|
Neoptera
Neoptera (Ancient Greek ''néos'' ("new") + ''pterón'' ("wing")) is a classification group that includes most orders of the winged insects, specifically those that can flex their wings over their abdomens. This is in contrast with the more basal orders of winged insects (the " Palaeoptera" assemblage), which are unable to flex their wings in this way. Classification The taxon Neoptera was proposed by А.М. Martynov in 1923 and 1924, in the following classification: Pterygota *division Palaeoptera **order Odonata **order Agnatha (correct name: Ephemeroptera) **†order Dictyoneuridea **†order Megasecoptera **†order Meganisoptera **†order Protephemeroidea *division Neoptera **superorder Endopterygota ***order Coleoptera ***order Strepsiptera ***order Neuroptera ***order Raphidioptera ***order Megaloptera ***order Diptera ***order Mecoptera ***order Trichoptera ***order Lepidoptera ***order Hymenoptera **subdivision Polyneoptera ***superorder Orthopteroid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoptera
The name Palaeoptera (from Greek ( 'old') + ( 'wing')) has been traditionally applied to those ancestral groups of winged insects (most of them extinct) that lacked the ability to fold the wings back over the abdomen as characterizes the Neoptera. The Diaphanopterodea, which are palaeopteran insects, had independently and uniquely evolved a different wing-folding mechanism. Both mayflies and dragonflies lack any of the smell centers in their brain found in Neoptera. Disputed status The complexities of the wing-folding mechanism, as well as the mechanical operation of the wings in flight ( indirect flight muscles), are such that it indicates that Neoptera is a monophyletic lineage. The plesiomorphic absence of wing-folding does not necessarily mean the Palaeoptera form a natural group – they may be an assemblage containing all insects, closely related or not, that "are not Neoptera", an example of a wastebasket taxon. If the extinct lineages are taken into account, it is lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, Thorax (insect anatomy), thorax and abdomen (insect anatomy), abdomen), three pairs of jointed Arthropod leg, legs, compound eyes, and a pair of antenna (biology), antennae. Insects are the most diverse group of animals, with more than a million described species; they represent more than half of all animal species. The insect nervous system consists of a insect brain, brain and a ventral nerve cord. Most insects reproduce Oviparous, by laying eggs. Insects Respiratory system of insects, breathe air through a system of Spiracle (arthropods), paired openings along their sides, connected to Trachea#Invertebrates, small tubes that take air directly to the tissues. The blood therefore does not carry oxygen; it is only partly contained in ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eumetabola
Eumetabola is an unranked clade of Neoptera. Two large unities known as the Eumetabola and Paurometabola are probably from the adelphotaxa of the Neoptera after exclusion of the Plecoptera. The monophyly of these unities appears to be weakly justified. According to a phylogenetic analysis, the Eumetabola clade originated 390–350 million years ago, in the Late Devonian. Phylogeny The phylogeny of Eumetabola is shown in the cladogram, using the molecular phylogeny of Wipfler et al. 2019 for the Polyneoptera, Johnson et al 2018 for the Paraneoptera (where Psocomorpha contains Phthiraptera), and Kjer et al 2016 for the Holometabola Holometabola (from Ancient Greek "complete" + "change"), also known as Endopterygota (from "inner" + "wing" + Neo-Latin "-having"), is a supra-order (biology), ordinal clade of insects within the infraclass Neoptera that go through distincti .... References External links Eumetabola Hennig 1953''insecta.bio.spbu.ru'' * Grimaldi, D.; En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterygota
Pterygota ( ) is a subclass of insects that includes all winged insects and groups who lost them secondarily. Pterygota group comprises 99.9% of all insects. The orders not included are the Archaeognatha (jumping bristletails) and the Zygentoma ( silverfishes and firebrats), two primitively wingless insect orders. Unlike Archaeognatha and Zygentoma, the pterygotes do not have styli or vesicles on their abdomen (also absent in some zygentomans), and with the exception of the majority of mayflies, are also missing the median terminal filament which is present in the ancestrally wingless insects. The oldest known representatives of the group appeared during the mid-Carboniferous, around 328–324 million years ago, and the group subsequently underwent rapid diversification. Claims that they originated substantially earlier during the Silurian or Devonian based on molecular clock estimates are unlikely based on the fossil record, and are likely analytical artefacts. __TOC__ Sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endopterygota
Holometabola (from Ancient Greek "complete" + "change"), also known as Endopterygota (from "inner" + "wing" + Neo-Latin "-having"), is a supra- ordinal clade of insects within the infraclass Neoptera that go through distinctive larval, pupal, and adult stages. They undergo a radical metamorphosis, with the larval and adult stages differing considerably in their structure and behaviour. This is called holometabolism, or complete metamorphism. Evolution The Holometabola constitute the most diverse insect superorder, with over 1 million living species divided between 11 orders, containing insects such as butterflies, flies, fleas, bees, ants, and beetles. The earliest holometabolan fossils date from the Carboniferous. The Holometabola are sometimes divided into three assemblages: Neuropterida (Neuroptera, Megaloptera, Raphidioptera, Strepsiptera and Coleoptera), Hymenopteroida (Hymenoptera), and Panorpida (Siphonaptera, Diptera, Trichoptera, Lepidoptera and Mecoptera). Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holometabola
Holometabola (from Ancient Greek "complete" + "change"), also known as Endopterygota (from "inner" + "wing" + Neo-Latin "-having"), is a supra-order (biology), ordinal clade of insects within the infraclass Neoptera that go through distinctive larval, pupal, and adult stages. They undergo a radical Metamorphosis (biology), metamorphosis, with the larval and adult stages differing considerably in their structure and behaviour. This is called holometabolism, or complete metamorphism. Evolution The Holometabola constitute the most diverse insect superorder, with over 1 million living species divided between 11 Order (biology), orders, containing insects such as butterfly, butterflies, fly, flies, fleas, bees, ants, and beetles. The earliest holometabolan fossils date from the Carboniferous. The Holometabola are sometimes divided into three assemblages: Neuropterida (Neuroptera, Megaloptera, Raphidioptera, Strepsiptera and Coleoptera), Hymenopteroida (Hymenoptera), and Panorpi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraneoptera
Paraneoptera or Acercaria is a Order (biology), superorder of insects which includes Psocodea, lice (Psocoptera, bark lice and Louse, true lice), thrips, and hemipterans, the true bugs. It also includes the extinct order Permopsocida, known from fossils dating from the Cisuralian, Early Permian to the mid-Cretaceous. All of the insects classified here exhibit various “reductions” or “simplifications” from the primitive body-plan found in typical polyneopterans. Cercus, Cerci, for example, are entirely absent in all living paraneopterans (Acercaria meaning without cerci). Other “reductions” occur in wing venation, in the number of tarsal segments (no more than three), only four Malpighian tubules, and only one complex of abdominal ganglia. The mouthparts of the Paraneoptera reflect diverse feeding habits. Basal groups are microbial surface feeders, whereas more advanced groups feed on plant or animal fluids. Phylogeny Paraneoptera consists of Psocodea (lice), along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyneoptera
The cohort Polyneoptera is one of the major groups of winged insects, comprising the Orthoptera (grasshoppers, crickets, etc.) and all other neopteran insects believed to be more closely related to Orthoptera than to any other insect orders. They were formerly grouped together with the Palaeoptera and Paraneoptera as the Hemimetabola or Exopterygota on the grounds that they have no pupa, the wings gradually developing externally throughout the nymphal stages. Many members of the group have leathery forewings ( tegmina) and hindwings with an enlarged anal field (vannus). When Carl Linnaeus started applying binomial names to animals in the 10th edition of his ''Systema Naturae'' in 1758, there were few animals included in the scheme, and consequently few groups. As more and more new species were discovered and differences recognised, the original groups proposed by Linnaeus were split up. Originally all polyneopteran insects were in the genus ''Gryllus'', this genus now con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plecoptera
Plecoptera is an order (biology), order of insects commonly known as stoneflies. Some 3,500 species are described worldwide, with new species still being discovered. Stoneflies are found worldwide, except Antarctica. Stoneflies are believed to be one of the most primitive groups of Neoptera, with close relatives identified from the Carboniferous and Lower Permian geological periods, while true stoneflies are known from fossils only a bit younger. Their modern diversity, however, apparently is of Mesozoic origin. Plecoptera are found in both the Southern hemisphere, Southern and Northern Hemispheres, and the populations are quite distinct, although the evolutionary evidence suggests species may have crossed the equator on a number of occasions before once again becoming geographically isolated. All species of Plecoptera are intolerant of water pollution, and the presence of their nymph (biology), nymphs in a stream or still water is usually an indicator of good or excellent water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthoptera
Orthoptera () is an order of insects that comprises the grasshoppers, locusts, and crickets, including closely related insects, such as the bush crickets or katydids and wētā. The order is subdivided into two suborders: Caelifera – grasshoppers, locusts, and close relatives; and Ensifera – crickets and close relatives. More than 20,000 species are distributed worldwide. The insects in the order have incomplete metamorphosis, and produce sound (known as a " stridulation") by rubbing their wings against each other or their legs, the wings or legs containing rows of corrugated bumps. The tympanum, or ear, is located in the front tibia in crickets, mole crickets, and bush crickets or katydids, and on the first abdominal segment in the grasshoppers and locusts. These organisms use vibrations to locate other individuals. Grasshoppers and other orthopterans are able to fold their wings (i.e. they are members of Neoptera). Etymology The name is derived from the Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
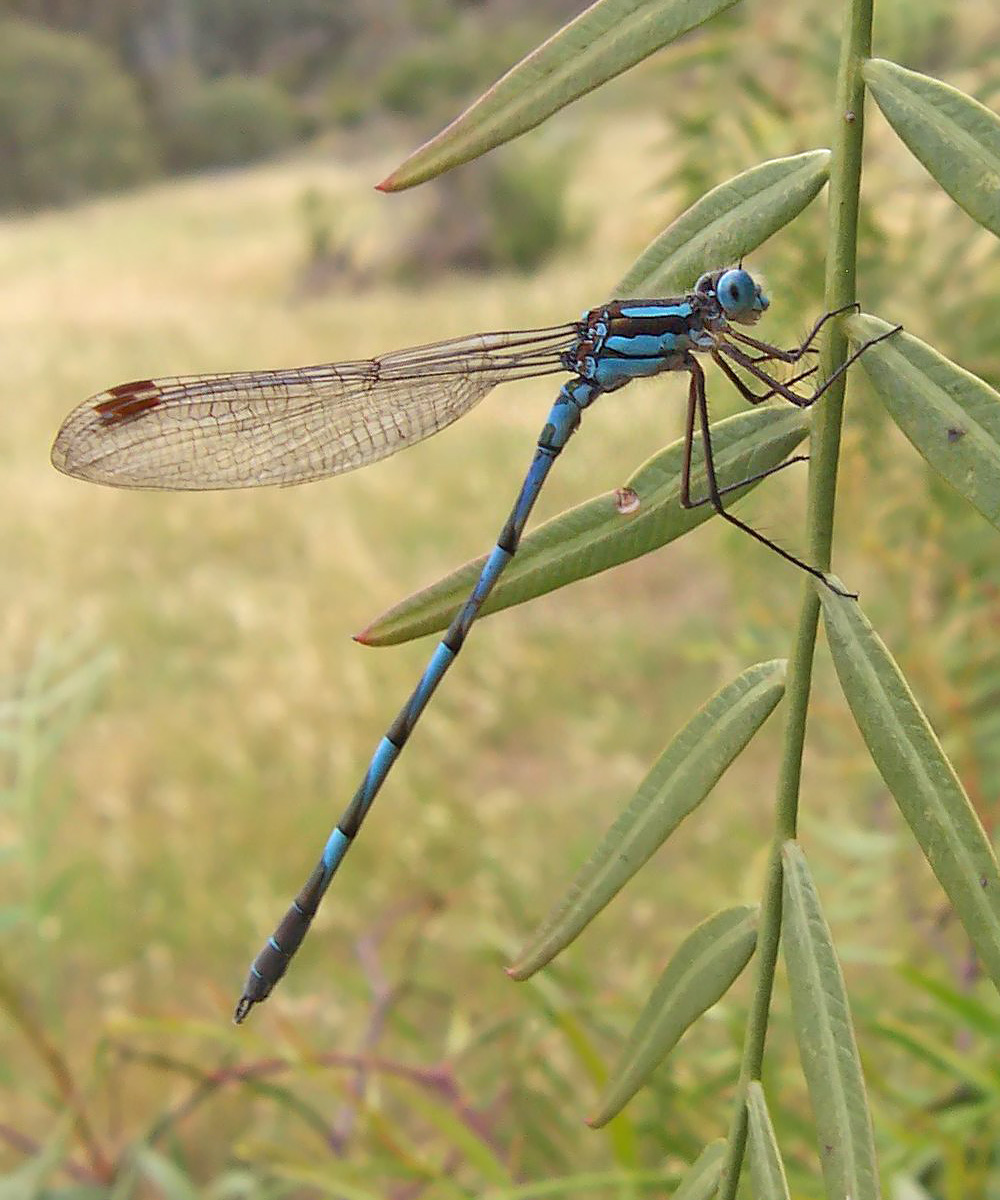
Odonata
Odonata is an order of predatory flying insects that includes the dragonflies and damselflies (as well as the '' Epiophlebia'' damsel-dragonflies). The two major groups are distinguished with dragonflies (Anisoptera) usually being bulkier with large compound eyes together and wings spread up or out at rest, while damselflies (suborder Zygoptera) are usually more slender with eyes placed apart and wings folded together along body at rest. Adult odonates can land and perch, but rarely walk. All odonates have aquatic larvae called naiads or nymphs, and all of them, larvae and adults, are carnivorous and are almost entirely insectivorous, although at the larval stage they will eat anything that they can overpower, including small fish, tadpoles, and even adult newts. The adults are superb aerial hunters and their legs are specialised for catching prey in flight. Odonata in its narrow sense forms a subgroup of the broader Odonatoptera, which contains other dragonfly-like insects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |