|
Low Franconian Languages
In historical and comparative linguistics, Low Franconian is a linguistic category used to classify a number of historical and contemporary West Germanic varieties closely related to, and including, the Dutch language. Most dialects and languages included within this category are spoken in the Netherlands, northern Belgium (Flanders), in the Nord department of France, in western Germany (Lower Rhine), as well as in Suriname, South Africa and Namibia. Terminology ''Low Franconian'' is a purely linguistic category and not used as a term of self-designation among any of the speakers of the Germanic dialects traditionally grouped within it. Within the field of historical philology, the terminology for the historical phases of Low Franconian is not analogous to the traditional Old High German / Middle High German and Old Low German / Middle Low German dichotomies, with the terms Old Dutch and Middle Dutch commonly being preferred to ''Old Low Franconian'' and ''Middle Low Francon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suriname
Suriname, officially the Republic of Suriname, is a country in northern South America, also considered as part of the Caribbean and the West Indies. It is a developing country with a Human Development Index, high level of human development; its economy of Suriname, economy is heavily dependent on its abundant Natural resource, natural resources, namely bauxite, gold, petroleum, and Agriculture, agricultural products. Suriname is a member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM), the United Nations, the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation and the Organization of American States. Situated Tropics, slightly north of the equator, over 90% of its territory is covered by rainforest, List of countries by forest area (percentage), the highest proportion of forest cover in the world. Borders of Suriname, Suriname is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west, and Brazil to the south. It is List of South American countries by area, the smalles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The Netherlands consists of Provinces of the Netherlands, twelve provinces; it borders Germany to the east and Belgium to the south, with a North Sea coastline to the north and west. It shares Maritime boundary, maritime borders with the United Kingdom, Germany, and Belgium. The official language is Dutch language, Dutch, with West Frisian language, West Frisian as a secondary official language in the province of Friesland. Dutch, English_language, English, and Papiamento are official in the Caribbean Netherlands, Caribbean territories. The people who are from the Netherlands is often referred to as Dutch people, Dutch Ethnicity, Ethnicity group, not to be confused by the language. ''Netherlands'' literally means "lower countries" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
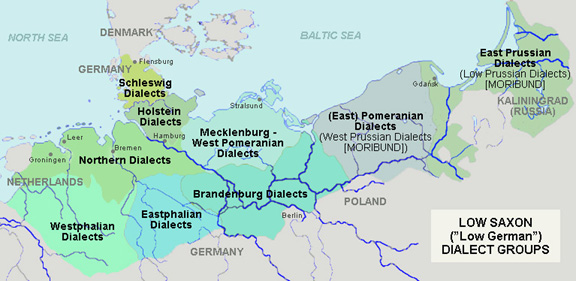
Low German
Low German is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language variety, language spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwide. "Low" refers to the altitude of the areas where it is typically spoken. Low German is most closely related to Frisian languages, Frisian and English language, English, with which it forms the North Sea Germanic group of the West Germanic languages. Like Dutch language, Dutch, it has historically been spoken north of the Benrath line, Benrath and Uerdingen line, Uerdingen isoglosses, while forms of High German languages, High German (of which Standard German is a standardized example) have historically been spoken south of those lines. Like Frisian, English, Dutch and the North Germanic languages, Low German has not undergone the High German consonant shift, as opposed to Standard German, Standard High German, which is based on High German langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Dutch Language
Dutch is a West Germanic language, that originated from the Old Frankish dialects. Among the words with which Dutch has enriched the English vocabulary are: ''brandy, coleslaw, cookie, cruiser, dock, easel, freight, landscape, spook, stoop, and yacht''. Dutch is noteworthy as the language of an outstanding literature, but it also became important as the tongue of an enterprising people, who, though comparatively few in number, made their mark on the world community through trade and empire. Dutch is also among some of the earliest recorded languages of Europe. Countries that have Dutch as an official language are the Netherlands, Belgium, Suriname, Sint Maarten, Curaçao and Aruba. Relation to the Germanic languages group Within the Indo-European language tree, Dutch is grouped within the Germanic languages, which means it shares a common ancestor with languages such as English, German, and Scandinavian languages. This common, but not direct, ancestor (proto-language) of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch is a collective name for a number of closely related West Germanic dialects whose ancestor was Old Dutch. It was spoken and written between 1150 and 1500. Until the advent of Modern Dutch after 1500 or , there was no overarching standard language, but all dialects were mutually intelligible. During that period, a rich Medieval Dutch literature developed, which had not yet existed during Old Dutch. The various literary works of the time are often very readable for speakers of Modern Dutch since Dutch is a rather conservative language. Phonology Differences with Old Dutch Several phonological changes occurred leading up to the Middle Dutch period. * Earlier Old Dutch , , merge into already in Old Dutch. * Voiceless fricatives become voiced syllable-initially: > , > (merging with from Proto-Germanic ), > . (10th or 11th century) * > * > or . The outcome is dialect-specific, with found in more western dialects and further east. This results in later pairs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch ( Modern Dutch: ') or Old Low Franconian (Modern Dutch: ') is the set of dialects that evolved from Frankish spoken in the Low Countries during the Early Middle Ages, from around the 6th Page 55: "''Uit de zesde eeuw dateren de oudst bekende geschreven woorden en tekstjes in de Lage Landen, waarmee de periode van het oud-Nederlands begint.''" rom the 6th century date the oldest known text from the Low Countries, with which the period of Old Dutch begins./ref> to the 12th century. Old Dutch is mostly recorded on fragmentary relics, and words have been reconstructed from Middle Dutch and Old Dutch loanwords in French. Old Dutch is regarded as the primary stage in the development of a separate Dutch language. It was spoken by the descendants of the Salian Franks who occupied what is now the southern Netherlands, northern Belgium, part of northern France, and parts of the Lower Rhine regions of Germany. It evolved into Middle Dutch around the 12th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Low German
Middle Low German is a developmental stage of Low German. It developed from the Old Saxon language in the Middle Ages and has been documented in writing since about 1225–34 (). During the Hanseatic period (from about 1300 to about 1600), Middle Low German was the leading written language in the north of Central Europe and served as a lingua franca in the northern half of Europe. It was used parallel to medieval Latin also for purposes of diplomacy and for deeds. Terminology While ''Middle Low German'' (MLG) is a scholarly term developed in hindsight, speakers in their time referred to the language mainly as (Saxon) or (the Saxon language). In contrast to Latin as the primary written language, speakers also referred to discourse in Saxon as speaking/writing , i.e. 'clearly, intelligibly'. This contains the same root as 'German' (cf., High German: , Dutch ( archaically ''N(i)ederduytsche'' to mean the contemporary version of the Dutch language) both from Proto-Germanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Low German
Old Saxon (), also known as Old Low German (), was a Germanic language and the earliest recorded form of Low German (spoken nowadays in Northern Germany, the northeastern Netherlands, southern Denmark, the Americas and parts of Eastern Europe). It is a West Germanic language, closely related to the Anglo-Frisian languages. It is documented from the 8th century until the 12th century, when it gradually evolved into Middle Low German. It was spoken throughout modern northwestern Germany, primarily in the coastal regions and in the eastern Netherlands by Saxons, a Germanic tribe that inhabited the region of Saxony. It partially shares Anglo-Frisian's (Old Frisian, Old English) Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law which sets it apart from Low Franconian and Irminonic languages, such as Dutch, Luxembourgish and German. The grammar of Old Saxon was fully inflected with five grammatical cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, and instrumental), three grammatical numbers (singu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle High German
Middle High German (MHG; or ; , shortened as ''Mhdt.'' or ''Mhd.'') is the term for the form of High German, High German language, German spoken in the High Middle Ages. It is conventionally dated between 1050 and 1350, developing from Old High German (OHG) into Early New High German (ENHG). High German is defined as those varieties of German which were affected by the High German consonant shift, Second Sound Shift; the Middle Low German (MLG) and Middle Dutch languages spoken to the North and North West, which did not participate in this sound change, are not part of MHG. While there is no ''standard'' MHG, the prestige of the Hohenstaufen court gave rise in the late 12th century to a supra-regional literary language () based on Swabian dialect, Swabian, an Alemannic German, Alemannic dialect. This historical interpretation is complicated by the tendency of modern editions of MHG texts to use ''normalised'' spellings based on this variety (usually called "Classical MHG"), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old High German
Old High German (OHG; ) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally identified as the period from around 500/750 to 1050. Rather than representing a single supra-regional form of German, Old High German encompasses the numerous West Germanic languages, West Germanic dialects that had undergone the set of sound change, consonantal changes called the High German consonant shift, Second Sound Shift. At the start of this period, dialect areas reflected the territories of largely independent tribal kingdoms, but by 788 the conquests of Charlemagne had brought all OHG dialect areas into a single polity. The period also saw the development of a stable linguistic border between German and Gallo-Romance languages, Gallo-Romance, later French language, French. Old High German largely preserved the synthetic language, synthetic inflectional system inherited from its ancestral Germanic forms. The eventual disruption of these patterns, which led to the more analytic language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philology
Philology () is the study of language in Oral tradition, oral and writing, written historical sources. It is the intersection of textual criticism, literary criticism, history, and linguistics with strong ties to etymology. Philology is also defined as the study of literary texts and oral and written records, the establishment of their authentication, authenticity and their original form, and the determination of their meaning. A person who pursues this kind of study is known as a philologist. In older usage, especially British, philology is more general, covering comparative linguistics, comparative and historical linguistics. Classical philology studies classical languages. Classical philology principally originated from the Library of Pergamum and the Library of Alexandria around the fourth century BC, continued by Greeks and Romans throughout the Roman Empire, Roman and Byzantine Empire. It was eventually resumed by European scholars of the Renaissance humanism, Renaissance, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Rhine
Lower Rhine (, ; kilometres 660 to 1,033 of the Rhine) is the section of the Rhine between Bonn in Germany and the North Sea at Hook of Holland in the Netherlands, including the '' Nederrijn'' () within the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta; alternatively, ''Lower Rhine'' may also refer to just the part upstream of Pannerdens Kop ( km 660–865.5), excluding the ''Nederrijn''. It is the last of the four sections of the Rhine between Lake Constance and the North Sea (the others being the High Rhine, Upper Rhine and Middle Rhine). Geography German section Downstream of Bonn, the river meanders through the Lower Rhine Bay (), passing through the city of Cologne (), and continues through the Lower Rhine Plain (). The German term ''Niederrhein'' refers both to the German section of the Lower Rhine as well as to parts of the surrounding Lower Rhine region. Netherlands section Almost immediately after entering the Netherlands, the Rhine splits into numerous branches. The main branch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |