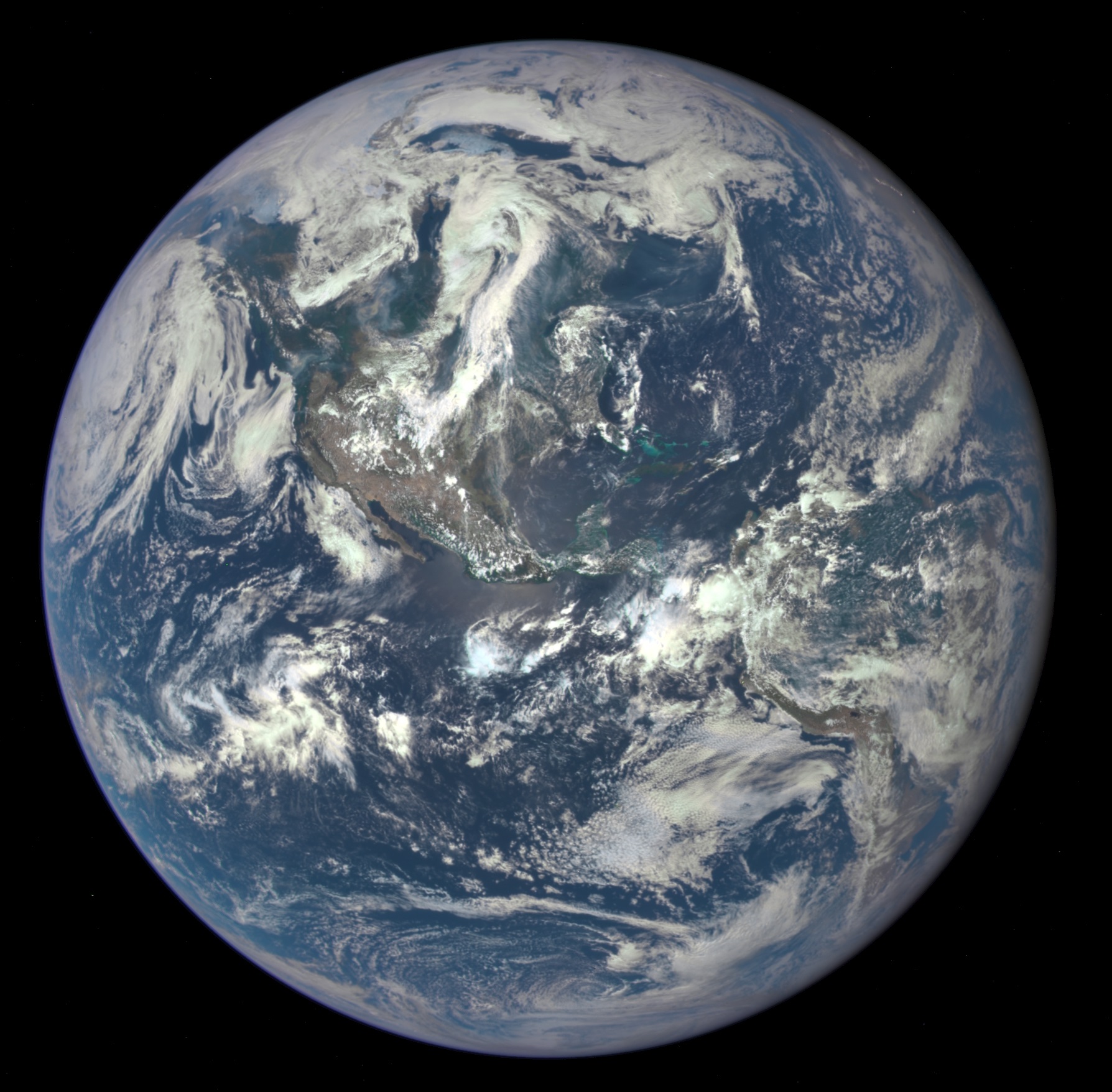
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Space Climate Observatory
Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR; formerly known as Triana, unofficially known as GoreSat) is a National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) space weather, space climate, and Earth observation satellite. It was launched by SpaceX on a Falcon 9 v1.1 launch vehicle on 11 February 2015, from Cape Canaveral. This is NOAA's first operational deep space satellite and became its primary system of warning Earth in the event of solar magnetic storms. DSCOVR was originally proposed as an Earth observation spacecraft positioned at the Sun-Earth Lagrange point, providing live video of the sunlit side of the planet through the Internet as well as scientific instruments to study climate change. Political changes in the United States resulted in the mission's cancellation, and in 2001 the spacecraft was placed into storage. Proponents of the mission continued to push for its reinstatement, and a change in presidential administration in 2009 resulted in DSCOVR being taken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Composition Explorer
Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE or Explorer 71) is a NASA Explorer program satellite and space exploration mission to study matter comprising energetic particles from the solar wind, the interplanetary medium, and other sources. Real-time data from ACE are used by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC) to improve forecasts and warnings of solar storms. The ACE robotic spacecraft was launched on 25 August 1997, and entered a Lissajous orbit close to the Lagrange point (which lies between the Sun and the Earth at a distance of some from the latter) on 12 December 1997. The spacecraft is currently operating at that orbit. Because ACE is in a non-Keplerian orbit, and has regular station-keeping maneuvers, the orbital parameters in the adjacent information box are only approximate. , the spacecraft is still in generally good condition. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center managed the development and integration of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |