|
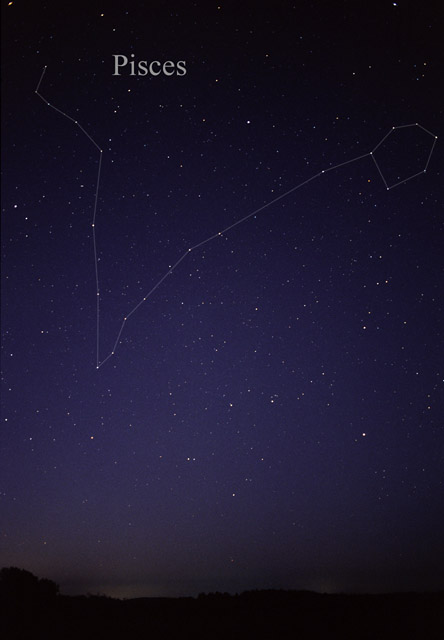
Pisces (constellation)
Pisces is a constellation of the zodiac. Its vast bulk – and main asterism viewed in most European cultures per Greco-Roman antiquity as a distant pair of fishes connected by one cord each that join at an apex – are in the Northern celestial hemisphere. Its old astronomical symbol is (♓︎). Its name is Latin for "fishes". It is between Aquarius (constellation), Aquarius, of similar size, to the southwest and Aries (constellation), Aries, which is smaller, to the east. The ecliptic and the celestial equator intersect within this constellation and in Virgo (constellation), Virgo. The Sun subsolar point, passes directly overhead of the equator, on average, at approximately this point in the sky, at the March equinox. The right ascension/declination 00 is located within the boundaries of Pisces. Features The March equinox is currently located in Pisces, due south of Psc, and, due to precession, slowly drifting due west, just below the western fish towards Aquari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishes
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Equator
The celestial equator is the great circle of the imaginary celestial sphere on the same plane as the equator of Earth. By extension, it is also a plane of reference in the equatorial coordinate system. Due to Earth's axial tilt, the celestial equator is currently inclined by about 23.44° with respect to the ecliptic (the plane of Earth's orbit), but has varied from about 22.0° to 24.5° over the past 5 million years due to Milankovitch cycles and perturbation from other planets. An observer standing on Earth's equator visualizes the celestial equator as a semicircle passing through the zenith, the point directly overhead. As the observer moves north (or south), the celestial equator tilts towards the opposite horizon. The celestial equator is defined to be infinitely distant (since it is on the celestial sphere); thus, the ends of the semicircle always intersect the horizon due east and due west, regardless of the observer's position on Earth. At the poles, the celesti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthly Notices Of The Royal Astronomical Society
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal in astronomy, astrophysics and related fields. It publishes original research in two formats: papers (of any length) and letters (limited to five pages). MNRAS publishes more articles per year than any other astronomy journal. The learned society journal has been in continuous existence since 1827 and became online only in 2020. It operates as a partnership between the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS), who select and peer-review the contents, and Oxford University Press (OUP), who publish and market the journal. Despite its name, MNRAS is no longer monthly, nor does it carry the notices of the RAS. In 2024 MNRAS became a purely gold open access journal. History The first issue of MNRAS was published on 9 February 1827 as ''Monthly Notices of the Astronomical Society of London'' and it has been in continuous publication ever since. It took its current name from the second vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta Piscium
Zeta Piscium (ζ Piscium, abbreviated Zet Psc, ζ Psc) is a quintuple star system in the zodiac constellation of Pisces. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is located roughly distant from the Sun. The system consists of a binary star (Zeta Piscium A) and a triple star system (BC), the latter consisting of a spectroscopic binary (B) and a single star (C). A's two components are themselves designated Zeta Piscium Aa (officially named Revati ) and Ab; B's two components as Ba and Bb. As the star system is 0.21° south of the ecliptic, it can be eclipsed (occulted) by the moon, when close to or at one of its two nodes of its orbit; and is eclipsed by the sun from about 8-10 April. Nomenclature ''ζ Piscium'' ( Latinised to ''Zeta Piscium'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the three constituents as ''Zeta Piscium A'', ''B'' and ''C'', and those of ''A's'' and ''B's'' components - ''Zeta Piscium Aa'', ''Ab'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Piscium
Epsilon Piscium (Epsilon Psc, ε Piscium, ε Psc) is the Bayer designation for a star approximately away from the Earth, in the constellation Pisces. It is a yellow-orange star of the G9 III or K0 III spectral type. This is a giant star, slightly cooler in surface temperature, yet brighter and larger than the Sun. It is a suspected occultation double, with both stars having the same magnitude, separated by 0.25 arcsecond. Naming In Chinese, (), meaning '' Outer Fence'', refers to an asterism consisting of ε Piscium, δ Piscium, ζ Piscium, μ Piscium, ν Piscium, ξ Piscium and α Piscium. Consequently, the Chinese name for ε Piscium itself is (, .) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Piscium
Delta Piscium (δ Piscium) is a solitary, orange-hued star in the zodiac constellation of Pisces. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +4.4, so it is bright enough to be faintly visible to the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 10.86 mas, it is around from the Sun. The visual magnitude of the star is diminished by an interstellar absorption factor of 0.08 due to interstellar dust. This is an evolved K-type giant star with a stellar classification of K4 IIIb. It has around 1.65 times the mass of the Sun and, at the age of three billion years, has expanded to 38 times the Sun's radius. The star is radiating 292 times the Sun's luminosity from its enlarged photosphere at an effective temperature of 3,868 K. Because Delta Piscium is positioned near the ecliptic, so it is subject to lunar occultations. It has a magnitude 13.99 visual companion at an angular separation of 135.0 arc seconds on a position angle of 12°, as of 2011. Nami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Piscium
Beta Piscium or β Piscium, formally named Fumalsamakah , is a blue-white hued star in the zodiac constellation of Pisces. Its apparent magnitude is 4.40, meaning it can be faintly seen with the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements taken during the Hipparcos mission, it is about 410 light-years (125 parsecs) distant from the Sun. Nomenclature ''β Piscium'' ( Latinised to ''Beta Piscium'') is the star's Bayer designation. It bore the traditional name ''Fum al Samakah'' from the Arabic فم السمكة ''fum al-samakah'' "mouth of the fish" (compare Fomalhaut). In 2016, the IAU organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name ''Fumalsamakah'' for this star on 1 June 2018 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names. In Chinese, (), meaning ''Thunderbolt'', refers to an asterism consisting of Beta Piscium and Gamma, Theta, Iota and Omega Piscium. Conseque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Piscium
Alpha Piscium (α Piscium) is a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Pisces. Based upon parallax measurements made by the Hipparcos spacecraft, it is about from the Solar System. The two components are designated Alpha Piscium A (officially named Alrescha , the traditional name of the system) and B. Nomenclature ''α Piscium'' ( Latinised to ''Alpha Piscium'') is the star's Bayer designation. The designations of the two components as ''Alpha Piscium A'' and ''B'' derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). The system bore the traditional name ''Alrescha'' (alternatively ''Al Rescha'', ''Alrischa'', ''Alrisha'') derived from the Arabic الرشآء ''ar-Rishā’'' "the cord" and less commonly ''Kaitain'' and ''Okda'', the latter from the Arabic عقدة ''ʽuqdah'' "knot" (see Ukdah. In 2016, the International Astronomical Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, if the axis of rotation of a body is itself rotating about a second axis, that body is said to be precessing about the second axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called '' nutation''. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced. In astronomy, ''precession'' refers to any of several slow changes in an astronomical body's rotational or orbital parameters. An important example is the steady change in the orientation of the axis of rotation of the Earth, known as the precession of the equinoxes. Torque-free or torque neglected Torque-free precession implies that no external moment (torque) is applied to the body. In torque-free precession, the angular momentum is a constant, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. The declination angle is measured north (positive) or south (negative) of the celestial equator, along the hour circle passing through the point in question. The root of the word ''declination'' (Latin, ''declinatio'') means "a bending away" or "a bending down". It comes from the same root as the words ''incline'' ("bend forward") and ''recline'' ("bend backward"). In some 18th and 19th century astronomical texts, declination is given as ''North Pole Distance'' (N.P.D.), which is equivalent to 90 – (declination). For instance an object marked as declination −5 would have an N.P.D. of 95, and a declination of −90 (the south celestial pole) would have an N.P.D. of 180. Explanation Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, projected onto the celestial sphere, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the equinox (celestial coordinates), March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in question above the Earth. When paired with declination, these celestial coordinate system, astronomical coordinates specify the location of a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system. An old term, ''right ascension'' (), "''Ascensio recta'' Solis, stellæ, aut alterius cujusdam signi, est gradus æquatorus cum quo simul exoritur in sphæra recta"; roughly translated, "''Right ascension'' of the Sun, stars, or any other sign, is the degree of the equator that rises together in a right sphere" refers to the ''ascension'', or the point on the celestial equator that rises with any celestial object as seen from Earth's equator, where the celestial equator perpendicular, intersects the horizon at a right angle. It contrasts wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |