|
Metal Matrix Composites
In materials science, a metal matrix composite (MMC) is a composite material with fibers or particles dispersed in a metallic matrix, such as copper, aluminum, or steel. The secondary phase is typically a ceramic (such as alumina or silicon carbide) or another metal (such as steel). They are typically classified according to the type of reinforcement: short discontinuous fibers (whiskers), continuous fibers, or particulates. There is some overlap between MMCs and cermets, with the latter typically consisting of less than 20% metal by volume. When at least three materials are present, it is called a hybrid composite. MMCs can have much higher strength-to-weight ratios, stiffness, and ductility than traditional materials, so they are often used in demanding applications. MMCs typically have lower thermal and electrical conductivity and poor resistance to radiation, limiting their use in the very harshest environments. Composition MMCs are made by dispersing a reinforcing mater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Materials Science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field of researching and discovering materials. Materials engineering is an engineering field of finding uses for materials in other fields and industries. The intellectual origins of materials science stem from the Age of Enlightenment, when researchers began to use analytical thinking from chemistry, physics, and engineering to understand ancient, phenomenological observations in metallurgy and mineralogy. Materials science still incorporates elements of physics, chemistry, and engineering. As such, the field was long considered by academic institutions as a sub-field of these related fields. Beginning in the 1940s, materials science began to be more widely recognized as a specific and distinct field of science and engineering, and major technical universities around the world created dedicated schools for its study. Materials scientists emphasize understanding how the history of a material (''processing'') influences its struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
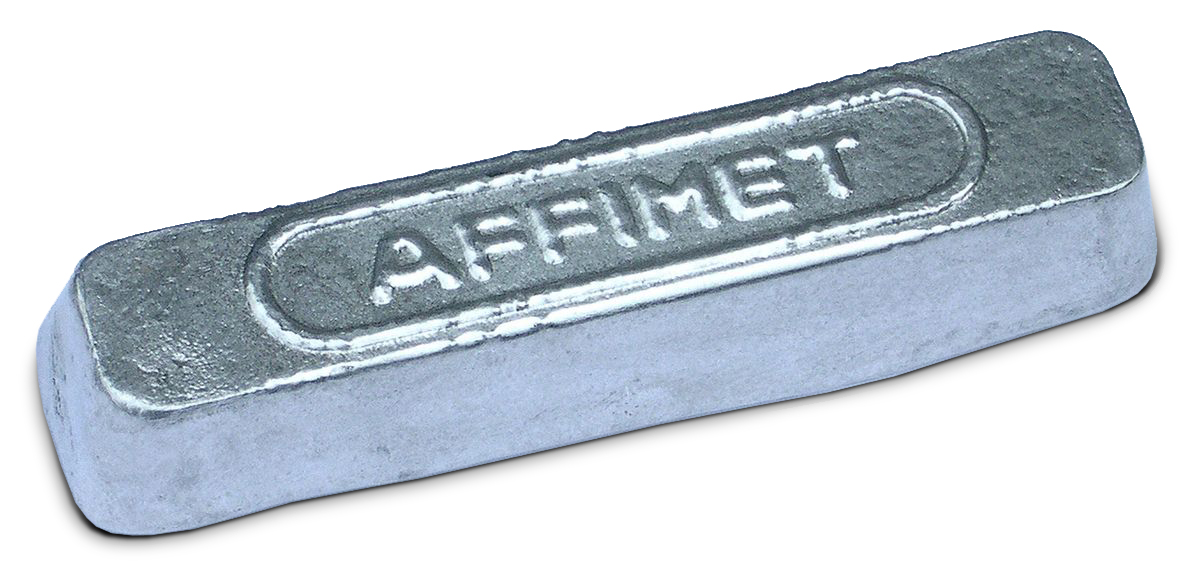
Aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has a great affinity towards oxygen, passivation (chemistry), forming a protective layer of aluminium oxide, oxide on the surface when exposed to air. It visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, magnetism, nonmagnetic, and ductility, ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al, which is highly abundant, making aluminium the abundance of the chemical elements, 12th-most abundant element in the universe. The radioactive decay, radioactivity of aluminium-26, 26Al leads to it being used in radiometric dating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
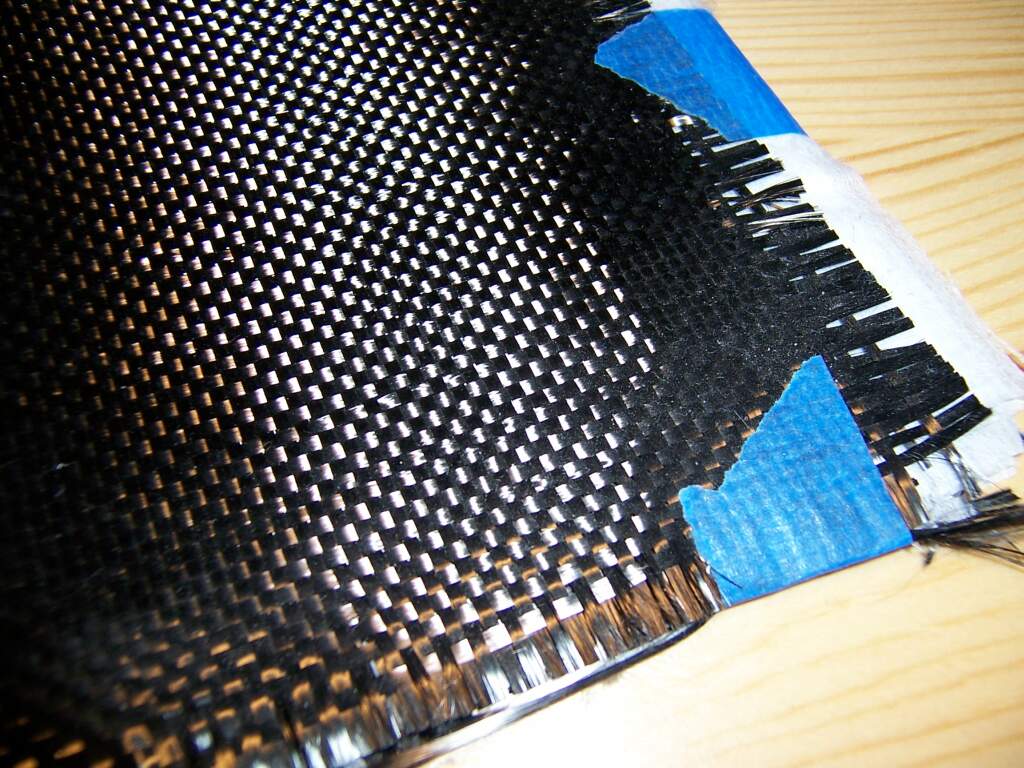
Carbon (fiber)
Carbon fibers or carbon fibres (alternatively CF, graphite fiber or graphite fibre) are fibers about in diameter and composed mostly of carbon atoms. Carbon fibers have several advantages: high stiffness, high tensile strength, high strength to weight ratio, high chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and low thermal expansion. These properties have made carbon fiber very popular in aerospace, civil engineering, military, motorsports, and other competition sports. However, they are relatively expensive compared to similar fibers, such as glass fiber, basalt fibers, or plastic fibers. To produce a carbon fiber, the carbon atoms are bonded together in crystals that are more or less aligned parallel to the fiber's long axis as the crystal alignment gives the fiber a high strength-to-volume ratio (in other words, it is strong for its size). Several thousand carbon fibers are bundled together to form a tow, which may be used by itself or woven into a fabric. Carb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotropic
In physics and geometry, isotropy () is uniformity in all orientations. Precise definitions depend on the subject area. Exceptions, or inequalities, are frequently indicated by the prefix ' or ', hence '' anisotropy''. ''Anisotropy'' is also used to describe situations where properties vary systematically, dependent on direction. Isotropic radiation has the same intensity regardless of the direction of measurement, and an isotropic field exerts the same action regardless of how the test particle is oriented. Mathematics Within mathematics, ''isotropy'' has a few different meanings: ; Isotropic manifolds: A manifold is isotropic if the geometry on the manifold is the same regardless of direction. A similar concept is homogeneity. ; Isotropic quadratic form: A quadratic form ''q'' is said to be isotropic if there is a non-zero vector ''v'' such that ; such a ''v'' is an isotropic vector or null vector. In complex geometry, a line through the origin in the direction of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to heat conduction, conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa and is measured in W·m−1·K−1. Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal conductivity. For instance, metals typically have high thermal conductivity and are very efficient at conducting heat, while the opposite is true for insulating materials such as mineral wool or Styrofoam. Metals have this high thermal conductivity due to free electrons facilitating heat transfer. Correspondingly, materials of high thermal conductivity are widely used in heat sink applications, and materials of low thermal conductivity are used as thermal insulation. The reciprocal of thermal conductivity is called thermal resistivity. The defining equation for thermal conductivity is \mathbf = - k \nabla T, where \mathbf is the heat flux, k is the thermal conductivity, and \nabla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. Types of friction include dry, fluid, lubricated, skin, and internal -- an incomplete list. The study of the processes involved is called tribology, and has a history of more than 2000 years. Friction can have dramatic consequences, as illustrated by the use of friction created by rubbing pieces of wood together to start a fire. Another important consequence of many types of friction can be wear, which may lead to performance degradation or damage to components. It is known that frictional energy losses account for about 20% of the total energy expenditure of the world. As briefly discussed later, there are many different contributors to the retarding force in friction, ranging from asperity deformation to the generation of charges and changes in local structure. When two bodies in contact move relative to each other, due to these variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wear Resistance
Wear is the damaging, gradual removal or deformation of material at solid surfaces. Causes of wear can be mechanical (e.g., erosion) or chemical (e.g., corrosion). The study of wear and related processes is referred to as tribology. Wear in machine elements, together with other processes such as fatigue and creep, causes functional surfaces to degrade, eventually leading to material failure or loss of functionality. Thus, wear has large economic relevance as first outlined in the Jost Report. Abrasive wear alone has been estimated to cost 1–4% of the gross national product of industrialized nations. Wear of metals occurs by plastic displacement of surface and near-surface material and by detachment of particles that form wear debris. The particle size may vary from millimeters to nanometers. This process may occur by contact with other metals, nonmetallic solids, flowing liquids, solid particles or liquid droplets entrained in flowing gasses. The wear rate is affected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, somewhat brittle, gray metal. Cobalt-based blue pigments (cobalt blue) have been used since antiquity for jewelry and paints, and to impart a distinctive blue tint to glass. The color was long thought to be due to the metal bismuth. Miners had long used the name ''kobold ore'' (German language, German for ''goblin ore'') for some of the blue pigment-producing minerals. They were so named because they were poor in known metals and gave off poisonous arsenic-containing fumes when smelted. In 1735, such ores were found to be reducible to a new metal (the first discovered since ancient times), which was ultimately named for the ''kobold''. Today, some cobalt is produced sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll and Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide (TiO2), is a popular photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments. Other compounds include titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), a component of smoke screens and cata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic table), it occurs naturally only in combination with other elements and almost always has an oxidation state of +2. It reacts readily with air to form a thin Passivation (chemistry), passivation coating of magnesium oxide that inhibits further corrosion of the metal. The free metal burns with a brilliant-white light. The metal is obtained mainly by electrolysis of magnesium Salt (chemistry), salts obtained from brine. It is less dense than aluminium and is used primarily as a component in strong and lightweight magnesium alloy, alloys that contain aluminium. In the cosmos, magnesium is produced in large, aging stars by the sequential addition of three Helium nucleus, helium nuclei to a carbon nucleus. When such stars explo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminum
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has a great affinity towards oxygen, passivation (chemistry), forming a protective layer of aluminium oxide, oxide on the surface when exposed to air. It visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, magnetism, nonmagnetic, and ductility, ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al, which is highly abundant, making aluminium the abundance of the chemical elements, 12th-most abundant element in the universe. The radioactive decay, radioactivity of aluminium-26, 26Al leads to it being used in radiometric dating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
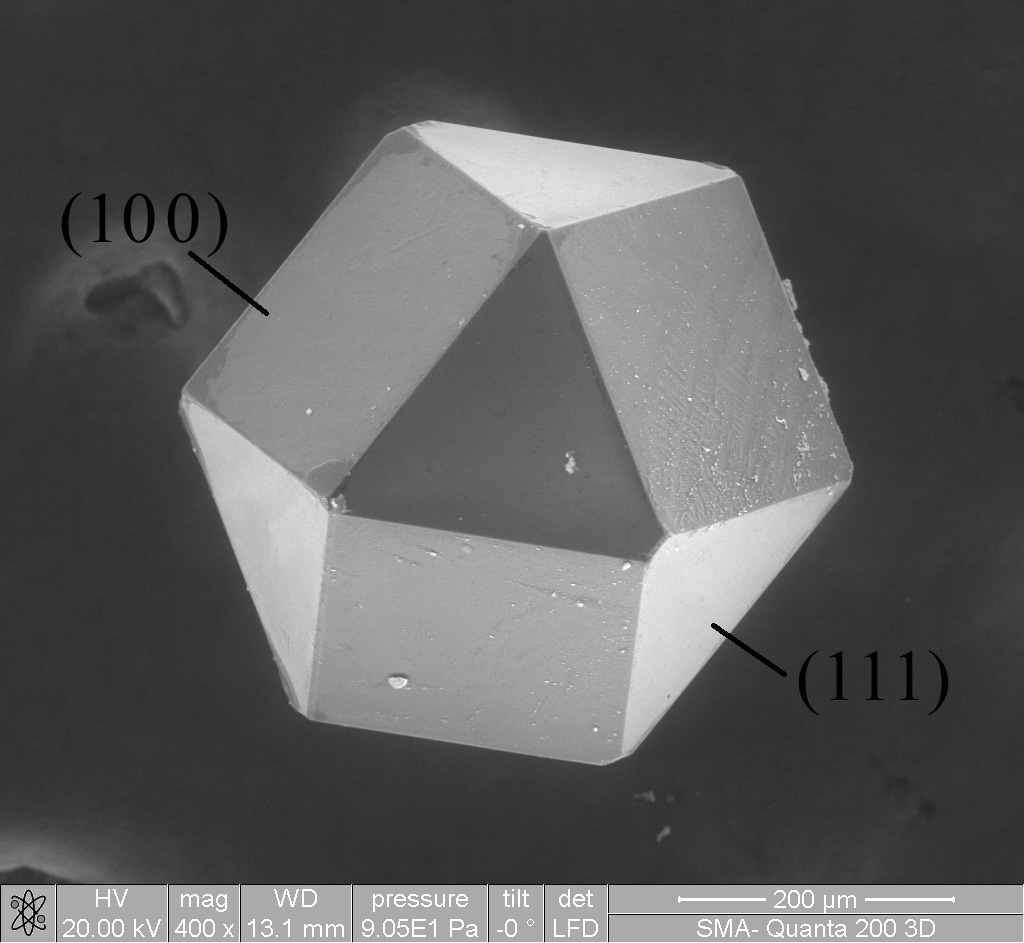
Single Crystal
In materials science, a single crystal (or single-crystal solid or monocrystalline solid) is a material in which the crystal lattice of the entire sample is continuous and unbroken to the edges of the sample, with no Grain boundary, grain boundaries. The absence of the crystallographic defect, defects associated with grain boundaries can give monocrystals unique properties, particularly mechanical, optical and electrical, which can also be anisotropic, depending on the type of crystallography, crystallographic structure. These properties, in addition to making some gems precious, are industrially used in technological applications, especially in optics and electronics. Because entropy, entropic effects favor the presence of some imperfections in the microstructure of solids, such as impurity, impurities, inhomogeneous strain and crystallographic defects such as dislocations, perfect single crystals of meaningful size are exceedingly rare in nature. The necessary laboratory condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |