|
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a group of international standards for the compression of digital audio and visual data, multimedia systems, and file storage formats. It was originally introduced in late 1998 as a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) (ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC29/WG11) under the formal standard ISO/IEC 14496 – ''Coding of audio-visual objects''. Uses of MPEG-4 include compression of audiovisual data for Internet video and CD distribution, voice (telephone, videophone) and broadcast television applications. The MPEG-4 standard was developed by a group led by Touradj Ebrahimi (later the JPEG president) and Fernando Pereira. Background MPEG-4 absorbs many of the features of MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 and other related standards, adding new features such as (extended) VRML support for 3D rendering, object-oriented composite files (including audio, video and VRML objects), support for externally specified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Audio Coding
Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) is an audio coding standard for lossy digital audio compression. It was developed by Dolby, AT&T, Fraunhofer and Sony, originally as part of the MPEG-2 specification but later improved under MPEG-4.ISO (2006ISO/IEC 13818-7:2006 – Information technology — Generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information — Part 7: Advanced Audio Coding (AAC), Retrieved on 2009-08-06ISO (2006, Retrieved on 2009-08-06 AAC was designed to be the successor of the MP3 format (MPEG-2 Audio Layer III) and generally achieves higher sound quality than MP3 at the same bit rate. AAC encoded audio files are typically packaged in an MP4 container most commonly using the filename extension .m4a. The basic profile of AAC (both MPEG-4 and MPEG-2) is called AAC-LC (''Low Complexity''). It is widely supported in the industry and has been adopted as the default or standard audio format on products including Apple's iTunes Store, Nintendo's Wii, DSi and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
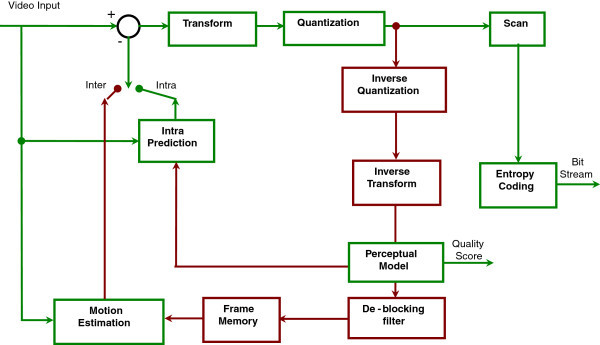
MPEG-4 Part 2
MPEG-4 Part 2, MPEG-4 Visual (formally International Organization for Standardization, ISO/International Electrotechnical Commission, IEC 14496-2) is a video encoding specification designed by the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG). It belongs to the MPEG-4 ISO/IEC family of encoders. It uses block-wise motion compensation and a discrete cosine transform (DCT), similar to previous encoders such as MPEG-1#Part 2: Video, MPEG-1 Part 2 and H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2. Examples of popular implementations of the encoder specifications include DivX, Xvid and Nero Digital. MPEG-4 Part 2 is H.263 compatible in the sense that a basic H.263 bitstream is correctly decoded by an MPEG-4 Video decoder. (MPEG-4 Video decoder is natively capable of decoding a basic form of H.263.) In MPEG-4 Visual, there are two types of video object layers: the video object layer that provides full MPEG-4 functionality, and a reduced functionality video object layer, the video object layer with short headers (which prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-4 Part 10
Advanced Video Coding (AVC), also referred to as H.264 or MPEG-4 Part 10, is a video compression standard based on block-oriented, motion-compensated coding. It is by far the most commonly used format for the recording, compression, and distribution of video content, used by 84–86% of video industry developers . It supports a maximum resolution of 8K UHD. The intent of the H.264/AVC project was to create a standard capable of providing good video quality at substantially lower bit rates than previous standards (i.e., half or less the bit rate of MPEG-2, H.263, or MPEG-4 Part 2), without increasing the complexity of design so much that it would be impractical or excessively expensive to implement. This was achieved with features such as a reduced-complexity integer discrete cosine transform (integer DCT), variable block-size segmentation, and multi-picture inter-picture prediction. An additional goal was to provide enough flexibility to allow the standard to be applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QuickTime
QuickTime (or QuickTime Player) is an extensible multimedia architecture created by Apple, which supports playing, streaming, encoding, and transcoding a variety of digital media formats. The term ''QuickTime'' also refers to the QuickTime Player front-end media player application, which is built-into macOS, and was formerly available for Windows. QuickTime was created in 1991, when the concept of playing digital video directly on computers was "groundbreaking." QuickTime could embed a number of advanced media types, including panoramic images (called QuickTime VR) and Adobe Flash. Over the 1990s, QuickTime became a dominant standard for digital multimedia, as it was integrated into many websites, applications, and video games, and adopted by professional filmmakers. The QuickTime File Format became the basis for the MPEG-4 standard. During its heyday, QuickTime was notably used to create the innovative ''Myst'' and '' Xplora1'' video games, and to exclusively distribute mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moving Picture Experts Group
The Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) is an alliance of working groups established jointly by ISO and IEC that sets standards for media coding, including compression coding of audio, video, graphics, and genomic data; and transmission and file formats for various applications.John Watkinson, ''The MPEG Handbook'', p. 1 Together with JPEG, MPEG is organized under ISO/IEC JTC 1/ SC 29 – ''Coding of audio, picture, multimedia and hypermedia information'' (ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee 1, Subcommittee 29). MPEG formats are used in various multimedia systems. The most well known older MPEG media formats typically use MPEG-1, MPEG-2, and MPEG-4 AVC media coding and MPEG-2 systems transport streams and program streams. Newer systems typically use the MPEG base media file format and dynamic streaming (a.k.a. MPEG-DASH). History MPEG was established in 1988 by the initiative of Dr. Hiroshi Yasuda ( NTT) and Dr. Leonardo Chiariglione ( CSELT). Chiariglione was th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X264
x264 is a free and open-source software library and a command-line utility developed by VideoLAN for encoding video streams into the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC video coding format. It is released under the terms of the GNU General Public License. History x264 was originally developed by Laurent Aimar, who stopped development in 2004 after being hired by ATEME. Loren Merritt then took over development. Later, in 2008, Fiona Glaser joined the project. They both stopped contributing in 2014. Today, x264 is primarily developed by Anton Mitrofanov and Henrik Gramner. Capabilities x264 provides a command line interface as well as an API. The former is used by many graphical user interfaces, such as Staxrip and MeGUI. The latter is used by many other interfaces, such as HandBrake and FFmpeg. x264 implements a large number of features compared to other H.264 encoders. x264 contains some psychovisual enhancements which aim to increase the subjective video quality of the encoded video. * Ada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Video
Internet video (also known as online video) is digital video that is distributed over the internet. Internet video exists in several formats, the most notable being MPEG-4i AVC, AVCHD, FLV, and MP4. There are several online video hosting services, including YouTube. In recent years, the platform of internet video has been used to stream live events. As a result of the popularity of online video, notable events like the 2012 U.S. presidential debates have been streamed live on the internet. Additionally, internet video has played an important role in the music industry as a medium to watch music videos and increase exposure of songs. Video file formats Practical online video streaming was only made possible with advances in data compression, due to the impractically high bandwidth requirements of uncompressed video. Raw digital video requires a bandwidth of 168Mbit/s for SD video, and over 1 Gbit/s for FHD video. MPEG-4 AVC (Advanced Video Coding) H.264/MPEG-4 A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Coding Format
A video coding format (or sometimes video compression format) is a content representation format of digital video content, such as in a data file or bitstream. It typically uses a standardized video compression algorithm, most commonly based on discrete cosine transform (DCT) coding and motion compensation. A computer software or hardware component that compresses or decompresses a specific video coding format is a video codec. Some video coding formats are documented by a detailed technical specification document known as a video coding specification. Some such specifications are written and approved by standardization organizations as technical standards, and are thus known as a video coding standard. There are ''de facto'' standards and formal standards. Video content encoded using a particular video coding format is normally bundled with an audio stream (encoded using an audio coding format) inside a multimedia container format such as AVI, MP4, FLV, RealMedia, or M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nero Digital
Nero Digital is a brand name applied to a suite of MPEG-4-compatible video and audio compression codecs developed by Nero AG of Germany and Ateme of France. The audio codecs are integrated into the ''Nero Digital Audio+'' audio encoding tool for Microsoft Windows, and the audio & video codecs are integrated into Nero's ''Recode'' DVD ripping software. Nero certifies certain DVD player/recorder devices as Nero Digital compatible, and licenses the codec technology to integrated circuit manufacturers. The video codecs were developed by Ateme, and according to an interview with Nero AG developer Ivan Dimkovic, the audio codecs are improved versions of Dimkovic's older ''PsyTEL AAC Encoder''. The audio codec is now available as a free stand-alone package called Nero AAC Codec. Functionality Nero Digital can generate streams in the 3GP/MPEG-4 Part 14 () container format and includes two video and two audio codecs: * ASP (one of about 20 profiles defined in MPEG-4 Part 2) * AVC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blu-ray Disc
Blu-ray (Blu-ray Disc or BD) is a Digital media, digital optical disc data storage format designed to supersede the DVD format. It was invented and developed in 2005 and released worldwide on June 20, 2006, capable of storing several hours of high-definition video (HDTV 720p and 1080p). The main application of Blu-ray is as a medium for video material such as feature films and for the physical distribution of video games for the PlayStation 3, PlayStation 4, PlayStation 5, Xbox One, and Xbox Series X and Series S, Xbox Series X. The name refers to the blue laser used to read the disc, which allows information to be stored at a greater density than is possible with the longer-wavelength red laser used for DVDs, resulting in an increased capacity. The polycarbonate disc is in diameter and thick, the same size as DVDs and Compact disc, CDs. Conventional (or "pre-BDXL") Blu-ray discs contain 25gigabyte, GB per layer, with dual-layer discs (50GB) being the industry standard for fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression reduces bits by identifying and eliminating Redundancy (information theory), statistical redundancy. No information is lost in lossless compression. Lossy compression reduces bits by removing unnecessary or less important information. Typically, a device that performs data compression is referred to as an encoder, and one that performs the reversal of the process (decompression) as a decoder. The process of reducing the size of a data file is often referred to as data compression. In the context of data transmission, it is called source coding: encoding is done at the source of the data before it is stored or transmitted. Source coding should not be confused with channel coding, for error detection and correction or line coding, the means ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3ivx
3ivx ( ) was an MPEG-4 compliant video codec suite, created by 3ivx Technologies, based in Sydney, Australia. 3ivx video codecs were released from 2001 to 2012, with releases of related technologies continuing until 2015. 3ivx provided plugins to allow the MPEG-4 data stream to be wrapped by the Microsoft ASF and AVI transports, as well as Apple's QuickTime transport. It also allowed the creation of elementary MP4 data streams combined with AAC audio streams. It only supported MPEG-4 Part 2, it did not support H.264 video (MPEG-4 Part 10). Official decoders and encoders were provided for Microsoft Windows, Mac OS, BeOS, Amiga and Linux. In addition, FFmpeg can decode 3ivx encoded video. The company was notable for its support of the Haiku OS, providing a port of the 3ivx codec. The 3ivx port maintainer also produced a QuickTime MOV extractor and an MPEG-4 extractor for Haiku. 3ivx developed an HTTP Live Streamingbr>Client SDK for Windows 8 and Windows 8 Phonesfor the pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |