|
Protista
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any Eukaryote, eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, Embryophyte, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a Clade, natural group, or clade, but are a Paraphyly, paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancestor excluding land plants, animals, and fungi. Protists were historically regarded as a separate taxonomic rank, taxonomic kingdom (biology), kingdom known as Protista or Protoctista. With the advent of phylogenetic analysis and electron microscopy studies, the use of Protista as a formal taxon was gradually abandoned. In modern classifications, protists are spread across several eukaryotic clades called supergroup (biology), supergroups, such as Archaeplastida (photoautotrophs that includes land plants), SAR supergroup, SAR, Obazoa (which includes fungi and animals), Amoebozoa and "Excavata". Protists represent an extremely large genetic diversity, genetic and ecological diversity in all environments, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malawimonadida
Malawimonads (order Malawimonadida) are a small group of microorganisms with a basal position in the evolutionary tree of eukaryotes, containing only three recognized species. They're considered part of a paraphyletic group known as "Excavata". Evolution It is clear that the malawimonads are a monophyletic clade at the base of Eukaryota, but there is no consensus on the specific relationships between other basal groups, such as Discoba, Metamonada, Ancyromonadida and Podiata. The sister group to Malawimonadida varies greatly between analyses. Some phylogenetic analyses find Malawimonadida as the sister group to Podiata. Other analyses recover Malawimonadida as the sister group of Discoba or Metamonada. Very few modern analyses recover the three clades, Malawimonadida, Discoba and Metamonada, as a monophyletic Excavata. Taxonomy History The malawimonads were first described as order Malawimonadida in 2003 by Thomas Cavalier-Smith. In 2013 they were also described as a cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizaria
The Rhizaria are a diverse and species-rich clade of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus '' Paulinella'' in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthetic, but many Foraminifera and Radiolaria have a symbiotic relationship with unicellular algae. A multicellular form, ''Guttulinopsis vulgaris'', a cellular slime mold, has been described. This group was used by Cavalier-Smith in 2002, although the term "Rhizaria" had been long used for clades within the currently recognized taxon. Being described mainly from rDNA sequences, they vary considerably in form, having no clear morphological distinctive characters ( synapomorphies), but for the most part they are amoeboids with filose, reticulose, or microtubule-supported pseudopods. In the absence of an apomorphy, the group is ill-defined, and its composition has been very fluid. Some Rhizaria possess mineral exoskeletons ( thecae or loricas), which are in diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
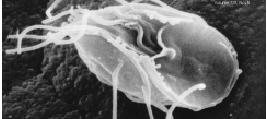
Amoeba
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; : amoebas (less commonly, amebas) or amoebae (amebae) ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of Cell (biology), cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopodia, pseudopods. Amoebae do not form a single Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group; instead, they are found in every major Lineage (evolution), lineage of eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms. Amoeboid cells occur not only among the protozoa, but also in fungi, algae, and animals. Microbiologists often use the terms "amoeboid" and "amoeba" interchangeably for any organism that exhibits amoeboid movement. In older classification systems, most amoebae were placed in the Class (biology), class or subphylum Sarcodina, a grouping of Unicellular organism, single-celled organisms that possess pseudopods or move by protoplasmic flow. However, molecular phylogenetic studies have shown that Sarcodina is not a monophyletic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphoretickes
Diaphoretickes is a major group of eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms spanning over 400,000 species. The majority of the earth's biomass that carries out photosynthesis belongs to Diaphoretickes. In older classification systems, members of the Diaphoretickes were variously placed in the Kingdom (biology), kingdoms Protozoa or Protist, Protista. Etymology The name Diaphoretickes derives (''diaforetikés'') meaning diverse, dissimilar, referring to the wide morphology (biology), morphological and cellular diversity among members of this clade. History Eukaryotes, organisms whose cells contain a cell nucleus, nucleus, have been traditionally grouped into four kingdom (biology), kingdoms: animals, plants, fungi and protists. In the late 20th century, molecular phylogenetic analyses revealed that protists are a paraphyletic assortment of many independent evolutionary lineages or clades, from which animals, fungi and plants evolved. However, the relationships between these clades re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of Amoeba, amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, Pseudopod#Morphology, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional classification schemes, Amoebozoa is usually ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom (biology), kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked "supergroup (biology), supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetics, Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, named Amorphea. Amoeboz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discoba
Excavata is an obsolete, extensive and diverse Paraphyly, paraphyletic group of unicellular Eukaryote, Eukaryota. The group was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and the name latinized and assigned a rank by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002. It contains a variety of free-living and symbiotic protists, and includes some important parasites of humans such as ''Giardia'' and ''Trichomonas''. Excavates were formerly considered to be included in the now- obsolete Protist, Protista kingdom. They were distinguished from other lineages based on electron-microscopic information about how the cells are arranged (they have a distinctive ultrastructural identity). They are considered to be a Basal_(phylogenetics), basal flagellate lineage. On the basis of phylogenomic analyses, the group was shown to contain three widely separated eukaryote groups, the discobids, metamonads, and malawimonads. A current view of the composition of the excavates is given below, indicating that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different wikt:undulating, undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their biological life cycle, life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils, including anoxic and oxygen-depleted habitats. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many Ectosymbiosis, ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some Obligate parasite, obligate and Facultative paras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancyromonadida
Ancyromonadida or Planomonadida is a small group of biflagellated eukaryotes found in the soil and in aquatic habitats, where they feed on bacteria.Cavalier-Smith, T. (2013)Early evolution of eukaryote feeding modes, cell structural diversity, and classification of the protozoan phyla Loukozoa, Sulcozoa, and Choanozoa European journal of protistology, 49(2), 115-178. They are freshwater or marine organisms, benthic, dorsoventrally compressed and with two unequal flagellae, each emerging from a separate pocket. The apical anterior flagellum can be very thin or end in the cell membrane, while the posterior flagellum is long and is inserted ventrally or laterally. The cell membrane is supported by a thin single-layered theca and the mitochondrial crests are discoidal/flat. The group's placement is doubtful, as it seems to fall outside the five supergroups of eukaryotes. Cavalier-Smith considers that they constitute a basal group to Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta and places it togeth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
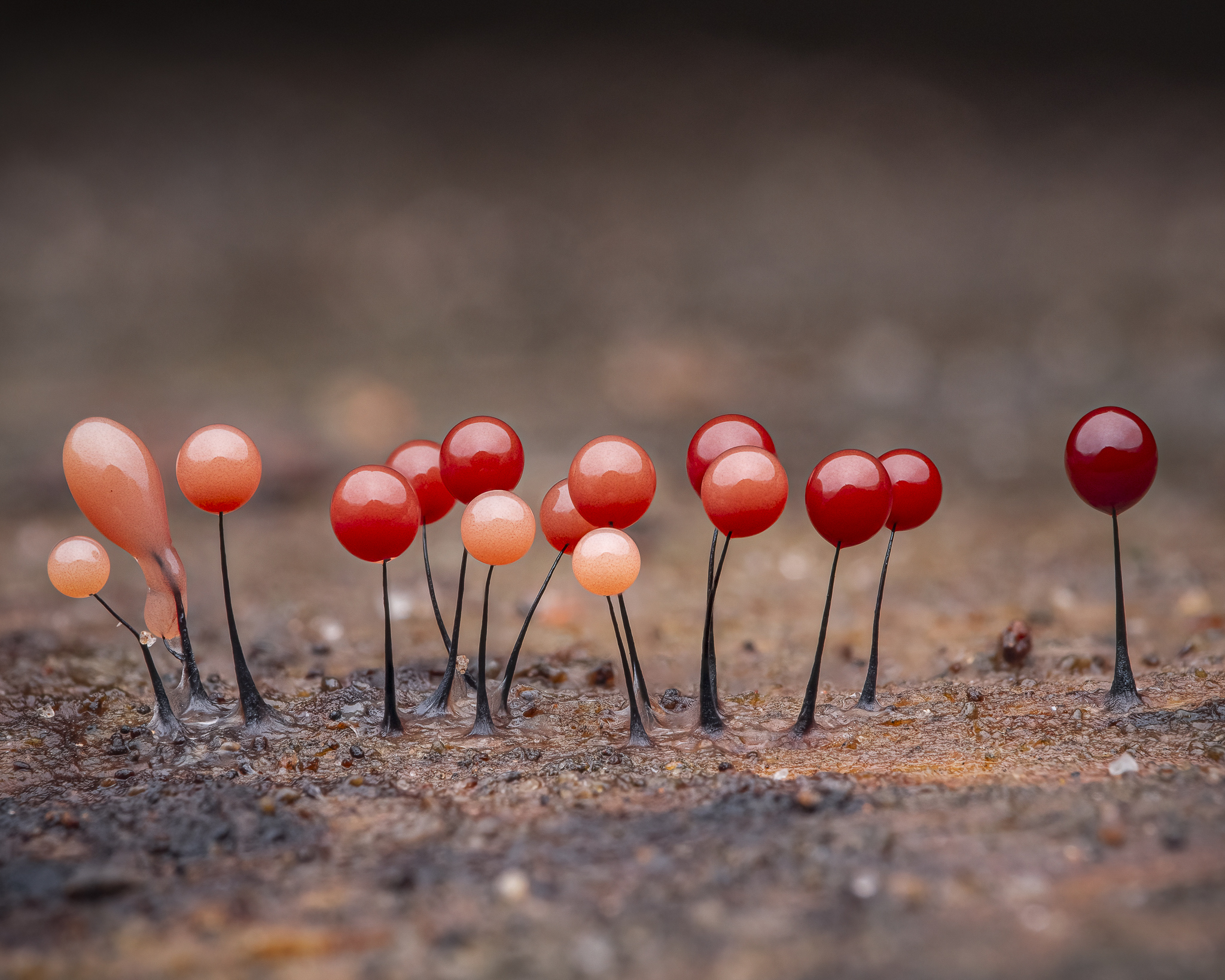
Slime Mold
Slime mold or slime mould is an informal name given to a polyphyletic assemblage of unrelated eukaryotic organisms in the Stramenopiles, Rhizaria, Discoba, Amoebozoa and Holomycota clades. Most are near-microscopic; those in the Myxogastria form larger plasmodial slime molds visible to the naked eye. The slime mold life cycle includes a free-living single-celled stage and the formation of spores. Spores are often produced in macroscopic multicellular or multinucleate fruiting bodies that may be formed through aggregation or fusion; aggregation is driven by chemical signals called acrasins. Slime molds contribute to the decomposition of dead vegetation; some are parasitic. Most slime molds are terrestrial and free-living, typically in damp shady habitats such as in or on the surface of rotting wood. Some myxogastrians and protostelians are aquatic or semi-aquatic. The phytomyxea are parasitic, living inside their plant hosts. Geographically, slime molds are cosmopo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obazoa
Obazoa is a proposed sister clade of Amoebozoa (which together form Amorphea). The term Obazoa is based on the OBA acronym for Opisthokonta, Breviatea, and Apusomonadidae, the group's three constituent clades. Determining the placement of Breviatea and Apusomonadida and their properties is of interest for the development of the opisthokonts in which the main lineages of animals and fungi A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ... emerged. The relationships among opisthokonts, breviates and apusomonads are not conclusively resolved (as of 2018), though Breviatea is usually inferred to be the most basal of the three lineages. The phylogeny of the Obazoa is shown in the cladogram. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q22087764 Amorphea taxa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are motility, able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million extant taxon, living animal species have been species description, described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and biological interaction, interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRuMs
CRuMs is a clade of microbial eukaryotes, whose name is an acronym of the following constituent groups: i) Diphylleids, ii) rigifilids and iii) mantamonads as sister of the Amorphea. A new CRuMs order Glissandrida was proposed in 2025 to place the yet unclassified genus Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ... '' Glissandra''. It more or less supersedes Varisulca, as Ancyromonadida are inferred not to be specifically related to the orders Diphylleida / Collodictyonida, Rigifilida and Mantamonadida. Phylogeny References {{Taxonbar, from1=Q134939335, from2=Q59153571 Eukaryote taxa Podiata Protist taxa CRuMs taxa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |