|
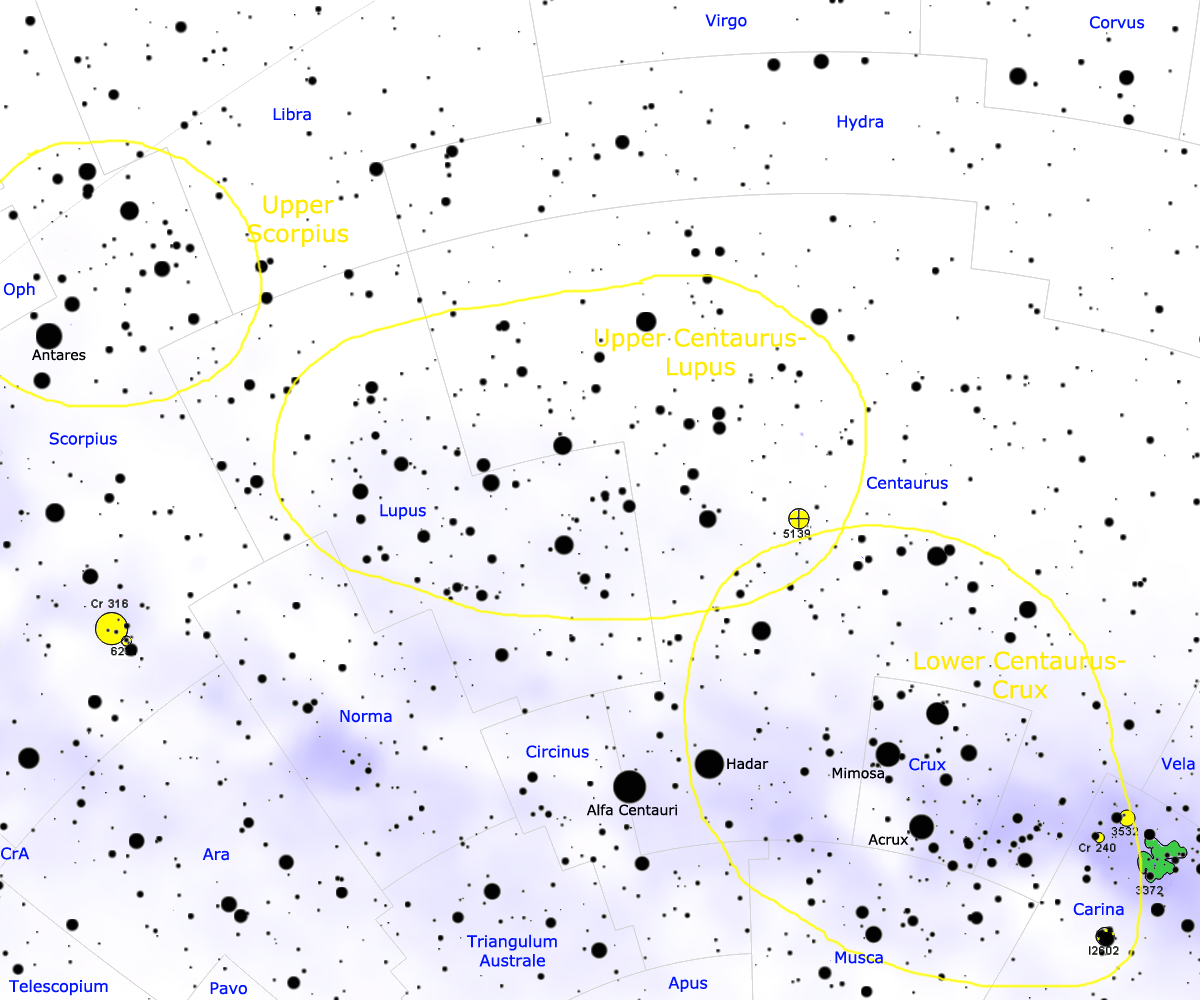
Scorpius–Centaurus Association
The Scorpius–Centaurus association (sometimes called Sco–Cen or Sco OB2) is the nearest OB association to the Sun. This stellar association is composed of three subgroups (Upper Scorpius, Upper Centaurus–Lupus, and Lower Centaurus–Crux) and its distance is about 130 parsecs or 420 light-years. Analysis using improved Hipparcos data has brought the number of known members to 436. The cluster shows a continuous spread of stars with no apparent need for subclassification. The Sco–Cen subgroups range in age from 11 million years (Upper Scorpius) to roughly 15 million years (Upper Centaurus–Lupus and Lower Centaurus–Crux). Many of the bright stars in the constellations Scorpius, Lupus, Centaurus, and Crux are members of the Sco–Cen association, including Antares (the most massive member of Upper Scorpius), and most of the stars in the Southern Cross. Hundreds of stars have been identified as members of Sco-Cen, with masses ranging from roughly 15 solar masses (Antares ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Dwarfs
Brown dwarfs are substellar objects that have more mass than the biggest gas giant planets, but less than the least massive main-sequence stars. Their mass is approximately 13 to 80 times that of Jupiter ()not big enough to sustain nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in their cores, but massive enough to emit some light and heat from the fusion of deuterium ( 2H). The most massive ones (> ) can fuse lithium ( 7Li). Astronomers classify self-luminous objects by spectral type, a distinction intimately tied to the surface temperature, and brown dwarfs occupy types M (2100–3500 K), L (1300–2100 K), T (600–1300 K), and Y (< 600 K). As brown dwarfs do not undergo stable hydrogen fusion, they cool down over time, progressively passing through later spectral types as they age. Their name comes not from the color of light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcseconds
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth's circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (abbreviated as arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a minute of arc, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal (base 60) subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcsec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proper Motions
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects as they move relative to the center of mass of the Solar System. It is measured relative to the distant stars or a stable reference such as the International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF). Patterns in proper motion reveal larger structures like stellar streams, the general rotation of the Milky Way disk, and the random motions of stars in the Galactic halo. The components for proper motion in the equatorial coordinate system (of a given epoch, often J2000.0) are given in the direction of right ascension (''μ''α) and of declination (''μ''δ). Their combined value is computed as the ''total proper motion'' (''μ''). It has dimensions of angle per time, typically arcseconds per year or milliarcseconds per year. Knowledge of the proper motion, distance, and radial velocity allows calculations of an object's motion from the Solar System's frame of reference and its m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IC 2602
IC 2602 (also known as the Southern Pleiades, Theta Carinae Cluster, or Caldwell 102) is an open cluster in the constellation Carina (constellation), Carina. Discovered by Abbe Lacaille in 1751 from South Africa, the cluster is easily visible to the Naked eye, unaided eye, and is one of the nearest star clusters, centred about 149 parsecs (486 Light-year, light-years) away from Earth. Description IC 2602 has a total apparent magnitude of 1.9, and contains about 75 stars. It is the third-brightest open cluster in the sky, following the Hyades (star cluster), Hyades and the Pleiades. Its apparent diameter is about 50 arcminutes. IC 2602 is likely about the same age as the open cluster IC 2391,, which has a lithium depletion boundary age of 50 million years old, though the age estimated from its Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is about 13.7 million years. IC 2602 is thought to form part of the Lower Scorpius–Centaurus association. Components Θ Carinae, Theta Carinae is the brighte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Pictoris Moving Group
The Beta Pictoris moving group is a young moving group of stars located relatively near Earth. A moving group, in astronomy, is a group of stars that share a common motion through space as well as a common origin. This moving group is named for Beta Pictoris, a A-type main-sequence star, A-type main sequence star with a debris disk. The Beta Pictoris moving group is an important object for astronomical study as it is the closest youthful group of stars to the Earth. The star Beta Pictoris is known to have a large disk of gas and dust, possibly a protoplanetary disk. There is also evidence of a young gas giant planet around the star. A free-floating planet has also been found in the moving group, PSO J318.5-22. It has recently been estimated, , that more than a third of the single Sun-like stars in the group have planets with more than four times the mass of Jupiter, and virtually all of the single Sun-like stars, 99%, possess at least one gas giant in orbit around them. The age and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TW Hydrae Association
The TW Hydrae association is a group of very young low-mass stars and substellar objects located approximately 25–75 parsecs (80–240 light years) from Earth. They share a common motion and appear to all be roughly the same age, 10±3 million years old. It is the youngest such association within 100 pc from Earth. As of 2017, 42 objects (in 23 systemsSingular objects are also regarded as "systems" here.) are assigned to the association confidently, and several dozens — uncertainly. Masses of its known members vary from 5 Jupiter masses to 2 solar masses, and their spectral types vary from A0 to L7. Some of the best studied members of this stellar association are TW Hydrae (nearest known accreting T Tauri star to the Earth), HR 4796 (an A-type star with resolved dusty debris disk; the most massive known group member), HD 98800 (a quadruple star system with debris disk), and 2M1207 (accreting brown dwarf with remarkable planetary-mass companion 2M1207b). Included in the assoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eta Chamaeleontis Moving Group
Eta Chamaeleontis, Latinized from η Chamaeleontis, is a star in the constellation Chamaeleon. It has an apparent magnitude of about 5.5, meaning that it is just barely visible to the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements, this star is located some light years (95 parsecs) away from the Sun. Eta Chamaeleontis has a spectral type of B8V, meaning it is a B-type main sequence star. Stars of this type are typically a few times more massive than the Sun and have effective temperatures of about 10,000 to 30,000 K. Eta Chamaeleontis is just over 3 times more massive than the Sun and has a temperature of about 12,000 K. Eta Chamaeleontis cluster Eta Chamaeleontis is the brightest and most massive member of the eponymous Eta Chamaeleontis cluster (also known as the Eta Chamaeleontis association or Mamajek 1, pronounced ), a very nearby (316 light years), and young (8 million years old) stellar moving group discovered in 1999. The cluster contains nearly 20 stellar membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Chamaeleontis Group
Epsilon Chamaeleontis, Latinized from ε Chamaeleontis, is a triple star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Chamaeleon. The primary and secondary have apparent magnitudes of 5.33 and 6.02, making them visible to the naked eye. Hipparcos parallax measurements place the system at a distance of 360 light years and is currently receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of . The primary has a stellar classification of B9 Vn:, indicating that it is a B-type main-sequence star with broad/nebulous absorption lines due to rapid rotation. However, there is uncertainty behind the suffix. It has 2.9 times the mass of the Sun and 2.3 times its solar radius. It radiates a bolometric luminosity 100 times that of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of , giving it a bluish-white hue. It is a relatively young star with an age of only 3 million years. Like many hot stars it spins rapidly, having a projected rotational velocity of . Epsilon Chamaeleont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coalsack
The Coalsack Nebula (Southern Coalsack, or simply ''the'' Coalsack) is a dark nebula, which is visible to the naked eye as a dark patch obscuring part of the Milky Way east of Acrux (Alpha Crucis) in the constellation of Crux. General information Historically any other dark cloud in the night sky was called coalsack. The Coalsack Nebula was juxtaposed in 1899 by Richard Hinckley Allen through naming the Northern Coalsack Nebula. The Coalsack Nebula covers nearly 7 ° by 5° and extends into the neighboring constellations Centaurus and Musca. The first observation was reported by Vicente Yáñez Pinzón in 1499. It was named "''il Canopo fosco''" (the dark Canopus) by Amerigo Vespucci and was also called "''Macula Magellani''" (Magellan's Spot) or "''Black Magellanic Cloud''" in opposition to the Magellanic Clouds. In Australian Aboriginal astronomy, the Coalsack forms the head of the '' emu in the sky'' in several Aboriginal cultures. Amongst the Wardaman people, it is said ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corona Australis
Corona Australis is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means "southern crown", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax. Although fainter than its northern counterpart, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamaeleon
Chamaeleon () is a small constellation in the deep southern sky. It is named after the chameleon, a kind of lizard. It was first defined in the 16th century. History Chamaeleon was one of twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. It first appeared on a 35-cm diameter celestial globe published in 1597 (or 1598) in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius. Johann Bayer was the first uranographer to put Chamaeleon in a celestial atlas. It was one of many constellations created by European explorers in the 15th and 16th centuries out of unfamiliar Southern Hemisphere stars. Features Stars There are four bright stars in Chamaeleon that form a compact diamond-shape approximately 10 degrees from the south celestial pole and about 15 degrees south of Acrux, along the axis formed by Acrux and Gamma Crucis. Alpha Chamaeleontis is a white-hued star of magnitude 4.1, 63 light-years from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |