|
Quantum Dots
Quantum dots (QDs) or semiconductor nanocrystals are semiconductor particles a few nanometres in size with optical and electronic properties that differ from those of larger particles via quantum mechanical effects. They are a central topic in nanotechnology and materials science. When a quantum dot is illuminated by UV light, an electron in the quantum dot can be excited to a state of higher energy. In the case of a semiconducting quantum dot, this process corresponds to the transition of an electron from the valence band to the conduction band. The excited electron can drop back into the valence band releasing its energy as light. This light emission ( photoluminescence) is illustrated in the figure on the right. The color of that light depends on the energy difference between the discrete energy levels of the quantum dot in the conduction band and the valence band. In other words, a quantum dot can be defined as a structure on a semiconductor which is capable of confi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QD S , a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship
* The EU Qualificat ...
QD may refer to: Businesses and organizations * QD (retailer), a chain of discount retail outlets in England * Dobrolet (airline) (IATA airline designator QD), a Russian low-cost carrier * JC International Airlines (IATA airline designator QD), a Cambodian airline Science and technology * Quantum dots, in nanotechnology * N-Gage QD, a handheld game console and smartphone * ''Dermatologicals'', a veterinary ATC code D * Queue depth, a measure of concurrency in SSD benchmarking; see IOPS * Quick Disk, a type of miniature floppy disk used primarily in the 1980s Other uses * '' Quaque die'', "every day" in Latin; mainly pharmaceutical usage * Quarterdeck The quarterdeck is a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship. Traditionally it was where the captain commanded his vessel and where the ship's colours were kept. This led to its use as the main ceremonial and reception area on bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle In A Box
In quantum mechanics, the particle in a box model (also known as the infinite potential well or the infinite square well) describes the movement of a free particle in a small space surrounded by impenetrable barriers. The model is mainly used as a hypothetical example to illustrate the differences between classical and quantum systems. In classical systems, for example, a particle trapped inside a large box can move at any speed within the box and it is no more likely to be found at one position than another. However, when the well becomes very narrow (on the scale of a few nanometers), quantum effects become important. The particle may only occupy certain positive energy levels. Likewise, it can never have zero energy, meaning that the particle can never "sit still". Additionally, it is more likely to be found at certain positions than at others, depending on its energy level. The particle may never be detected at certain positions, known as spatial nodes. The particle in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-emitting Diodes
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in Remote control, remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small Incandescent light bulb, incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. Later developments produced LEDs ava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Dot Solar Cell
A quantum dot solar cell (QDSC) is a solar cell design that uses quantum dots as the captivating photovoltaic material. It attempts to replace bulk materials such as silicon, copper indium gallium selenide ( CIGS) or cadmium telluride ( CdTe). Quantum dots have bandgaps that are adjustable across a wide range of energy levels by changing their size. In bulk materials, the bandgap is fixed by the choice of material(s). This property makes quantum dots attractive for multi-junction solar cells, where a variety of materials are used to improve efficiency by harvesting multiple portions of the solar spectrum. As of 2022, efficiency exceeds 18.1%. Quantum dot solar cells have the potential to increase the maximum attainable thermodynamic conversion efficiency of solar photon conversion up to about 66% by utilizing hot photogenerated carriers to produce higher photovoltages or higher photocurrents. Typical quantum dots solar cells consist of a glass substrate followed by a transpare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
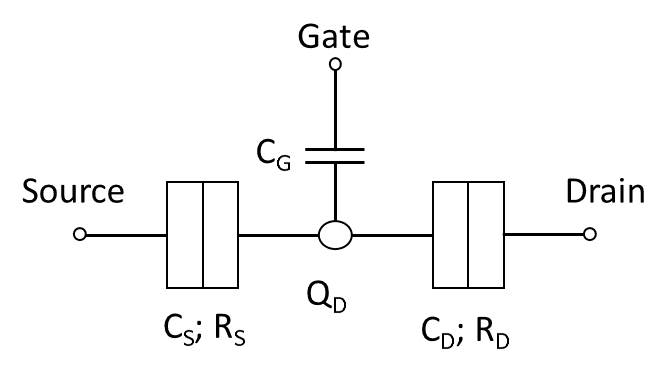
Single-electron Transistor
A single-electron transistor (SET) is a sensitive electronic device based on the Coulomb blockade effect. In this device the electrons flow through a tunnel junction between source/drain to a quantum dot (conductive island). Moreover, the electrical potential of the island can be tuned by a third electrode, known as the gate, which is capacitively coupled to the island. The conductive island is sandwiched between two tunnel junctions modeled by capacitors, C_ and C_, and resistors, R_ and R_, in parallel. History A new subfield of condensed matter physics began in 1977 when David Thouless pointed out that, when made small enough, the size of a conductor affects its electronic properties. This was followed by mesoscopic physics research in the 1980s based on the submicron-size of systems investigated. Thus began research related to the single-electron transistor. The first single-electron transistor based on the phenomenon of Coulomb blockade was reported in 1986 by Sov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves), phase'' on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings. Wavelength is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The multiplicative inverse, inverse of the wavelength is called the ''spatial frequency''. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter lambda (''λ''). For a modulated wave, ''wavelength'' may refer to the carrier wavelength of the signal. The term ''wavelength'' may also apply to the repeating envelope (mathematics), envelope of modulated waves or waves formed by Interference (wave propagation), interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed phase velocity, wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Review Of Materials Research
The ''Annual Review of Materials Research'' is a peer-reviewed journal that publishes review articles about materials science. It has been published by the nonprofit Annual Reviews since 1971, when it was first released under the title the ''Annual Review of Materials Science''. Four people have served as editors, with the current editor Ram Seshadri stepping into the position in 2024. It has an impact factor of 10.6 as of 2024. As of 2023, it is being published as open access, under the Subscribe to Open model. History The ''Annual Review of Materials Science'' was first published in 1971 by the nonprofit publisher Annual Reviews, making it their sixteenth journal. Its first editor was Robert Huggins. In 2001, its name was changed to the current form, the ''Annual Review of Materials Research''. The name change was intended "to better reflect the broad appeal that materials research has for so many diverse groups of scientists and not simply those who identify themselves w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optoelectronics
Optoelectronics (or optronics) is the study and application of electronic devices and systems that find, detect and control light, usually considered a sub-field of photonics. In this context, ''light'' often includes invisible forms of radiation such as gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet and infrared, in addition to visible light. Optoelectronic devices are electrical-to-optical or optical-to-electrical transducers, or instruments that use such devices in their operation. '' Electro-optics'' is often erroneously used as a synonym, but is a wider branch of physics that concerns all interactions between light and electric fields, regardless of whether they form part of an electronic device. Optoelectronics is based on the quantum mechanical effects of light on electronic materials, especially semiconductors, sometimes in the presence of electric fields. * Photoelectric or photovoltaic effect, used in: ** photodiodes (including solar cells) ** phototransistors ** photomult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Function
In quantum physics, a wave function (or wavefunction) is a mathematical description of the quantum state of an isolated quantum system. The most common symbols for a wave function are the Greek letters and (lower-case and capital psi (letter), psi, respectively). Wave functions are complex number, complex-valued. For example, a wave function might assign a complex number to each point in a region of space. The Born rule provides the means to turn these complex probability amplitudes into actual probabilities. In one common form, it says that the squared modulus of a wave function that depends upon position is the probability density function, probability density of measurement in quantum mechanics, measuring a particle as being at a given place. The integral of a wavefunction's squared modulus over all the system's degrees of freedom must be equal to 1, a condition called ''normalization''. Since the wave function is complex-valued, only its relative phase and relative magnitud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics Today
''Physics Today'' is the membership magazine of the American Institute of Physics. First published in May 1948, it is issued on a monthly schedule, and is provided to the members of ten physics societies, including the American Physical Society. It is also available to non-members as a paid annual subscription. The magazine informs readers about important developments in overview articles written by experts, shorter review articles written internally by staff, and also discusses issues and events of importance to the science community in politics, education, and other fields. The magazine provides a historical resource of events associated with physics. For example it discussed debunking the physics of the Star Wars program of the 1980s, and the state of physics in China and the Soviet Union during the 1950s and 1970s. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2017 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic jou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features Peer review, peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2022 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 50.5), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in the autumn of 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander MacMillan (publisher), Alexander MacMillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (molecule), water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |