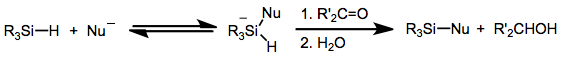|
Silanes
In organosilicon chemistry, silanes are a diverse class of charge-neutral organic compounds with the general formula . The R substituents can be any combination of organic or inorganic groups. Most silanes contain Si-C bonds, and are discussed under organosilicon compounds. Some contain Si-H bonds and are discussed under hydrosilanes. Examples *Silane , the parent. * Binary silicon-hydrogen compounds (which are sometimes called silanes also) includes silane itself but also compounds with Si-Si bonds including disilane and longer chains. *Silanes with one, two, three, or four Si-H bonds are called hydrosilanes. Silane is again the parent member. Examples: triethylsilane () and triethoxysilane (). * Polysilanes are organosilicon compounds with the formula . They feature Si-Si bonds. Attracting more interest are the organic derivatives such as polydimethylsilane . Dodecamethylcyclohexasilane is an oligomer of such materials. Formally speaking, polysilanes also include co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Silicon-hydrogen Compounds
Silanes are saturated chemical compounds with the empirical formula . They are hydrosilanes, a class of compounds that includes compounds with and other bonds. All contain tetrahedral silicon and terminal hydrides. They only have and single bonds. The bond lengths are 146.0 pm for a bond and 233 pm for a bond. The structures of the silanes are analogues of the alkanes, starting with silane, , the analogue of methane, continuing with disilane , the analogue of ethane, etc. They are mainly of theoretical or academic interest. Inventory 132px, cyclopentane.html" ;"title="Cyclopentasilane is structurally similar to cyclopentane">Cyclopentasilane is structurally similar to cyclopentane, just larger. The simplest isomer of a silane is the one in which the silicon atoms are arranged in a single chain with no branches. This isomer is sometimes called the ''n''-isomer (''n'' for "normal", although it is not necessarily the most common). However the chain of silicon atoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silane
Silane (Silicane) is an inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a colorless, pyrophoric gas with a sharp, repulsive, pungent smell, somewhat similar to that of acetic acid. Silane is of practical interest as a precursor to elemental silicon. Silanes with alkyl groups are effective water repellents for mineral surfaces such as concrete and masonry. Silanes with both organic and inorganic attachments are used as coupling agents. They are commonly used to apply coatings to surfaces or as an adhesion promoter. Production Commercial-scale routes Silane can be produced by several routes. Typically, it arises from the reaction of hydrogen chloride with magnesium silicide: : It is also prepared from metallurgical-grade silicon in a two-step process. First, silicon is treated with hydrogen chloride at about 300 °C to produce trichlorosilane, HSiCl3, along with hydrogen gas, according to the chemical equation : The trichlorosilane is then converted to a mixture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disilane
Disilane is a chemical compound with general chemical formula Si2R6 that was first identified in 1902 by Henri Moissan and Samuel Smiles (1877–1953) where R = H. Moissan and Smiles reported disilane as being among the products formed by the action of dilute acids on metal silicides. Although these reactions had been previously investigated by Friedrich Woehler and Heinrich Buff between 1857 and 1858, Moissan and Smiles were the first to explicitly identify disilane. They referred to disilane as ''silicoethane''. Higher members of the homologous series formed in these reactions were subsequently identified by Carl Somiesky (sometimes spelled "Karl Somieski") and Alfred Stock. At standard temperature and pressure, disilane is a colourless, acrid gas. Disilane and ethane have similar structures, although disilane is much more reactive. Other compounds of the general formula (X = hydrogen, halogen, alkyl, aryl, and mixtures of these groups) are called disilanes. Disilane is a group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silanes
In organosilicon chemistry, silanes are a diverse class of charge-neutral organic compounds with the general formula . The R substituents can be any combination of organic or inorganic groups. Most silanes contain Si-C bonds, and are discussed under organosilicon compounds. Some contain Si-H bonds and are discussed under hydrosilanes. Examples *Silane , the parent. * Binary silicon-hydrogen compounds (which are sometimes called silanes also) includes silane itself but also compounds with Si-Si bonds including disilane and longer chains. *Silanes with one, two, three, or four Si-H bonds are called hydrosilanes. Silane is again the parent member. Examples: triethylsilane () and triethoxysilane (). * Polysilanes are organosilicon compounds with the formula . They feature Si-Si bonds. Attracting more interest are the organic derivatives such as polydimethylsilane . Dodecamethylcyclohexasilane is an oligomer of such materials. Formally speaking, polysilanes also include co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrosilanes
Hydrosilanes are tetravalent silicon compounds containing one or more Si-H bond. The parent hydrosilane is silane (SiH4). Commonly, hydrosilane refers to organosilicon derivatives. Examples include phenylsilane (PhSiH3) and triethoxysilane ((C2H5O)3SiH). Polymers and oligomers terminated with hydrosilanes are resins that are used to make useful materials like caulks. Synthesis Trichlorosilane is produced commercially by the reaction of hydrogen chloride with silicon: :Si + 3 HCl → HSiCl3 + H2 Many alkoxy hydrosilanes are generated by alcoholysis of trichlorosilane. One example is triethoxysilane: :HSiCl3 + 3EtOH → HSi(OEt)3 + 3 HCl Organohydrosilanes can be prepared by partial hydrosilation of silane itself: :SiH4 + 3 C2H4 → HSi(C2H5)3 In the laboratory, hydrosilanes classically are prepared by treating chlorosilanes with hydride reagents, such as lithium aluminium hydride: :4ClSi(C2H5)3 + LiAlH4 → 4HSi(C2H5)3 + LiAlCl4 Structure The silicon-to-hydrogen bond is longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysilanes
Polysilanes are organosilicon compounds with the formula (R2Si)n. They are relatives of traditional organic polymers but their backbones are composed of silicon atoms. They exhibit distinctive optical and electrical properties. They are mainly used as precursors to silicon carbide. The simplest polysilane would be (SiH2)n, which is mainly of theoretical, not practical interest. Synthesis left, Dodecamethylcyclohexasilane shares some properties of high molecular weight polysilanes. The first polysilane, poly(dimethylsilylene), CH3)2Sisub>''x'', was reported in 1949 by Charles A. Burkhard (1916 - 1991) of General Electric. It was prepared by heating sodium metal with dimethyldichlorosilane: :(CH3)2SiCl2 + 2 Na → CH3)2Sisub>n + 2 NaCl The modified Wurtz coupling of dichlorosilanes remains a viable and general route to high molecular weight, linear polysilane derivatives. This reaction is conducted at elevated temperature in an inert solvent using a dispersion of the alkali me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silane Quats
Silane-Quats are a class of antimicrobials developed by Dow Corning and first patented in the United States of America in February 1971 (U.S. Patent Number 3560385). Subsequent patents were filed in the 1970s by Dow Corning for utilizing its silane-quat as an effective antimicrobial. In doing so, Dow Corning had invented a durable, non-leaching, persistent, surface bonding antimicrobial effective against a wide range of unicellular microorganisms on a variety of surfaces. There are at least four private companies in the United States that are the primary manufacturers of Silane-Quats, which are widely known by various names such as Quat-Silane, SiQuats, Si-Qacs, Organosilane and Sil-Quats. Synthesis is typically conducted in a methanol, however, there are water-synthesized formulations which range in stability depending on the dilution process and/or the presence of stabilizers and additives. Chemical composition Current manufacturing methods produce concentrated Silane-Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodecamethylcyclohexasilane
Dodecamethylcyclohexasilane is the organosilicon compound with the formula . It is one of the more readily prepared and easily handled polysilanes. Dodecamethylcyclohexasilane is produced by reduction of dimethyldichlorosilane with sodium-potassium alloy: : where M is Na or K. The reaction also produces a polymer poly(dimethylsilylene) and a cyclic compound decamethylcyclopentasilane . The chair conformer of dodecamethylcyclohexasilane was confirmed by X-ray crystallography X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring th .... Reactions Dodecamethylcyclohexasilane reacts with potassium ''tert''-butoxide to give the potassium derivative: :{{chem2, (CH3)12Si6 + KOC(CH3)3 → K(CH3)11Si6 + CH3OC(CH3)3 References Carbosilanes Silanes Six-membered rings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Process
The direct process, also called the direct synthesis, Rochow process, and Müller-Rochow process is the most common technology for preparing organosilicon compounds on an industrial scale. It was first reported independently by Eugene G. Rochow and Richard Müller in the 1940s.. The process involves copper-catalyzed reactions of alkyl halides with elemental silicon, which take place in a fluidized bed reactor. Although theoretically possible with any alkyl halide, the best results in terms of selectivity and yield occur with chloromethane (CH3Cl). Typical conditions are 300°C and 2–5bar. These conditions allow for 90–98% conversion for silicon and 30–90% for chloromethane. Approximately 1.4 Mton of dimethyldichlorosilane (Me2SiCl2) is produced annually using this process.Elschenbroich, Christoph Organometallics VCH, Weinheim, Germany: 1992. . Few companies actually carry out the Rochow process, because of the complex technology and high capital requirements. Since the silic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-linked Polyethylene
Cross-linked polyethylene, commonly abbreviated PEX, XPE or XLPE, is a form of polyethylene with cross-links. It is used predominantly in building services pipework systems, hydronic radiant heating and cooling systems, domestic water piping, insulation for high tension (high voltage) electrical cables, and baby play mats. It is also used for natural gas and offshore oil applications, chemical transportation, and transportation of sewage and slurries. PEX is an alternative to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC) or copper tubing for use as residential water pipes. Properties Low-temperature impact strength, abrasion resistance and environmental stress cracking resistance can be increased significantly by crosslinking, whereas hardness and rigidity are somewhat reduced. Compared to thermoplastic polyethylene, PEX does not melt (analogous to elastomers) and is thermally resistant (over longer periods of up to 120 °C, for short periods without ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexamethyldisiloxane
Hexamethyldisiloxane (HMDSO or MM) is an organosilicon compound with the formula O[Si(CH3)3]2. This volatile colourless liquid is used as a solvent and as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the hydrolysis of trimethylsilyl chloride. The molecule is the protypical disiloxane and resembles a subunit of polydimethylsiloxane. Synthesis and reactions Hexamethyldisiloxane can be produced by the addition of trimethylsilyl chloride to purified water: : 2 Me3SiCl + H2O → 2 HCl + O[Si(CH3)3]2 It also results from the hydrolysis of silyl ethers and other silyl-protected functional groups. HMDSO can be converted back to the chloride by reaction with Me2SiCl2.Röshe, L.; John, P.; Reitmeier, R. “Organic Silicon Compounds” ''Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry''. John Wiley and Sons: San Francisco, 2003. . Hexamethyldisiloxane is mainly used as source of the trimethylsilyl functional group (-Si(CH3)3) in organic synthesis. For example, in the presence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |