|
NASA Programs
This is a list of NASA missions, both Human spaceflight, crewed and Robotic spacecraft, robotic, Creation of NASA, since the establishment of NASA in 1957. There are over 80 currently active science missions. X-Plane program Since 1945, NACA (NASA's predecessor) and, since January 26, 1958, NASA has conducted the X-Plane Program. The program was originally intended to create a family of experimental aircraft not intended for production beyond the limited number of each design built solely for flight research. The first X-Plane, the Bell X-1, was the first rocket-powered airplane to break the sound barrier on October 14, 1947. X-Planes have set numerous milestones since then, both crewed and unpiloted. Human spaceflight NASA has successfully launched over 200 crewed flights. Three have ended in failure, causing the death of the entire crew: Apollo 1 (which never launched) in 1967 lost three crew members, STS-51-L (Space Shuttle Challenger disaster, the ''Challenger'' disa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Spacecraft Comparison2
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-107
STS-107 was the 113th flight of the Space Shuttle program, and the 28th(twenty eigth) and final flight of Space Shuttle ''Columbia''. The mission ended on the 1st of February 2003, with the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster which killed all seven crew members and destroyed the space shuttle. It was the 88th post- ''Challenger'' disaster mission. The flight launched from Kennedy Space Center in Florida on January 16, 2003. It spent 15 days, 22 hours, 20 minutes, 32 seconds in orbit. The crew conducted a multitude of international scientific experiments. The disaster occurred during reentry while the orbiter was over Texas. Immediately after the disaster, NASA convened the ''Columbia'' Accident Investigation Board to determine the cause of the disintegration. The source of the failure was determined to have been caused by a piece of foam that broke off during launch and damaged the thermal protection system ( reinforced carbon-carbon panels and thermal protection tiles) on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skylab
Skylab was the United States' first space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three trios of astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Skylab was constructed from a repurposed Saturn V third stage (the S-IVB), and took the place of the stage during launch. Operations included an orbital workshop, a solar observatory, Earth observation and hundreds of experiments. Skylab's orbit eventually decayed and it disintegrated in the atmosphere on July 11, 1979, scattering debris across the Indian Ocean and Western Australia. Overview Skylab was the only space station operated exclusively by the United States. A permanent station was planned starting in 1988, but its funding was canceled and U.S. participation shifted to the International Space Station in 1993. Skylab had a mass of with a Apollo command and service module (CSM) attached and included a workshop, a solar observatory, and sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
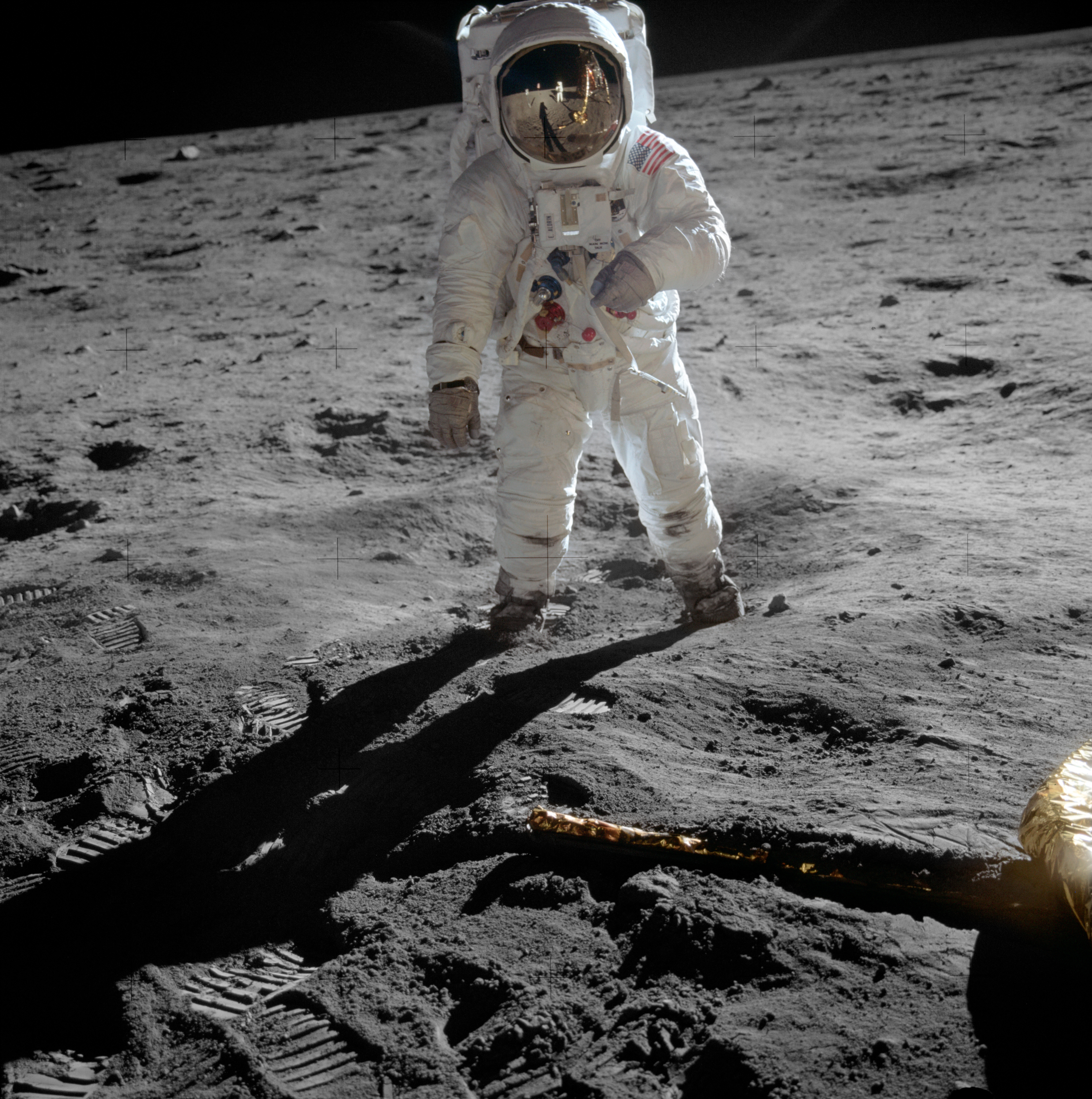
List Of Apollo Missions
The Apollo program was a United States human spaceflight program carried out from 1961 to 1972 by the NASA, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), which landed the first List of Apollo astronauts, astronauts on the Moon. The program used the Saturn IB and Saturn V launch vehicles to lift the Apollo command and service module, Command/Service Module (CSM) and Apollo Lunar Module, Lunar Module (LM) spacecraft into space, and the Little Joe II rocket to test a launch escape system which was expected to carry the astronauts to safety in the event of a Saturn failure. Uncrewed test flights beginning in 1966 demonstrated the safety of the launch vehicles and spacecraft to carry astronauts, and four crewed flights beginning in October 1968 demonstrated the ability of the spacecraft to carry out a lunar landing mission. Apollo achieved the first crewed lunar landing on the Apollo 11 mission, when Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin landed their Lunar Module Eagle, LM ''Eagle'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo 17
Apollo 17 (December 7–19, 1972) was the eleventh and final mission of NASA's Apollo program, the sixth and most recent time humans have set foot on the Moon. Commander Gene Cernan and Lunar Module Pilot Harrison Schmitt walked on the Moon, while Command Module Pilot Ronald Evans (astronaut), Ronald Evans orbited above. Schmitt was the only professional geologist to land on the Moon; he was selected in place of Joe Engle, as NASA had been under pressure to send a scientist to the Moon. The mission's heavy emphasis on science meant the inclusion of a number of new experiments, including a Fe, Fi, Fo, Fum, and Phooey, biological experiment containing five mice that was carried in the command module. Mission planners had two primary goals in deciding on the landing site: to sample Lunar highlands, lunar highland material older than that at Mare Imbrium and to investigate the possibility of relatively recent Volcano, volcanic activity. They therefore selected Taurus–Littrow, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo 7
Apollo 7 (October 11–22, 1968) was the first crewed flight in NASA's Apollo program, and saw the resumption of human spaceflight by the agency after the fire that had killed the three Apollo 1 astronauts during a launch rehearsal test on January 27, 1967. The Apollo7 crew commander (Apollo program), was commanded by Wally Schirra, Walter M. Schirra, with Command Module Pilot Donn F. Eisele and Lunar Module pilot Walter Cunningham, R. Walter Cunningham (so designated even though Apollo7 did not carry a Apollo Lunar Module, Lunar Module). The three astronauts were originally designated for the second crewed Apollo flight, and then as backups for Apollo1. After the Apollo1 fire, crewed flights were suspended while the cause of the accident was investigated and improvements made to the spacecraft and safety procedures, and uncrewed test flights made. Determined to prevent a repetition of the fire, the crew spent long periods monitoring the construction of their Apollo comma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo Program
The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the United States human spaceflight program led by NASA, which Moon landing, landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969. Apollo followed Project Mercury that put the first Americans in space. It was conceived in 1960 as a three-person spacecraft during President Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower, Dwight D. Eisenhower's administration. Apollo was later dedicated to President John F. Kennedy's national goal for the 1960s of "landing a man on the Moon and returning him safely to the Earth" in an address to United States Congress, Congress on May 25, 1961. It was the third American human spaceflight program to fly, preceded by Project Gemini conceived in 1961 to extend spaceflight capability in support of Apollo. Kennedy's goal was accomplished on the Apollo 11 mission when astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin landed their Apollo Lunar Module (LM) on July 20, 1969, and walked on the lunar surface, while Michael Collins ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extra-vehicular Activity
Extravehicular activity (EVA) is any activity done by an astronaut in outer space outside a spacecraft. In the absence of a breathable Earthlike atmosphere, the astronaut is completely reliant on a space suit for environmental support. EVA includes spacewalks and lunar or planetary surface exploration (commonly known from 1969 to 1972 as moonwalks). In a stand-up EVA (SEVA), an astronaut stands through an open hatch but does not fully leave the spacecraft. EVAs have been conducted by the Soviet Union/Russia, the United States, Canada, the European Space Agency and China. On March 18, 1965, Alexei Leonov became the first human to perform a spacewalk, exiting the Voskhod 2 capsule for 12 minutes and 9 seconds. On July 20, 1969, Neil Armstrong became the first human to perform a moonwalk, outside his lunar lander on Apollo 11 for 2 hours and 31 minutes. In 1984, Svetlana Savitskaya became the first woman to perform a spacewalk, conducting EVA outside the Salyut 7 space stati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemini 12
Gemini 12 (officially Gemini XII) With Gemini IV, NASA changed to Roman numerals for Gemini mission designations. was a 1966 crewed spaceflight in NASA's Project Gemini. It was the 10th and final crewed Gemini flight (Gemini 1 and Gemini 2 were uncrewed missions), the 18th crewed American spaceflight, and the 26th spaceflight of all time, including X-15 flights over . Commanded by Gemini 7, Gemini VII veteran Jim Lovell, James A. Lovell, the flight featured three periods of extravehicular activity (EVA) by rookie Buzz Aldrin, Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin, lasting a total of 5 hours and 30 minutes. It also achieved the fifth space rendezvous, rendezvous and fourth docking and berthing of spacecraft, docking with an Agena target vehicle. Gemini XII marked a successful conclusion of the Gemini program, achieving the last of its goals by successfully demonstrating that astronauts can effectively work outside of spacecraft. This was instrumental in paving the way for the Apollo program to achi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemini 3
Gemini 3 was the first crewed mission in NASA's Project Gemini and was the first time two American astronauts flew together into space. On March 23, 1965, astronauts Gus Grissom and John Young flew three low Earth orbits in their spacecraft, which they nicknamed '' Molly Brown''. It was the first U.S. mission in which the crew fired thrusters to change the size and shape of their orbit, a key test of spacecraft maneuverability vital for planned flights to the Moon. It was also the final crewed flight controlled from Cape Kennedy Air Force Station in Florida, before mission control functions were moved to a new control center at the newly opened Manned Spacecraft Center in Houston, Texas. Crew Backup crew Original crew Support crew * Roger B. Chaffee (Houston CAPCOM) * L. Gordon Cooper Jr. (Cape CAPCOM) Mission parameters * Mass: * Perigee: * Apogee: * Inclination: 32.6 degrees * Period: 88.3 minutes Objectives The mission's primary goal was to test the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Gemini
Project Gemini () was the second United States human spaceflight program to fly. Conducted after the first American crewed space program, Project Mercury, while the Apollo program was still in early development, Gemini was conceived in 1961 and concluded in 1966. The Gemini spacecraft carried a two-astronaut crew. Ten Gemini crews and 16 individual astronauts flew low Earth orbit (LEO) missions during 1965 and 1966. Gemini's objective was the development of space travel techniques to support the Apollo mission to Moon landing, land astronauts on the Moon. In doing so, it allowed the United States to catch up and overcome the lead in human spaceflight capability the Soviet Union had obtained in the early years of the Space Race, by demonstrating mission endurance up to just under 14 days, longer than the eight days required for a round trip to the Moon; methods of performing extravehicular activity (EVA) without tiring; and the orbital maneuvers necessary to achieve space rendezv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
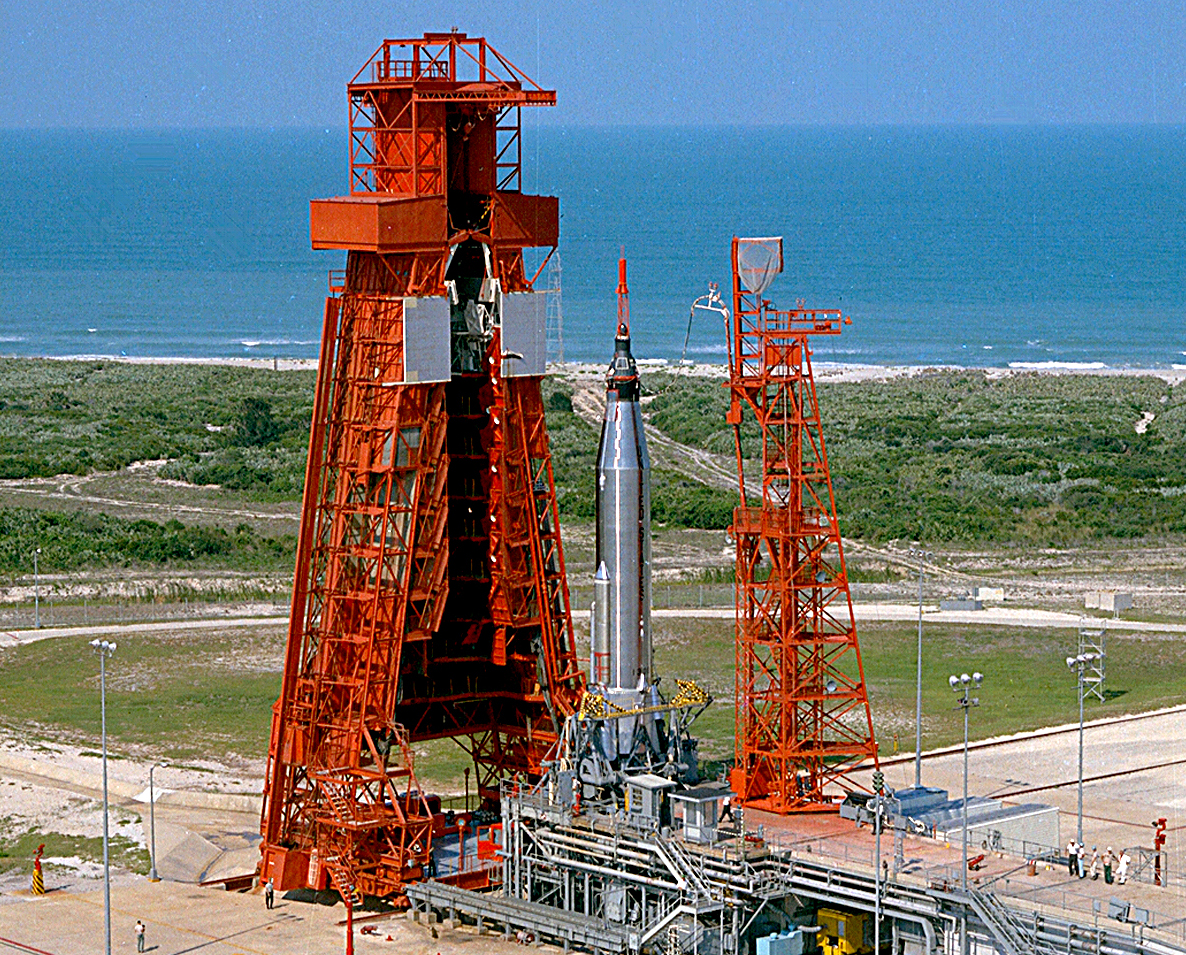
Mercury-Atlas 9
Mercury-Atlas 9 was the final crewed space mission of the U.S. Mercury program, launched on May 15, 1963, from Launch Complex 14 at Cape Canaveral, Florida. The spacecraft, named ''Faith 7'', completed 22 Earth orbits before splashing down in the Pacific Ocean, piloted by astronaut Gordon Cooper, then a United States Air Force major. The Atlas rocket was No. 130-D, and the Mercury spacecraft was No. 20. As of , this mission marks the last time an American was launched alone to conduct an entirely solo orbital mission. Flight directors * Chris KraftRed team * John HodgeBlue team Mission parameters *Mass: *Perigee: 161 km *Apogee: 267 km *Inclination: 32.5° * Period: 88.5 min Mission background Debate over Mercury project continuation The Mercury-Atlas 8 flight of Walter Schirra on October 3, 1962, had been so nearly perfect that some at NASA thought that the United States should quit while it was ahead and make MA-8 the last Mercury mission rather than ris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |