|
Science And Technology In Chile
Science and Technology in Chile is led by the National Commission of Scientific and Technological Investigation. History The study of physics in Chile traces to the chairs of experimental physics funded by Juan Martínez de Rozas between 1781 and 1783 in the Convictorio Carolino. When the Chilean Instituto Nacional General José Miguel Carrera, National Institute began teaching on 10 August 1813, one of the institute's eighteen chairs was for experimental physics. This was dictated by presbyter José Alejo Bezanilla and taught as part of the course of Natural Sciences. After the Battle of Rancagua, Disaster of Rancagua, General Mariano Osorio assumed control of the country, abolishing the republican initiatives decreed by José Miguel Carrera and Bernardo O'Higgins, and restoring the colony's governmental, administrative and judicial institutions. These initiatives affected the National Institute. One of the first scientists who spoke on the development of science in Chile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pablo DT Valenzuela
Pablo Valenzuela (; born June 13, 1941) is a Chilean biochemist dedicated to biotechnology development. He is known for his genetic studies of hepatitis viruses; participated as a research and development director in the discovery of hepatitis C virus and the invention of the world's first recombinant vaccine (against hepatitis B virus). He is one of the cofounders of the biotechnology company Chiron Corporation and of Fundacion Ciencia para la Vida, a private non profit institution where he is currently working. Biography Pablo Valenzuela studied biochemistry at Universidad de Chile and earned his Ph.D. degree (1970) in chemistry at Northwestern University. He completed postdoctoral training at the University of California, San Francisco and held a position as professor in the biochemistry department there. In 1981, he, with William J. Rutter and Edward Penhoet, founded the biotechnology company Chiron Corporation, that in 1997 was the second-largest biotechnology company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centro De Estudios Científicos
Centro de Estudios Científicos (CECs; Center for Scientific Studies) is a private, non-profit corporation based in Valdivia, Chile, devoted to the development, promotion and diffusion of scientific research. History CECs research areas include biophysics, molecular physiology, theoretical physics, glaciology and climate change. The centre was created in 1984 as Centro de Estudios Científicos de Santiago, with a grant of 150,000 dollars a year (for three years) from the Tinker Foundation of New York City. In 2004-2005 glaciologists from CECs organized the Chilean South Pole Expedition in collaboration with the Chilean Navy and Instituto Antártico Chileno. CECs was founded in Santiago but is since 2000 housed in the recently modernized, German-style Hotel Schuster located by Valdivia River. Claudio Bunster, a physicist and winner of Chile's National Prize for Exact Sciences, is the director of CECs. In 2014 CECs discovered what would be a subglacial lake in the W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Science, Technology, Knowledge And Innovation
The Ministry of Science, Technology, Knowledge and Innovation () is the Ministry of State of Chile in charge of structuring, promoting, coordinating and promoting science, humanities and Research and development, technological development activities in all their stages, to contribute to the sustainable development and social welfare of the country. It was created as a replacement for the CONICYT, National Commission for Scientific and Technological Research, which was in charge of the Ministry of Education (Chile), Ministry of Education. The current minister of the ministry is Silvia Díaz, who was appointed by Gabriel Boric on September 6, 2022. It was created during the second government of President Sebastián Piñera promulgated on 27 July 2018, and published in the Diario Oficial de la República de Chile, Official Journal on 13 August of the same year. According to the norm, the President of the Republic had one year to set the date on which the ministry began to operate and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Intellectual Property Organization
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO; (OMPI)) is one of the 15 specialized agencies of the United Nations (UN). Pursuant to the 1967 Convention Establishing the World Intellectual Property Organization, WIPO was created to promote and protect intellectual property (IP) across the world by cooperating with countries as well as international organizations. It began operations on 26 April 1970 when the convention entered into force. The current Director General is Singaporean Daren Tang, former head of the Intellectual Property Office of Singapore, who began his term on 1 October 2020. WIPO's activities include: hosting forums to discuss and shape international IP rules and policies, providing global services that register and protect IP in different countries, resolving transboundary IP disputes, helping connect IP systems through uniform standards and infrastructure, and serving as a general reference database on all IP matters; this includes providing report ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
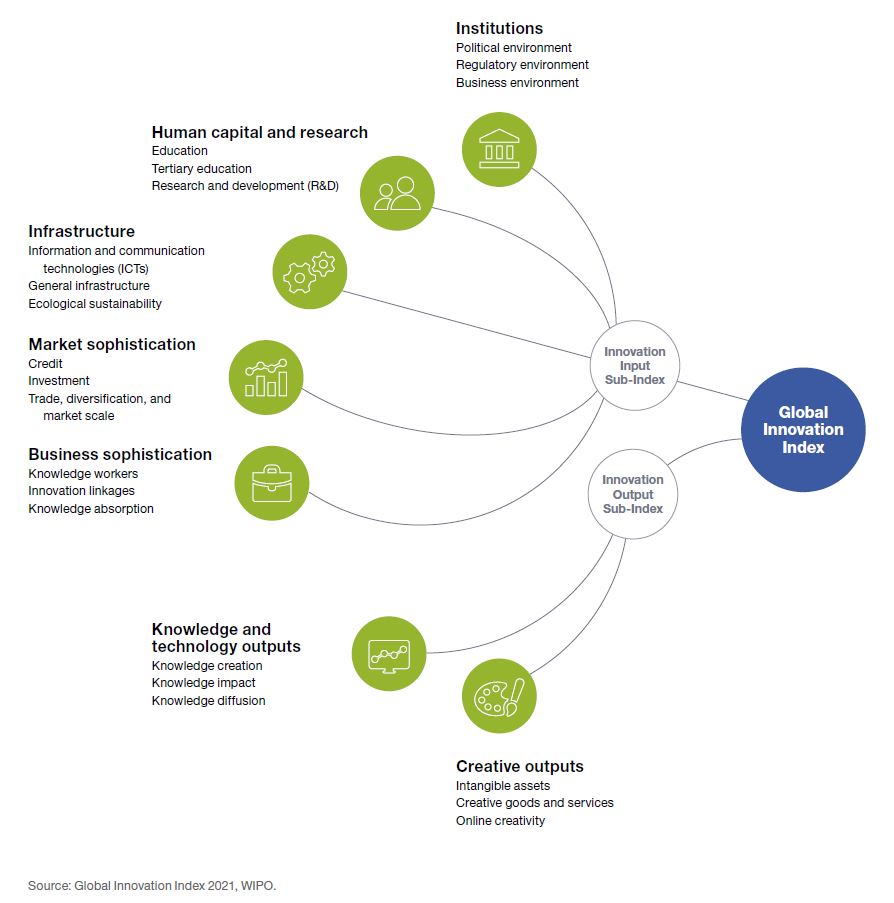
Global Innovation Index
The Global Innovation Index is an annual ranking of countries by their capacity for and success in innovation, published by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO). It was started in 2007 by INSEAD and ''World Business'', a British magazine. Until 2021, it was published by WIPO in partnership with Cornell University, INSEAD, and other organisations and institutions. It is based on both subjective and objective data derived from several sources, including the International Telecommunication Union, the World Bank, and the World Economic Forum. History The Global Innovation Index was started in 2007 by INSEAD and ''World Business'', a British magazine. It was created by Soumitra Dutta. Methodology The Global Innovation Index is computed by taking a simple average of the scores in two sub-indices (the Innovation Input Index and Innovation Output Index), which are composed of respectively five and two pillars. Each of those pillars describes an attribute of innova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HIV/AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, preventable disease. It can be managed with treatment and become a manageable chronic health condition. While there is no cure or vaccine for HIV, Management of HIV/AIDS, antiretroviral treatment can slow the course of the disease, and if used before significant disease progression, can extend the life expectancy of someone living with HIV to a nearly standard level. An HIV-positive person on treatment can expect to live a normal life, and die with the virus, not of it. Effective #Treatment, treatment for HIV-positive people (people living with HIV) involves a life-long regimen of medicine to suppress the virus, making the viral load undetectable. Treatment is recommended as soon as the diagnosis is made. An HIV-positive person who has an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Some yeast species have the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae, or quickly evolve into a Multicellular organism, multicellular cluster with specialised Organelle, cell organelles function. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 micrometre, μm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 μm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexual reproduction, asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding. With their single-celled growth habit, yeasts can be contrasted with Mold (fungus), molds, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into cells of the liver, fat cell, fat, and skeletal muscles. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen, via glycogenesis, or Fatty acid metabolism#Glycolytic end products are used in the conversion of carbohydrates into fatty acids, fats (triglycerides), via lipogenesis; in the liver, glucose is converted into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver are strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is thus an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
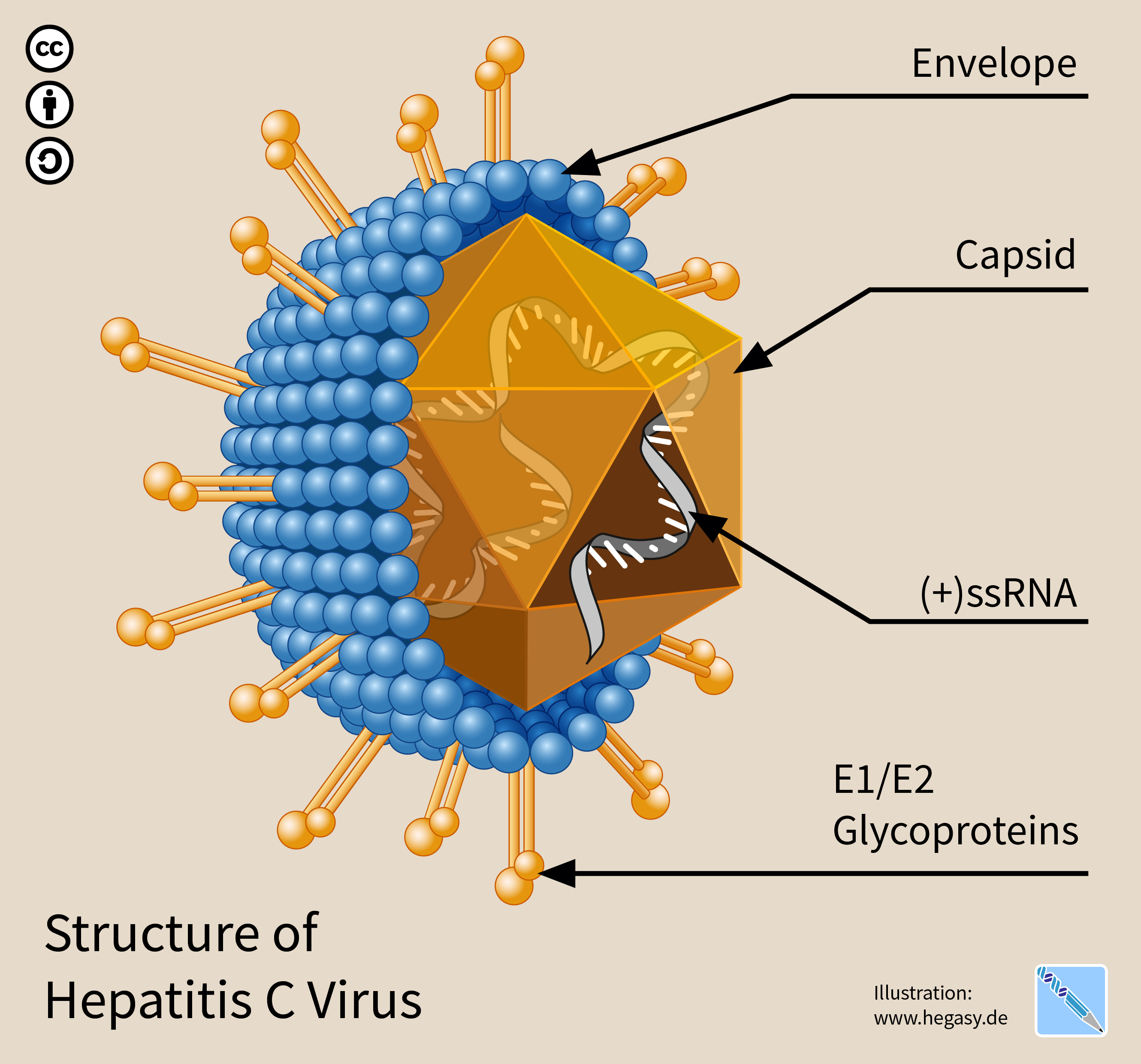
Hepatitis C Virus
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer ( hepatocellular carcinoma, abbreviated HCC) and lymphomas in humans. Taxonomy The hepatitis C virus belongs to the genus '' Hepacivirus'', a member of the family ''Flaviviridae''. Before 2011, it was considered to be the only member of this genus. However a member of this genus has been discovered in dogs: canine hepacivirus. There is also at least one virus in this genus that infects horses. Several additional viruses in the genus have been described in bats and rodents. Structure The hepatitis C virus particle consists of a lipid membrane envelope that is 55 to 65 nm in diameter. Two viral envelope glycoproteins, E1 and E2, are embedded in the lipid envelope. They take part in viral attachment and entry into the cell. Within the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, a species of the genus '' Orthohepadnavirus'' and a member of the '' Hepadnaviridae'' family of viruses. This virus causes the disease hepatitis B. Classification Hepatitis B virus is classified in the genus '' Orthohepadnavirus'', which contains 11 other species. The genus is classified as part of the '' Hepadnaviridae'' family, which contains four other genera, '' Avihepadnavirus'', '' Herpetohepadnavirus'', '' Metahepadnavirus'' and '' Parahepadnavirus''. This family of viruses is the only member of the viral order ''Blubervirales''. Viruses similar to hepatitis B have been found in all apes (orangutans, gibbons, bonobos, gorillas and chimpanzees), in Old World monkeys, and in New World woolly monkeys (the woolly monkey hepatitis B virus), suggesting an ancient origin for this virus in primates. The virus is divided into four major serotypes (adr, adw, ayr, ayw) based on antigenic epitopes present on it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is a multidisciplinary field that involves the integration of natural sciences and Engineering Science, engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms and parts thereof for products and services. Specialists in the field are known as biotechnologists. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used by Károly Ereky in 1919 to refer to the production of products from raw materials with the aid of living organisms. The core principle of biotechnology involves harnessing biological systems and organisms, such as bacteria, yeast, and plants, to perform specific tasks or produce valuable substances. Biotechnology had a significant impact on many areas of society, from medicine to agriculture to environmental science. One of the key techniques used in biotechnology is genetic engineering, which allows scientists to modify the genetic makeup of organisms to achieve desired outcomes. This can involve inserting genes from one organism into another, and con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |