|
Nordenskjöld Coast
The Nordenskjöld Coast (64° 30' S 60° 30' W) is located on the Antarctic Peninsula, more specifically Graham Land, which is the top region of the Peninsula. The Peninsula is a thin, long ice sheet with an Alpine-style mountain chain. The coast consists of 15m tall ice cliffs with ice shelves. The Nordenskjöld Coast was discovered by Otto Nordenskjöld, a Swedish explorer and geographer, and Carl Anton Larsen, a Norwegian explorer and whaler, during the Swedish Antarctic Expedition in 1901–1904. The name was suggested by Edwin Swift Balch in 1909, who was part of the Antarctic Exhibition alongside Dr. Nordenskjöld. The Nordenskjöld coast extends 50 miles west-southwest from Cape Longing to Drygalski Bay and Cape Fareweather, with Oscar II Coast located to the south. The Nordenskjöld Coast faces the Weddell Sea at the top of the Antarctic continent. The thinness of the Antarctic Peninsula and its northerly location makes it prone to change due to global warming. The length ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arisen from the same cause, usually an orogeny. Mountain ranges are formed by a variety of geological processes, but most of the significant ones on Earth are the result of plate tectonics. Mountain ranges are also found on many planetary mass objects in the Solar System and are likely a feature of most terrestrial planets. Mountain ranges are usually segmented by highlands or mountain passes and valleys. Individual mountains within the same mountain range do not necessarily have the same geologic structure or petrology. They may be a mix of different orogenic expressions and terranes, for example thrust sheets, uplifted blocks, fold mountains, and volcanic landforms resulting in a variety of rock types. Major ranges Most geolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as crevasses and seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land“Glacier, N., Pronunciation.” Oxford English Dictionary, Oxford UP, June 2024, https://doi.org/10.1093/OED/7553486115. Accessed 25 Jan. 2025. and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on ever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an mean, average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal Body of water, bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised geodetic datumthat is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and Navigation, marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to Calibration, calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead a long-term average of tide gauge readings at a particular reference location. The term ''above sea level'' generally refers to the height above mean sea level (AMSL). The term APSL means above present sea level, comparing sea levels in the past with the level today. Earth's radius at sea level is 6,378.137 km (3,963.191 mi) at the equator. It is 6,356.752 km (3,94 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the world ocean, generally taken to be south of 60th parallel south, 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is the second-smallest of the five principal oceanic divisions, smaller than the Pacific Ocean, Pacific, Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic and Indian Ocean, Indian oceans, and larger than the Arctic Ocean. The maximum depth of the Southern Ocean, using the definition that it lies south of 60th parallel, was surveyed by the Five Deeps Expedition in early February 2019. The expedition's multibeam sonar team identified the deepest point at 60° 28' 46"S, 025° 32' 32"W, with a depth of . The expedition leader and chief submersible pilot Victor Vescovo, has proposed naming this deepest point the "Factorian Deep", based on the name of the crewed submersible ''DSV Limiting Factor'', in which he successfully visited the bottom for the first time on February 3, 2019 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
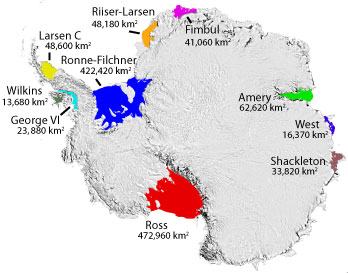
Ice Shelf
An ice shelf is a large platform of glacial ice floating on the ocean, fed by one or multiple tributary glaciers. Ice shelves form along coastlines where the ice thickness is insufficient to displace the more dense surrounding ocean water. The boundary between the ice shelf (floating) and grounded ice (resting on bedrock or sediment) is referred to as the grounding line; the boundary between the ice shelf and the open ocean (often covered by sea ice) is the ice front or calving front. Ice shelves are found in Antarctica and the Arctic (Greenland, Northern Canada, and the Russian Arctic), and can range in thickness from about . The world's largest ice shelves are the Ross Ice Shelf and the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf in Antarctica. The movement of ice shelves is principally driven by gravity-induced pressure from the grounded ice. That flow continually moves ice from the grounding line to the seaward front of the shelf. Typically, a shelf front will extend forward for years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, has increased in concentration by about 50% since the pre-industrial era to levels not seen for millions of years. Climate change has an increasingly large impact on the environment. Deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Amplified warming in the Arctic has c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below a meter (3 ft), the deepest is greater than . Similarly, the area of individual permafrost zones may be limited to narrow mountain summits or extend across vast Arctic regions. The ground beneath glaciers and ice sheets is not usually defined as permafrost, so on land, permafrost is generally located beneath a so-called active layer of soil which freezes and thaws depending on the season. Around 15% of the Northern Hemisphere or 11% of the global surface is underlain by permafrost, covering a total area of around . This includes large areas of Alaska, Canada, Greenland, and Siberia. It is also located in high mountain regions, with the Tibetan Plateau being a prominent example. Only a minority of permafrost exists in the Southern Hemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larsen Ice Shelf
The Larsen Ice Shelf is a long ice shelf in the northwest part of the Weddell Sea, extending along the east coast of the Antarctic Peninsula from Cape Longing to Smith Peninsula. It is named after Captain Carl Anton Larsen, the master of the Norwegian whaling vessel ''Jason'', who sailed along the ice front as far as 68°10' South during December 1893. In finer detail, the Larsen Ice Shelf is a series of shelves that occupy (or occupied) distinct embayments along the coast. From north to south, the segments are called Larsen A (the smallest), Larsen B, and Larsen C (the largest) by researchers who work in the area. Further south, Larsen D and the much smaller Larsen E, F and G are also named. The breakup of the ice shelf since the mid-1990s has been widely reported, with the collapse of Larsen B in 2002 being particularly dramatic. A large section of the Larsen C shelf broke away in July 2017 to form an iceberg known as A-68. The ice shelf originally covered an area of , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacier, glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are the Antarctic ice sheet and the Greenland ice sheet. Ice sheets are bigger than ice shelf, ice shelves or alpine glaciers. Masses of ice covering less than 50,000 km2 are termed an ice cap. An ice cap will typically feed a series of glaciers around its periphery. Although the surface is cold, the base of an ice sheet is generally warmer due to Geothermal activity, geothermal heat. In places, melting occurs and the melt-water lubricates the ice sheet so that it flows more rapidly. This process produces fast-flowing channels in the ice sheet — these are ice streams. Even stable ice sheets are continually in motion as the ice gradually flows outward from the central plateau, which is the tallest point of the ice sheet, and towards the margins. The ice sheet slope is low around the plate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Shelf
An ice shelf is a large platform of glacial ice floating on the ocean, fed by one or multiple tributary glaciers. Ice shelves form along coastlines where the ice thickness is insufficient to displace the more dense surrounding ocean water. The boundary between the ice shelf (floating) and grounded ice (resting on bedrock or sediment) is referred to as the grounding line; the boundary between the ice shelf and the open ocean (often covered by sea ice) is the ice front or calving front. Ice shelves are found in Antarctica and the Arctic (Greenland, Northern Canada, and the Russian Arctic), and can range in thickness from about . The world's largest ice shelves are the Ross Ice Shelf and the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf in Antarctica. The movement of ice shelves is principally driven by gravity-induced pressure from the grounded ice. That flow continually moves ice from the grounding line to the seaward front of the shelf. Typically, a shelf front will extend forward for years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Cap Climate
An ice cap climate is a polar climate where no mean monthly temperature exceeds . The climate generally covers areas at high altitudes and Polar regions of Earth, polar regions (60–90° north and south latitude), such as Antarctica and some of the northernmost islands of Canada and Russia. Most of Greenland is under the influence of an ice cap climate, although the coasts are prone to more influence from the sea, providing more Tundra climate, tundra climates. Some regions on the islands of Norway's Svalbard, Svalbard Archipelago facilitate an ice cap climate. Areas with ice cap climates are normally covered by a permanent layer of ice and have no vegetation. There is limited animal life in most ice cap climates, which are usually found near the oceanic margins. Although ice cap climates are inhospitable to human life and no civilian communities lie in such climates, there are some research stations scattered in Antarctica and interior Greenland. Description Under the Köppen cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |