|
Phycologists
Phycology () is the scientific study of algae. Also known as algology, phycology is a branch of life science. Algae are important as primary producers in aquatic ecosystems. Most algae are eukaryotic, photosynthetic organisms that live in a wet environment. They are distinguished from the higher plants by a lack of true roots, stems or leaves. They do not produce flowers. Many species are single-celled and microscopic (including phytoplankton and other microalgae); many others are multicellular to one degree or another, some of these growing to large size (for example, seaweeds such as kelp and ''Sargassum''). A number of microscopic algae also occur as symbionts in lichens. Phycologists typically focus on either freshwater or ocean algae, and further within those areas, either diatoms or soft algae. History of phycology While both the ancient Greeks and Romans knew of algae, and the ancient Chinese even cultivated certain varieties as food, the scientific study of algae b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Henry Harvey
William Henry Harvey, FRS FLS (5 February 1811 – 15 May 1866) was an Irish botanist and phycologist who specialised in algae. Biography Harvey was born at Summerville near Limerick, Ireland, in 1811, the youngest of 11 children. His father Joseph Massey Harvey, was a Quaker and prominent merchant. William started his education at Ballitore School in County Kildare and by the age of 15 had already established algae as his over-riding interest.Papenfuss, G.F. 1976. pp.21–46. Landmarks in Pacific North American Marine Phycology. ''in'' Abbott, I.A. and Hollenberg, G.J. 1976. ''Marine Algae of California''. Stanford University Press, California. After leaving school he joined the family business. Harvey was an authority on algae and bryophytes (mosses), and author of ''A Manual of the British Algae'' (1841), ''Phycologia Britannica'' (4 vols., 1846–51), ''Nereis Boreali-Americana.'' (3 parts 1852–85) and '' Phycologia Australica'' (5 vol., 1858–63). He spent several ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Pierre Étienne Vaucher
Jean Pierre Étienne Vaucher (17 April 1763 – 5 or 6 January 1841) was a Swiss Protestant pastor and botanist who was a native of the Republic of Geneva. He studied theology at Geneva, and from 1795 to 1821 was a pastor at the Church of Saint-Gervais. From 1808 to 1840 he was a professor of church history at the University of Geneva, and for a number of years he also taught classes in botany. Among his better-known students were botanist Augustin Pyramus de Candolle (1778-1841), scientist Hans Conrad Escher von der Linth (1767-1823) and Charles Albert of Sardinia, Charles-Albert (1798-1849), the future King of Sardinia. Vaucher is remembered for his research involving the developmental history of algae. In his 1803 treatise ''Histoire des Conferves d'eau douce'', he described the process of Sexual conjugation, conjugation in certain algae as a distinct sexual process. The phenomena of conjugation is a means of fertilization that takes place in green algae such as ''Spirogyra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelp In Freycinet Tasmania
Kelps are large brown algae or seaweeds that make up the order Laminariales. There are about 30 different genera. Despite its appearance and use of photosynthesis in chloroplasts, kelp is technically not a plant but a stramenopile (a group containing many protists). Kelp grow from stalks close together in very dense areas like forests under shallow temperate and Arctic oceans. They were previously thought to have appeared in the Miocene, 5 to 23 million years ago based on fossils from California. New fossils of kelp holdfasts from early Oligocene rocks in Washington State show that kelps were present in the northeastern Pacific Ocean by at least 32 million years ago. The organisms require nutrient-rich water with temperatures between . They are known for their high growth rate—the genera ''Macrocystis'' and ''Nereocystis'' can grow as fast as half a metre a day (that is, about 20 inches a day), ultimately reaching .Thomas, D. 2002. ''Seaweeds.'' The Natural History Museum, Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecklonia Maxima
''Ecklonia maxima'', or sea bamboo, is a species of kelp native to the southern oceans. It is typically found along the southern Atlantic coast of Africa, from the very south of South Africa to northern Namibia. In these areas the species dominates the shallow, temperate water, reaching a depth of up to in the offshore kelp forests. The kelp anchors itself by attaching itself to a rock or other kelp via its holdfast. From this root-like structure a single long stipe rises to the surface waters, where a large pneumatocyst keeps a tangle of blades at the surface to aid photosynthesis. The species is of economic importance as it is harvested for both an agricultural supplement and as food for farmed abalone Abalone ( or ; via Spanish , from Rumsen language, Rumsen ''aulón'') is a common name for any small to very large marine life, marine gastropod mollusc in the family (biology), family Haliotidae, which once contained six genera but now cont .... References maxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isogamy
Isogamy is a form of sexual reproduction that involves Gamete, gametes of the same Morphology (biology), morphology (indistinguishable in shape and size), and is found in most Unicellular organism, unicellular eukaryotes. Because both gametes look alike, they generally cannot be classified as male or female. Instead, organisms that reproduce through isogamy are said to have different Mating type, mating types, most commonly noted as "+" and "−" strains. Etymology The etymology of isogamy derives from the Greek adjective ''isos'' (meaning equal) and the Greek verb ''gameo'' (meaning to have sex/to reproduce), eventually meaning "equal reproduction" which refers to a hypothetical initial model of equal contribution of resources by both gametes to a zygote in contrast to a later evolutional stage of anisogamy. The term isogamy was first used in the year 1891. Characteristics of isogamous species Isogamous species often have two Mating type, mating types (heterothallism), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
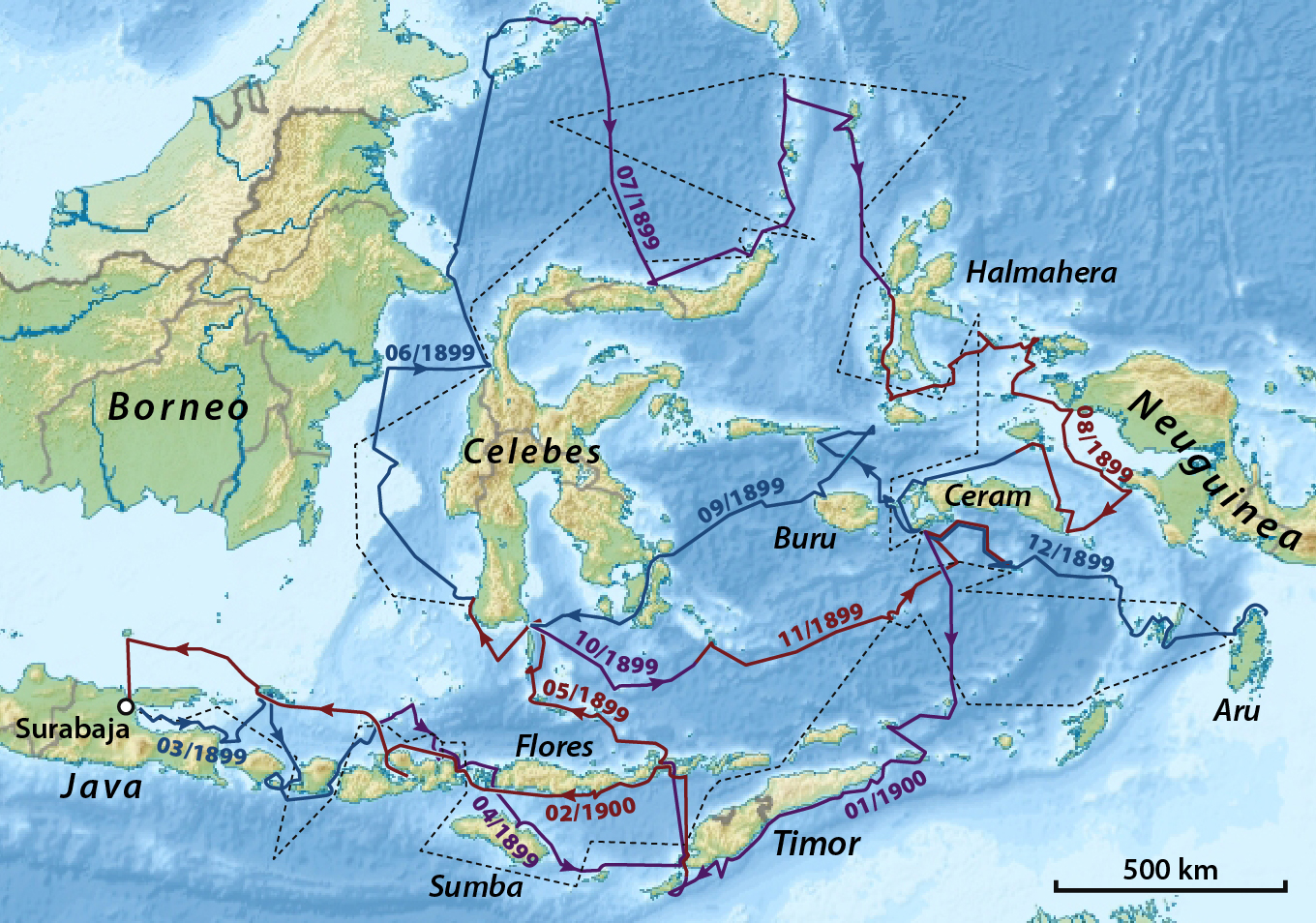
Siboga Expedition
The Siboga expedition was a Dutch zoological and hydrographic expedition to Indonesia from March 1899 to February 1900. The leader of the expedition was Max Carl Wilhelm Weber. Other members of the crew were his wife Anna Weber-Van Bosse, Anna Weber-van Bosse, the zoologist and first assistant Jan Versluys, the zoologist and second assistant Hugo Frederik Nierstrasz, the physician A. Schmidt, and the artist Jozef Willem Huysmans. Captain Gustaaf Frederik Tydeman was responsible for making hydrographic measurements. Gallery File:Leden der expeditie.jpg, Siboga expedition group portrait File:Siboga expedition group portrait in laboratory.jpg, Siboga expedition laboratory File:UvA-BC 300.261 - Siboga - de drooggevallen rivierbedding van de Sifoe (Sifu) op het eiland Buru.jpg, Max Carl Wilhelm Weber (left) and Gustaaf Frederik Tydeman in Buru File:UvA-BC 300.054 - Siboga - Poeloe Barang, eilandje voor de kust bij Makassar (Pulau Barang).jpg, Anna Weber-van Bosse and natives Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identification Key
In biology, an identification key, taxonomic key, or frequently just key, is a printed or computer-aided device that aids in the identification of biological organisms. Historically, the most common type of identification key is the dichotomous key, a type of single-access key which offers a fixed sequence of identification steps, each with two alternatives. The earliest examples of identification keys originate in the seventeenth, but their conceptual history can be traced back to antiquity. Modern multi-access keys allow the user to freely choose the identification steps and any order. They were traditionally performed using punched cards but now almost exclusively take the form of computer programs. History The conceptual origins of the modern identification key can be traced back to antiquity. Theophrastus categorized organisms into "subdivisions" based on dichotomous characteristics. The seventeenth-century Chinese herbalist, Pao Shan, in his treatise ''Yeh-ts'ai Po-Iu'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Kaye Greville
Dr. Robert Kaye Greville FRSE FLS LLD (13 December 1794 – 4 June 1866) was an England, English mycologist, bryology, bryologist, and botanist. He was an accomplished artist and illustrator of natural history. In addition to art and science he was interested in causes like Abolitionism in the United Kingdom, abolitionism, capital punishment, keeping Sunday special and the temperance movement. He has a mountain in Queensland named after him. Biography Greville was born at Bishop Auckland, County Durham, Durham, but was brought up in Derbyshire by his parents Dorothy ( Chaloner) and Robert Greville. His father who liked to compose was the rector of St James' Church, Edlaston, the parish church in Edlaston in Derbyshire. Greville had an interest in natural history since he was very young, but he originally studied medicine. Realising that he did not need an income he discarded four years of medical education in London and Edinburgh and decided to concentrated on botany which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kintarô Okamura
was a Japanese botanist and educationalist (1867 - 1935). He is the author of important studies about seaweed Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of ''Rhodophyta'' (red), '' Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...s. He's also well known for his educational books collection, the ''Ohraimono''. Okamura is the editor of two exsiccatae, namely ''An Album of Japanese Bryophyta'' and ''Algae Japonicae exsiccatae''. Bibliography * * * * - published between 1907 and 1937, Japanese text with English summary. Total 10 volumes were bound to seven. Reprint in 2016. ** * * * * * * * References Short biography 1867 births 1935 deaths 20th-century Japanese botanists 19th-century Japanese botanists Japanese phycologists Scientists from Tokyo {{Japan-botanist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Traugott Kützing
Friedrich Traugott Kützing (8 December 1807 in Ritteburg – 9 September 1893) was a German pharmacist, botanist and phycologist. Despite his limited background in regard to higher education, Kützing made significant scientific contributions. In 1833, he demonstrated differences between diatoms and desmids, thus separating the two groups into families of their own. Also, independent of Charles Cagniard-Latour (1777–1859) and Theodor Schwann (1810–1882), he was among the first to provide comprehensive answers in regard to yeast and the role it played in fermentation. In 1849, he published ''Species Algarum'', a large work that provided descriptions for 6000 species of algae. He is the taxonomic authority of the genera '' Syringodium'' (family Cymodoceaceae) and ''Phlebothamnion'' (family Ceramiaceae). Early life As a young man, he worked in several pharmacies in Germany, also serving as assistant for a few semesters at the chemical-pharmaceutical institute of Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Vincent Félix Lamouroux
Jean Vincent Félix Lamouroux (3 May 1779 – 26 March 1825) was a French biologist and naturalist, noted for his seminal work with algae. Biography Lamouroux was born in Agen in the Aquitaine of southwestern France, the son of Claude Lamouroux, an intellectual who made his livelihood in manufacturing, but who was also a musician, a one-term mayor of Agen, and a co-founder of the Academic Society of Agen. Jean Vincent Lamouroux studied botany at the Boudon de Saint-Amans school in Agen. Lamouroux was particularly interested in marine organisms such as algae and hydrozoans. In 1805 he published a dissertation on several species of ''Fucus'' before settling in Paris in 1807, after his father went into bankruptcy. In 1807, Lamouroux was appointed to the French Academy of Sciences and in 1808 he became an assistant professor of natural history at the University of Caen, rising to full professorship by 1811. He joined the Linnean Society of Calvados and contributed to its publicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |