|
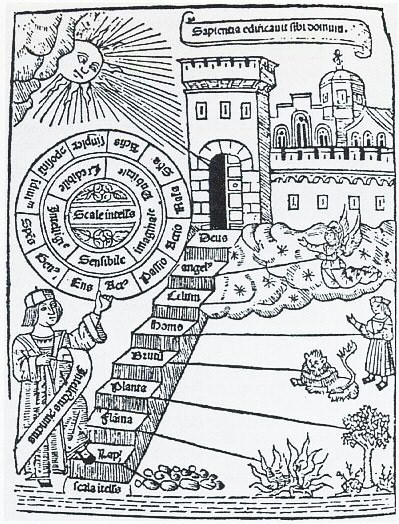
Orthogenesis
Orthogenesis, also known as orthogenetic evolution, progressive evolution, evolutionary progress, or progressionism, is an Superseded theories in science, obsolete biological hypothesis that organisms have an innate tendency to evolution, evolve in a definite direction teleology, towards some goal (teleology) due to some internal mechanism or "driving force". According to the theory, the largest-scale trends in evolution have an absolute goal such as Evolution of biological complexity, increasing biological complexity. Prominent historical figures who have championed some form of evolutionary progress include Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, Teilhard de Chardin, Pierre Teilhard de Chardin, and Henri Bergson. The term ''orthogenesis'' was introduced by Wilhelm Haacke in 1893 and popularized by Theodor Eimer five years later. Proponents of orthogenesis had rejected the theory of natural selection as the organizing mechanism in evolution for a rectilinear (straight-line) model of directed evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternatives To Darwinism
Alternatives to Darwinian evolution have been proposed by scholars investigating biology to explain signs of evolution and the Homology (biology), relatedness of different groups of living things. The alternatives in question do not deny that evolutionary changes over time are the origin of the diversity of life, nor that the organisms alive today share a common ancestor from the distant past (or ancestors, in some proposals); rather, they propose alternative mechanisms of evolutionary change over time, arguing against mutations acted on by natural selection as the most important driver of evolutionary change. This distinguishes them from certain other kinds of arguments that deny that large-scale evolution of any sort has taken place, as in some forms of creationism, which do not propose alternative mechanisms of evolutionary change but instead deny that evolutionary change has taken place at all. Not all forms of creationism deny that evolutionary change takes place; notably, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Synthesis (20th Century)
The modern synthesis was the early 20th-century synthesis of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution and Gregor Mendel's ideas on Mendelian inheritance, heredity into a joint mathematical framework. Julian Huxley coined the term in his 1942 book, ''Evolution: The Modern Synthesis''. The synthesis combined the ideas of natural selection, Mendelian inheritance, Mendelian genetics, and population genetics. It also related the broad-scale macroevolution seen by paleontology, palaeontologists to the small-scale microevolution of local population, populations. The synthesis was defined differently by its founders, with Ernst Mayr in 1959, G. Ledyard Stebbins in 1966, and Theodosius Dobzhansky in 1974 offering differing basic postulates, though they all include natural selection, working on heritable variation supplied by mutation. Other major figures in the synthesis included E. B. Ford, Bernhard Rensch, Ivan Schmalhausen, and George Gaylord Simpson. An early event in the modern synthesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Eimer
Gustav Heinrich Theodor Eimer (22 February 1843 – 29 May 1898) was a German zoologist. He was a popularizer of orthogenesis, a form of directed evolution through mutations that made use of Lamarckian principles. Life and work Eimer was born in Stäfa, Switzerland, where his father, who had taken refuge following an attempted coup against the German Confederation in Frankfurt in 1833, practiced medicine. Eimer's mother, Albertine Pfenniger, was Swiss. After studying at gymnasiums in Bruchsal and Freiburg where his father worked, Eimer matriculated at Tübingen, where he was influenced by Franz von Leydig. He then studied from 1863 at Freiburg, and 1864 at Heidelberg to pass examinations in natural sciences. He spent the winter semester of 1865 at the University of Tübingen and in 1866 he worked in Berlin at Rudolf Virchow’s laboratory. He obtained a medical degree in 1867 and then studied zoology at Freiburg under August Weismann followed by studies in Paris. He received a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Haacke
Johann Wilhelm Haacke (23 August 1855 – 6 December 1912) was a German zoologist born in Clenze, which is now Lower Saxony, who served as Director of the South Australian Museum in Adelaide from 1882 to 1884. Career He studied zoology at the University of Jena, earning his doctorate in 1878. Afterwards he worked as an assistant of Ernst Haeckel in Jena and at the university of Kiel. In 1881 he emigrated to New Zealand, working at the Otago Museum in Dunedin, under Professor Parker, and the Canterbury Museum, Christchurch under Professor von Haast. The following year he moved to Australia, where he replaced F. G. Waterhouse as Director of the South Australian Museum in Adelaide, and was a founding member of the Field Naturalists Society of South Australia. Haacke was one of a number of influential German-speaking residents such as Ludwig Becker, Hermann Beckler, William Blandowski, Amalie Dietrich, Diedrich Henne, Gerard Krefft, Johann Luehmann, Johann Menge, L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Ruse
Michael Escott Ruse (21 June 1940 – 1 November 2024) was a British-born Canadian philosopher of science who specialised in the philosophy of biology and worked on the relationship between science and religion, the creation–evolution controversy, and the demarcation problem within science. Ruse began his career teaching at The University of Guelph and spent many years at Florida State University. Early life and career Ruse was born in Birmingham, England, attending Bootham School, York. He took his undergraduate degree at the University of Bristol (1962), his master's degree at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario (1964), and Ph.D. at the University of Bristol (1970). Ruse taught at the University of Guelph in Ontario, Canada for 35 years. Since his retirement from Guelph, he had taught at Florida State University and was the Lucyle T. Werkmeister Professor of Philosophy (2000–20??). In 1986, he was elected as a Fellow of both the Royal Society of Canada and the Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution Of Biological Complexity
The evolution of biological complexity is one important outcome of the process of evolution. Evolution has produced some remarkably complex organisms – although the actual level of complexity is very hard to define or measure accurately in biology, with properties such as gene content, the number of cell types or morphology all proposed as possible metrics. Many biologists used to believe that evolution was progressive (orthogenesis) and had a direction that led towards so-called "higher organisms", despite a lack of evidence for this viewpoint. This idea of "progression" introduced the terms "high animals" and "low animals" in evolution. Many now regard this as misleading, with natural selection having no intrinsic direction and that organisms selected for either increased or decreased complexity in response to local environmental conditions. Although there has been an increase in the maximum level of complexity over the history of life, there has always been a large majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, chevalier de Lamarck (1 August 1744 – 18 December 1829), often known simply as Lamarck (; ), was a French naturalist, biologist, academic, and soldier. He was an early proponent of the idea that biological evolution occurred and proceeded in accordance with Naturalism (philosophy), natural laws. Lamarck fought in the Seven Years' War against Prussia, and was awarded a commission for bravery on the battlefield. Posted to Monaco, Lamarck became interested in natural history and resolved to study medicine.#Packard, Packard (1901), p. 15. He retired from the army after being injured in 1766, and returned to his medical studies. Lamarck developed a particular interest in botany, and later, after he published the three-volume work ''Flore françoise'' (1778), he gained membership of the French Academy of Sciences in 1779. Lamarck became involved in the Jardin des Plantes and was appointed to the Chair of Botany in 1788. When the French Nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teilhard De Chardin
Pierre Teilhard de Chardin (; 1 May 1881 – 10 April 1955) was a French Jesuit, Catholic priest, scientist, palaeontologist, theologian, and teacher. He was Darwinian and progressive in outlook and the author of several influential theological and philosophical books. His mainstream scientific achievements include his palaeontological research in China, taking part in the discovery of the significant Peking Man fossils from the Zhoukoudian cave complex near Beijing. His more speculative ideas, sometimes criticized as pseudoscientific, have included a vitalist conception of the Omega Point. Along with Vladimir Vernadsky, they also contributed to the development of the concept of a noosphere. In 1962, the Holy Office condemned several of Teilhard's works based on their alleged ambiguities and doctrinal errors. Some eminent Catholic figures, including Pope Benedict XVI and Pope Francis, have made positive comments on some of his ideas since. The response to his writings by scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more or less common within a population over successive generations. The process of evolution has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation. The scientific theory of evolution by natural selection was conceived independently by two British naturalists, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, in the mid-19th century as an explanation for why organisms are adapted to their physical and biological environments. The theory was first set out in detail in Darwin's book ''On the Origin of Species''. Evolution by natural selection is established by observable facts about living organisms: (1) more offspring are often produced than can possibly survive; (2) phenotypic variatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the Heredity, heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charles Darwin popularised the term "natural selection", contrasting it with selective breeding, artificial selection, which is intentional, whereas natural selection is not. Genetic diversity, Variation of traits, both Genotype, genotypic and phenotypic, exists within all populations of organisms. However, some traits are more likely to facilitate survival and reproductive success. Thus, these traits are passed the next generation. These traits can also become more Allele frequency, common within a population if the environment that favours these traits remains fixed. If new traits become more favoured due to changes in a specific Ecological niche, niche, microevolution occurs. If new traits become more favoured due to changes in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March Of Progress
''The March of Progress'', originally titled ''The Road to Homo Sapiens'', is an illustration that presents 25 million years of human evolution. It was created for the ''Early Man'' volume of the ''Life Nature Library'', published in 1965, and drawn by the artist Rudolph Zallinger. It has been widely parodied and imitated to create images of progress of other kinds. Illustration Context The illustration is part of a section of text and images commissioned by Time-Life Books for the ''Early Man'' volume (1965) of the ''Life Nature Library'', by Francis Clark Howell, F. Clark Howell.Howell, F. Clark and the Editors of Time-Life Books (1965), ''Early Man'', New York City, New York: TIME-LIFE Books, pp. 41–45. The illustration is a spread (typography), foldout entitled "The Road to Homo Sapiens". It shows a sequence of figures, drawn by natural history painter and muralist Rudolph Zallinger (1919–1995). The 15 human evolutionary forebears are lined up as if they were marchin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |