|
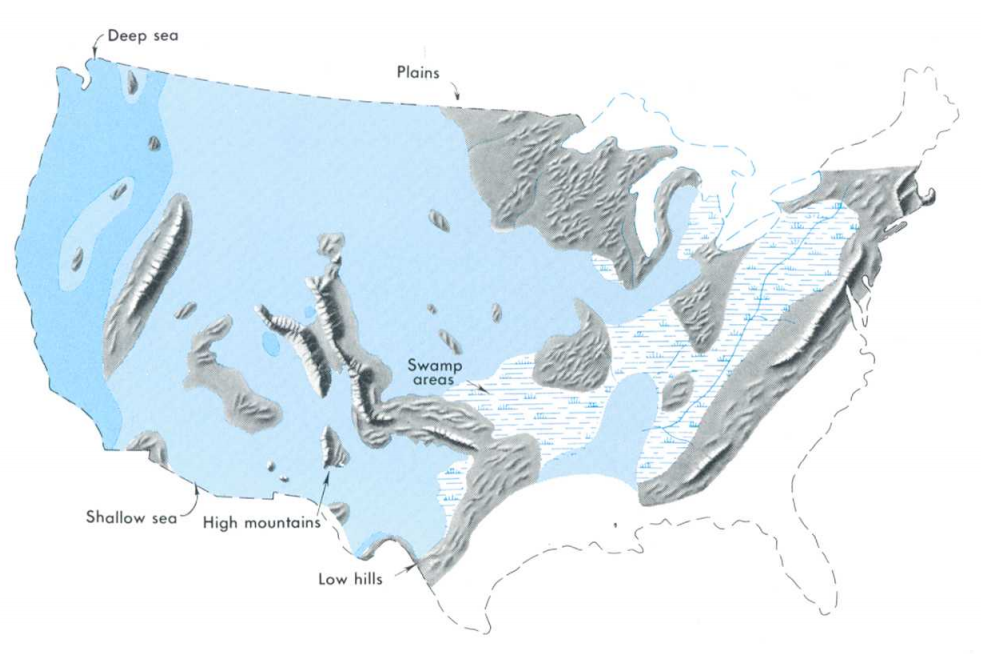
Paleontology In Kansas
Paleontology in Kansas refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the United States, U.S. state of Kansas. Kansas has been the source of some of the most spectacular fossil discoveries in US history. The fossil record of Kansas spans from the Cambrian to the Pleistocene. From the Cambrian to the Devonian, Kansas was covered by a shallow sea. During the ensuing Carboniferous the local sea level began to rise and fall. When sea levels were low the state was home to richly vegetated deltaic swamps where early amphibians and reptiles lived. Seas expanded across most of the state again during the Permian, but on land the state was home to thousands of different insect species. The popular pterosaur ''Pteranodon'' is best known from this state. During the early part of the Cenozoic era Kansas became a savannah environment. Later, during the Quaternary glaciation, Ice Age, glaciers briefly entered the state, which was home to camels, mammoths, mastodons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of USA KS
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geography, geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savannah
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to support an unbroken herbaceous layer consisting primarily of grasses. Four savanna forms exist; ''savanna woodland'' where trees and shrubs form a light canopy, ''tree savanna'' with scattered trees and shrubs, ''shrub savanna'' with distributed shrubs, and ''grass savanna'' where trees and shrubs are mostly nonexistent.Smith, Jeremy M.B.. "savanna". Encyclopedia Britannica, 5 Sep. 2016, https://www.britannica.com/science/savanna/Environment. Accessed 17 September 2022. Savannas maintain an open canopy despite a high tree density. It is often believed that savannas feature widely spaced, scattered trees. However, in many savannas, tree densities are higher and trees are more regularly spaced than in forests.Manoel Cláudio da S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nautiloids
Nautiloids are a group of cephalopods (Mollusca) which originated in the Late Cambrian and are represented today by the living ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. Fossil nautiloids are diverse and species rich, with over 2,500 recorded species. They flourished during the early Paleozoic era, when they constituted the main predatory animals. Early in their evolution, nautiloids developed an extraordinary diversity of shell shapes, including coiled morphologies and giant straight-shelled forms ( orthocones). No orthoconic and only a handful of coiled species, the nautiluses, survive to the present day. In a broad sense, "nautiloid" refers to a major cephalopod subclass or collection of subclasses (Nautiloidea ''sensu lato''). Nautiloids are typically considered one of three main groups of cephalopods, along with the extinct ammonoids (ammonites) and living coleoids (such as squid, octopus, and kin). While ammonoids and coleoids are monophyletic clades with exclusive ancestor-desce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvanian (geology)
The Pennsylvanian ( , also known as Upper Carboniferous or Late Carboniferous) is, on the International Commission on Stratigraphy, ICS geologic timescale, the younger of two period (geology), subperiods of the Carboniferous Period (or the upper of two system (stratigraphy), subsystems of the Carboniferous System). It lasted from roughly . As with most other geochronology, geochronologic units, the stratum, rock beds that define the Pennsylvanian are well identified, but the exact date of the start and end are uncertain by a few hundred thousand years. The Pennsylvanian is named after the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, where the coal Bed (geology), beds of this age are widespread. The division between Pennsylvanian and Mississippian (geology), Mississippian comes from North American stratigraphy. In North America, where the early Carboniferous beds are primarily marine limestones, the Pennsylvanian was in the past treated as a full-fledged geologic period between the Mississippian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma at the start of the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic is subdivided into six period (geology), geologic periods (from oldest to youngest), Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. Some geological timescales divide the Paleozoic informally into early and late sub-eras: the Early Paleozoic consisting of the Cambrian, Ordovician and Silurian; the Late Paleozoic consisting of the Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. The name ''Paleozoic'' was first used by Adam Sedgwick (1785–1873) in 1838 to describe the Cambrian and Ordovician periods. It was redefined by John Phillips (geologist), John Phillips (1800–1874) in 1840 to cover the Cambrian to Permian periods. It is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek ''palaiós'' (π� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precambrian
The Precambrian ( ; or pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pC, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the Phanerozoic Eon, which is named after Cambria, the Latinized name for Wales, where rocks from this age were first studied. The Precambrian accounts for 88% of the Earth's geologic time. The Precambrian is an informal unit of geologic time, subdivided into three eons ( Hadean, Archean, Proterozoic) of the geologic time scale. It spans from the formation of Earth about 4.6 billion years ago ( Ga) to the beginning of the Cambrian Period, about million years ago ( Ma), when hard-shelled creatures first appeared in abundance. Overview Relatively little is known about the Precambrian, despite it making up roughly seven-eighths of the Earth's history, and what is known has largely been discovered from the 1960s onwards. The Precambrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Interior Seaway - 95Ma
Western may refer to: Places *Western, Nebraska, a village in the US *Western, New York, a town in the US * Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia * Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia *Western world, countries that identify with shared "Western" culture *Western United States, a region of the United States Arts and entertainment Films * ''Western'' (1997 film), a French road movie directed by Manuel Poirier * ''Western'' (2017 film), a German-Austrian film Genres *Western (genre), a category of fiction and visual art centered on the American Old West **Western fiction, the Western genre as featured in literature **Western film, the western genre in film **Western music (North America), a type of American folk music Music * ''Westerns'' (EP), an EP by Pete Yorn * WSTRN, a British hip hop group from west London *"Western" a song by Black Midi from ''Schlagenheim'' Business * The Western, a closed hotel/casino in Las Vegas, United States *Western Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiphactinus
''Xiphactinus'' (from Latin and Greek for "sword-ray") is an extinct genus of large predatory marine ray-finned fish that lived during the late Albian to the late Maastrichtian. The genus grew up to in length, and superficially resembled a gargantuan, fanged tarpon. It is a member of the extinct order Ichthyodectiformes, which represent close relatives of modern teleosts. The species ''Portheus molossus'' described by Cope is a junior synonym of ''X. audax''. Skeletal remains of ''Xiphactinus'' have come from the Carlile Shale and Greenhorn Limestone of Kansas (where the first ''Xiphactinus'' fossil was discovered during the 1850s in the Niobrara Chalk),''Xiphactinus'' at .org< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Americans In The United States
Native Americans (also called American Indians, First Americans, or Indigenous Americans) are the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples of the United States, particularly of the Contiguous United States, lower 48 states and Alaska. They may also include any Americans whose origins lie in any of the indigenous peoples of North or South America. The United States Census Bureau publishes data about "American Indians and Alaska Natives", whom it defines as anyone "having origins in any of the original peoples of North and South America ... and who maintains tribal affiliation or community attachment". The census does not, however, enumerate "Native Americans" as such, noting that the latter term can encompass a broader set of groups, e.g. Native Hawaiians, which it tabulates separately. The European colonization of the Americas from 1492 resulted in a Population history of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, precipitous decline in the size of the Native American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saber-toothed Cat
Machairodontinae (from Ancient Greek μάχαιρα '' machaira,'' a type of Ancient Greek sword and ὀδόντος ''odontos'' meaning tooth) is an extinct subfamily of carnivoran mammals of the cat family Felidae, representing the earliest diverging major branch of the family. Machairodonts varied in size from comparable to lynxes to exceeding that of lions. The Machairodontinae contain many of the extinct predators commonly known as "saber-toothed cats", including those with greatly elongated upper maxillary canines, such as the famed genus ''Smilodon'' and '' Megantereon,'' though the degree of elongation was variable, and in some machairodontines like '' Dinofelis'' the length of the upper canines was much more modest. Sometimes, other carnivorous mammals with elongated teeth are also called saber-toothed cats, although they do not belong to the felids. Besides the machairodonts, other saber-toothed predators also arose in the nimravids, barbourofelids, machaeroidine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
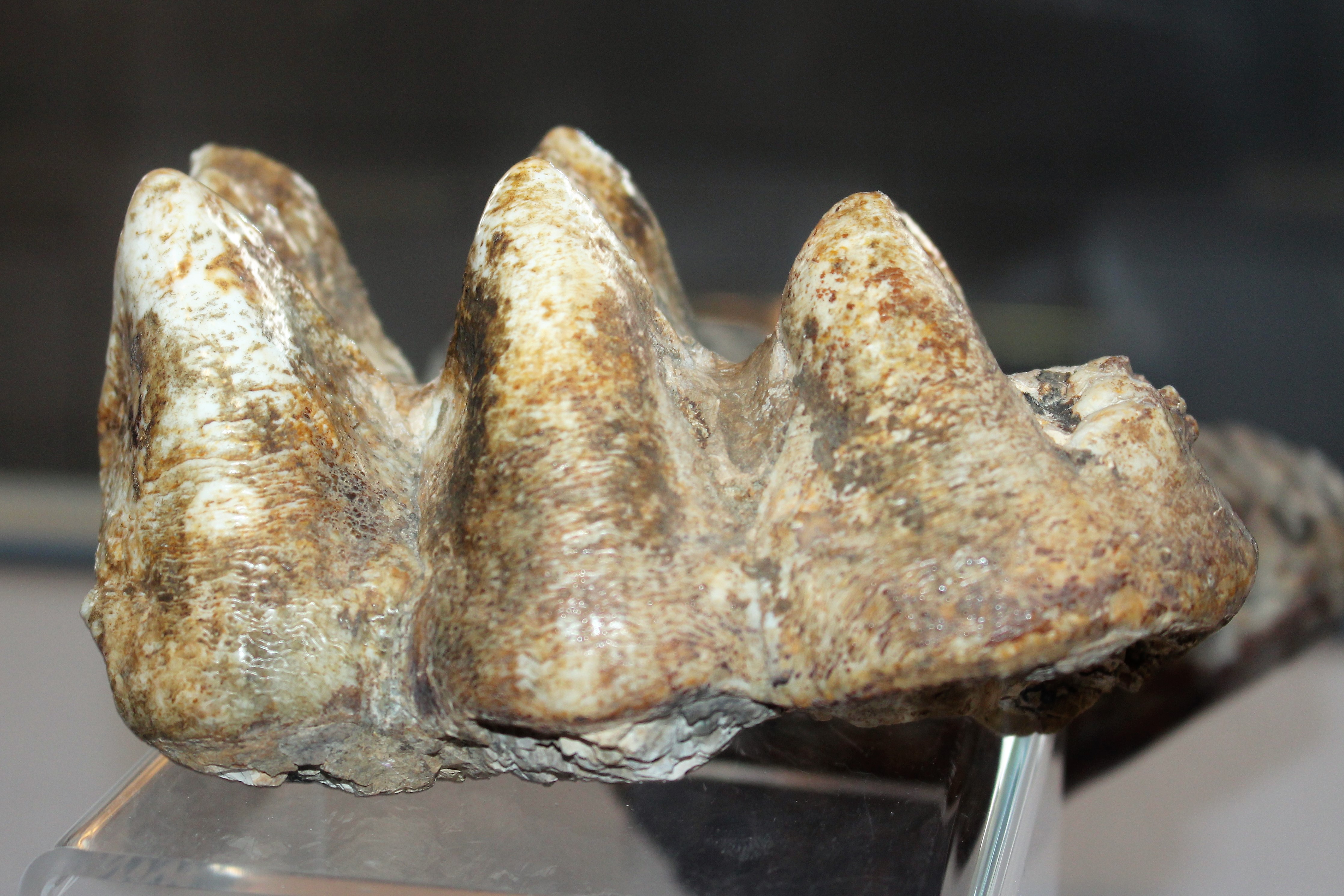
Mastodons
A mastodon, from Ancient Greek μαστός (''mastós''), meaning "breast", and ὀδούς (''odoús'') "tooth", is a member of the genus ''Mammut'' (German for 'mammoth'), which was endemic to North America and lived from the late Miocene to the early Holocene. Mastodons belong to the order Proboscidea, the same order as elephants and mammoths (which belong to the family Elephantidae). ''Mammut'' is the type genus of the extinct family Mammutidae, which diverged from the ancestors of modern elephants at least 27–25 million years ago, during the Oligocene. Like other members of Mammutidae, the molar teeth of mastodons have zygodont morphology (where parallel pairs of cusps are merged into sharp ridges), which strongly differ from those of elephantids. In comparison to its likely ancestor '' Zygolophodon'', ''Mammut'' is characterized by particularly long and upward curving upper tusks, reduced or absent tusks on the lower jaw, as well as the shortening of the mandibu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammoths
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus.'' They lived from the late Miocene epoch (from around 6.2 million years ago) into the Holocene until about 4,000 years ago, with mammoth species at various times inhabiting Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America. Mammoths are distinguished from living elephants by their (typically large) spirally twisted tusks and in some later species, the development of numerous adaptions to living in cold environments, including a thick layer of fur. Mammoths and Asian elephants are more closely related to each other than they are to African elephants. The oldest mammoth representative, '' Mammuthus subplanifrons'', appeared around 6 million years ago during the late Miocene in what is now southern and Eastern Africa.'''' Later in the Pliocene, by about three million years ago, mammoths dispersed into Eurasia, eventually covering most of Eurasia before migrating into North America around 1.5–1.3 million years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |