|
Poppaea Sabina
Poppaea Sabina (30 AD – 65 AD), also known as Ollia, was a Roman empress as the second wife of the emperor Nero. She had also been wife to the future emperor Otho. The historians of antiquity describe her as a beautiful woman who used intrigues to become empress. The large Villa Poppaea at Oplontis near Pompeii bears her name because of the archaeological finds there. It has been largely excavated and can be visited today. Early life Birth Poppaea Sabina the Younger was born in Pompeii in AD 30 as the daughter of Titus Ollius and Poppaea Sabina the Elder.Simon Hornblower, Antony Spawforth-E.A. (edd.), Oxford Classical Dictionary, Oxford University Press, 2003 , 1221. At birth and for most of her childhood she went by her proper patronymic nomen "Ollia", belonging to women of her father's gens, the Ollii, but at some point, probably before her first marriage, decided to start going by her mother's name instead, potentially due to her father's disgrace and suicide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augusta (honorific)
Augusta may refer to: Places Australia * Augusta, Western Australia Brazil * Rua Augusta (São Paulo) Canada * Augusta, Ontario * North Augusta, Ontario * Augusta Street (Hamilton, Ontario) France * Augusta Suessionum ("Augusta of the Suessii"), Soissons * Augusta Viromanduorum ("Augusta of the Viromandui"), Saint-Quentin Germany * Augusta Treverorum ("Augusta of the Treveri") or Trier * Augusta Vangionum ("Augusta of the Vangiones") or Worms * Augusta Vindelicorum ("Augusta of the Vindelici") or Augsburg Italy * Augusta, Sicily * Augusta Praetoria Salassorum ("Praetorian Augusta of the Salassi") or Aosta * Augusta Taurinorum ("Augusta of the Taurini") or Turin * Perugia or ''Augusta Perusia'' Spain * Emerita Augusta, Mérida, Spain * Caesar Augusta, Zaragoza, Spain United States * Augusta, Arkansas * Augusta Charter Township, Michigan * Augusta County, Virginia * Augusta, Georgia ** Augusta National Golf Club ("Augusta"), home of the Masters Tournament * Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
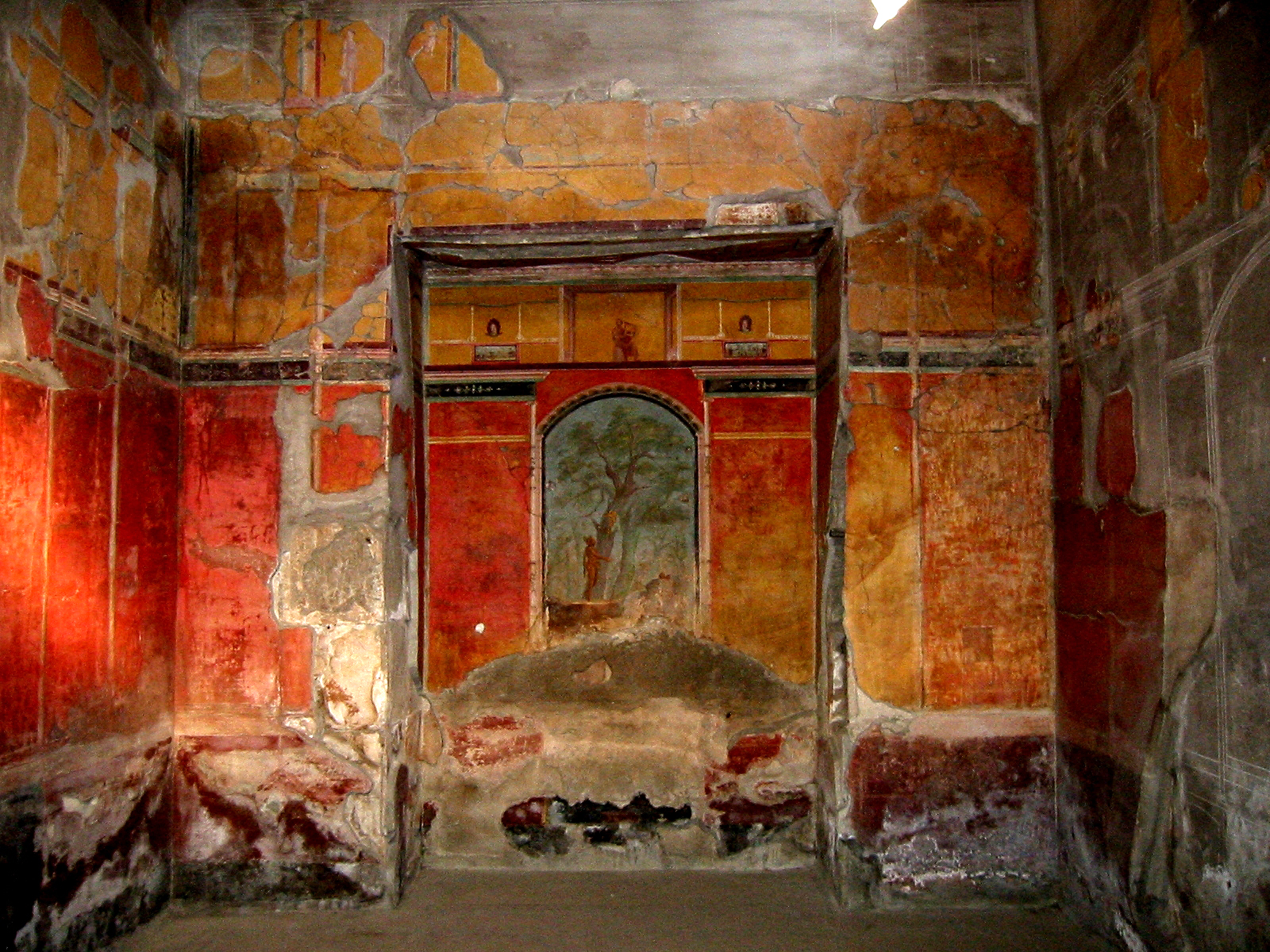
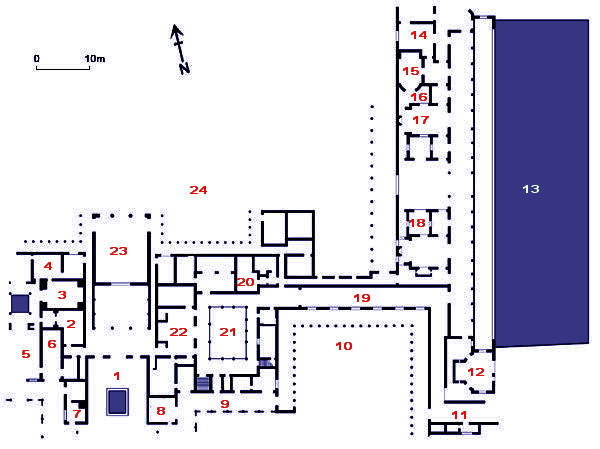
Villa Poppaea
The Villa Poppaea is an ancient luxurious Roman seaside villa (''villa maritima'') located in Torre Annunziata between Naples and Sorrento, in Southern Italy. It is also called the Villa Oplontis or Oplontis Villa A as it was situated in the ancient Roman town of Oplontis. It was buried and preserved in the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD, like the nearby cities of Herculaneum and Pompeii, about below modern ground level. The quality of the decorations and construction suggests that it was owned by the Emperor Nero and a pottery shard bearing the name of a freedman of Poppaea Sabina, the second wife of the emperor Nero was found at the site, which suggests the villa may have been her residence when she was away from Rome and which gives it its popular name. It was sumptuously decorated with fine works of art. Its marble columns and capitals mark it out as being especially luxurious compared with others in this region which usually had stuccoed brick columns. Many artifacts f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marche
Marche ( ; ), in English sometimes referred to as the Marches ( ) from the Italian name of the region (Le Marche), is one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. The region is located in the Central Italy, central area of the country, and has a population of about 1.5 million people, being the thirteenth largest region in the country by number of inhabitants. The region's capital and largest city is Ancona. The Marche region is bordered by Emilia-Romagna and the republic of San Marino to the north, Tuscany and Umbria to the west, Lazio to the southwest, Abruzzo to the south, and the Adriatic Sea to the east. Except for river valleys and the often very narrow coastal strip, the land is hilly. A railway from Bologna to Brindisi, built in the 19th century, runs along the coast of the entire territory. Inland, the mountainous nature of the region, even today, allows relatively little travel north and south, except by twisting roads over the passes. From the Middle ages t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picenum
Picenum was a region of ancient Italy. The name was assigned by the Romans, who conquered and incorporated it into the Roman Republic. Picenum became ''Regio V'' in the Augustan territorial organisation of Roman Italy. It is now in Marche and the northern part of Abruzzo. The Piceni or Picentes were the native population of Picenum, but they were not of uniform ethnicity. They maintained a sanctuary to the Sabine goddess Cupra in Cupra Marittima. Picenum was also the birthplace of such Roman notables as Pompey the Great and his father, Pompeius Strabo. Historical geography Picenum and the Picentes were described in some detail by the Roman geographers: Strabo Strabo places Picenum between the Apennines and the Adriatic Sea from the mouth of the Aesis River southward to Castrum at the mouth of the Truentinus River, some 800 stadia, which is using 185 m/stadion. For coastal cities he includes from north to south Ancona, Auxumum, Septempeda ( San Severino March ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herculaneum
Herculaneum is an ancient Rome, ancient Roman town located in the modern-day ''comune'' of Ercolano, Campania, Italy. Herculaneum was buried under a massive pyroclastic flow in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Like the nearby city of Pompeii, Herculaneum is famous as one of the few ancient cities to be preserved nearly intact, as the solidified material from the volcano that blanketed the town protected it against looting and the elements. Although less known than Pompeii today, it was the first and, for a long time, the only discovered Vesuvian city (in 1709). Pompeii was revealed in 1748 and identified in 1763. Unlike Pompeii, the mainly Pyroclastic rock, pyroclastic material that covered Herculaneum carbonization, carbonized and preserved more wooden objects such as roofs, beds, and doors, as well as other organic-based materials such as Herculaneum loaf, food and papyrus. According to the traditional tale, the city was rediscovered by chance in 1709 during the dri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eruption Of Mount Vesuvius In 79
In 79 AD, Mount Vesuvius, a stratovolcano located in the modern-day region of Campania, erupted, causing one of the deadliest eruptions in history. Vesuvius violently ejected a cloud of super-heated tephra and gases to a height of , ejecting molten rock, pulverized pumice and hot ash at 1.5 million tons per second, ultimately releasing 100,000 times the thermal energy of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. The event gives its name to the Vesuvian type of volcanic eruption, characterised by columns of hot gases and ash reaching the stratosphere, although the event also included pyroclastic flows associated with Peléan eruptions. The event destroyed several Roman towns and settlements in the area. Pompeii and Herculaneum, obliterated and buried underneath massive pyroclastic surges and ashfall deposits, are the most famous examples. Archaeological excavations have revealed much of the towns and the lives of the inhabitants, leading to the area becoming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menander
Menander (; ; c. 342/341 – c. 290 BC) was a Greek scriptwriter and the best-known representative of Athenian Ancient Greek comedy, New Comedy. He wrote 108 comedies and took the prize at the Lenaia festival eight times. His record at the City Dionysia is unknown. He was one of the most popular writers and most highly admired poets in antiquity, but his work was considered lost before the early Middle Ages. It now survives only in Latin-language adaptations by Terence and Plautus and, in the original Greek, in highly fragmentary form, most of which were discovered on papyrus in Egyptian tombs during the early to mid-20th-century. In the 1950s, to the great excitement of Classicists, it was announced that a single play by Menander, ''Dyskolos'', had finally been rediscovered in the Bodmer Papyri intact enough to be performed. Life and work Menander was the son of well-to-do parents; his father Diopeithes is identified by some with the Athenian general and governor of the Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gens
In ancient Rome, a gens ( or , ; : gentes ) was a family consisting of individuals who shared the same ''nomen gentilicium'' and who claimed descent from a common ancestor. A branch of a gens, sometimes identified by a distinct cognomen, was called a ''stirps'' (: ''stirpes''). The gens was an important social structure at Rome and throughout ''Italia'' during the period of the Roman Republic. Much of individuals' social standing depended on the gens to which they belonged. Certain gentes were classified as patrician, others as plebeian; some had both patrician and plebeian branches. The importance of the gens as a social structure declined considerably in imperial times, although the ''gentilicium'' continued to define the origins and dynasties of the ancient Romans, including the emperors. ''Harper's Dictionary of Classical Literature and Antiquities'', Second Edition, Harry Thurston Peck, Editor (1897).'' Oxford Classical Dictionary'', 2nd Ed. (1970). Origins The word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomen (ancient Rome)
The (; or simply ) was a hereditary name borne by the peoples of Roman Italy and later by the citizens of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. It was originally the name of one's (family or clan) by patrilineal descent. However, as Rome expanded its frontiers and non-Roman peoples were progressively granted citizenship and concomitant , the latter lost its value in indicating patrilineal ancestry. For men, the was the middle of the ("three names"), after the and before the . For women, the was often the only name used until the late Republic. For example, three members of gens ''Julia'' were Gaius ''Julius'' Caesar and his sisters ''Julia'' Major and ''Julia'' Minor ("Julia the elder" and "Julia the younger"). History The ''nomen gentilicium'', or "gentile name" designated a Roman citizen as a member of a ''gens''. A ''gens'', which may be translated as "race", "family", or "clan", constituted an extended Roman family, all of whom shared the same ''nomen'' and clai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586. It is the second-oldest university press after Cambridge University Press, which was founded in 1534. It is a department of the University of Oxford. It is governed by a group of 15 academics, the Delegates of the Press, appointed by the Vice Chancellor, vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, Oxford, Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho, Oxford, Jericho. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |